P200 ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA (AVF) THROMBOSIS. RISK
advertisement

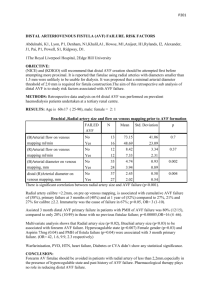
P200 ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA (AVF) THROMBOSIS. RISK FACTORS AND ROLE OF ANTIPLATELET THERAPY, WARFARINISATION AND THOMBOPHILIA SCREEN? K Abdulnabi1, M Morcos1, N Denham1, A Ullah1, A Khalil1, M Howse1, H Anijeet1, J Alexander1, P pai1, I Rylands4, S Powell2, Mr D Ridgway3 Nephrology department1, Radiology department2, Renal transplant department3, The Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Edge Hill University4 INTRODUCTION: AVF thrombosis is the most common cause of fistulae failure and related complications. It is almost always associated with the presence of stenosis. The evidence for using anticoagulation and antiplatelet therapy and testing for thrombophilia is conflicting. This study was designed to assess the effect of comorbidities, pharmacological therapy on AVF/ graft thrombosis. Andrassy et al (cumulative survival), Dember et al, Gorbani et al (primary patency) illustrated that antiplatelet therapy decreases AVF failure while Yevzlin and Kooistra et al show worse outcome or no benefit for the later. Crowther et al and DOOPS demonstrated that warfarin increases failure risk for fistulae and grafts respectively. METHODS: Retrospective data analysis on 426 AVF and 54 arteriovenous graft (AVG) on prevalent haemodialysis patients at a tertiary renal centre. Thrombosis was defined as thrombosis which renders AVF/AVG non-functioning and requiring intervention. Data on AVG was not processed due to small sample RESULTS: Thrombosis was reported in 63% of AVG compared only to 28% of AVF, p≤0.0001. With regards of AVF; univariate analysis shows that age, gender, AF, PVD, IHD, CVA, LVD, HTN, type 2 DM, hypercoagulable state, and intra-dialytic hypotension were not associated with the risk of thrombosis. However, type 1 DM, Aspirin (75mg) proximal AVF site and vascular calcification, metallic fistula stent, vintage on dialysis, previous AVF failure and history of sever venous stenosis were associated with thrombosis. On multivariate analysis, only sever venous stenosis, metallic stent and Aspirin were predictors of fistula thrombosis. Variable Sever venous stenosis Aspirin Clopidogrel Dipyridamole Warfarin Previous AVF Failure Calcification Hypercoagulable state Previous VTE Positive HIT test Proximal AVF site OR, CI 95% 3.57(2.22 – 5.75) 1.66 (1.05 – 2.63) 0.80 (0.35 – 1.83) 0.36 (0.04 – 3.44) 1.19 (0.47 – 2.99) 1.63 (0.99 – 2.69) 1.49 (0.88 – 2.50) 1.36 (0.77 – 2.38) 1.56 (0.64 – 3.80) 2.08 (0.38 – 11.38) 1.39 (0.88 – 2.27) P 0.0001 0.03 0.59 0.38 0.72 0.057 0.13 0.29 0.32 0.34 0.20 Thrombophilia screen was performed in 18 patients. Only one of them had positive test but his fistula has been functioning for 4 years with no thrombotic event reported. CONCLUSION: Aspirin with a dose of 75 mg was associated with risk of thrombosis. Other Anti-platelet including dual therapy did not decrease the risk of AVF thrombosis. Warfarin didn’t decrease the risk of thrombosis in AVF. Thrombophilia screen in patients with recurrent fistula thrombosis might not be justified based on its complexity, cost and this study results. Finally, not surprisingly, significant correlation was noted between sever stenosis requiring angioplasty and thrombosis