A D C B
advertisement

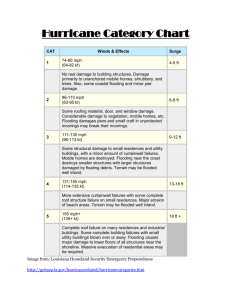
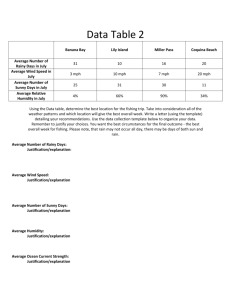
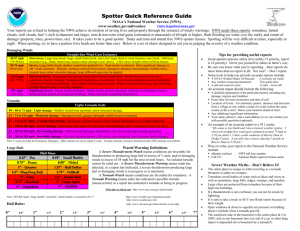
Weather patterns Study guide *Be able to identify the cloud types if given pictures Cumulus fog/ Stratus cirrus altostratus cirrostratus nimbostratus cumulonimbus stratocumulus cirrocumulus altocumulus Matching: draw a line connecting the term with description Sleet 0 0 Formed in thunderstorm clouds where rain and snow can coexist Snow 0 0 Can start off as a liquid or a solid, and lands as a liquid. Freezing Rain 0 0 Crystals do not pass through a surface of warm air. Rain 0 0 Partially melts in a thin warm layer of air and refreezes before hitting the surface. 0 Liquid water hits ground and freezes. Hail 0 Fill In or Answer 11. Which type of air mass forms over cold, and dry areas?CP 12. What type of air masses bring warm temperatures and cloudy skies. MT 13. Maritime Polar air masses form over cold/moist areas. 14. Tornadoes are classified on which scales? fujita 15. Hurricanes are classified on which scales? Saffir-simpson 16. List 3 things that CAN be caused by thunderstorms? Flash floods, lightning, hail 17. Wind always flows from high pressure to low pressure 18. Summers in the Southwest United States are hot and dry because of what air mass? CT 19. The eye is the low-pressure area of a hurricane. 20. Thunder is the rapid heating of the air around a lightning bolt. Use the diagrams below to answer the following questions 26. Which area of the United States is most likely to experience SHORT term periods of precipitation?atlanta 27. Which city is most likely experiencing precipitation Salt Lake City or Cheyenne? 28. Which city is having warmer temperatures Memphis or Atlanta? B D A C 29. What is the air pressure at point B? 1020 mb 30. What kind of weather would you expect at point C? clear/fair Open Ended: After reading the following answer the questions that follow. From 1950 to 1952, tropical cyclones of the North Atlantic Ocean were identified by the phonetic alphabet (Able-Baker-Charlie-etc.), but in 1953 the US Weather Bureau switched to women's names. The rest of the world eventually caught on, and naming rights now go by the World Meteorological Organization, which uses different sets of names depending on the part of the world the storm is in. Around the U.S., only women's names were used until 1979, when it was decided that they should alternate a list that included men's names too. There's 6 different name lists that alternate each year. If a hurricane does significant damage, its name is retired and replaced with another. 31. Hurricane Barbara is currently affecting the Florida coast. Come up with the next three possible hurricane names. 1 C-boys name 2 D-girls name 3 E-boys name Fujita Scale of Tornado Intensity Enhanced, SCALE WIND SPEED POSSIBLE DAMAGE Operational Fujita Scale F0 40-72 mph Light damage: Branches broken off EFO trees; minor roof damage 65-85 mph Moderate damage: Trees snapped; F1 73-112 mph mobile home pushed off foundations; roofs damaged Considerable damage: Mobile homes F2 113-157 mph demolished; trees uprooted; strong built homes unroofed EF1 86-110 mph EF2 111-135 mph Severe damage: Trains overturned; F3 158-206 mph cars lifted off the ground; strong built EF3 homes have outside walls blown 136-165 mph away Devastating damage: Houses leveled F4 207-260 mph leaving piles of debris; cars thrown 300 yards or more in the air Incredible damage: Strongly built F5 261-318 mph homes completely blown away; automobile-sized missiles generated EF4 166-200 mph EF5 over 200 mph 32. Use the Fujita Scale Chart above to determine what level of tornado caused the damage described in the following statement and give a reason for why you chose that rating: “I went to find my car and could look inside of my neighbor’s brick house. It was like all the outside walls were gone and I could see into her living room. I finally got to my car and it was upside down on its roof”. F3---see above on scale