Exam 1 Sample Questions
advertisement

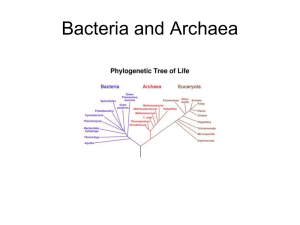
Exam Review: Exam I (chap 1, 22, 26-28) Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Tyler Course: Biology 211 (7,8) Instructor: Dr. Colbert Date: 1. The field of biology that is concerned with the describing, naming, and classifying living and extinct organisms. a. Systematics b. Ontogeny c. Taxonomy d. Phylogeny 2. Study of biological diversity and evolutionary relationships. a. Systematics b. Ontogeny c. Taxonomy d. Phylogeny 3. Which order of hierarchical groups is correct? a. Kingdom, Phylum, Order, Class, Family, Genus, Species b. Genus, Family, Genus, Phylum, Order, Kingdom, Species c. Phylum, Kingdom, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species. d. Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species 4. Prokaryotes have which of the following? a. Nucleus b. Golgi Apparatus c. Ribosomes d. Mitocondria 5. Which domain has membrane lipids with ether linkages,that help resist damage by heat and extreme conditions? a. Archaea b. Bacteria c. Bryophytes d. Protists 6. Which of the following is an Archaea but also thrives in salty environments? a. Hyperthermophiles b. Cyanobacteria c. Halophiles d. Protezoa 7. What produced earth’s first oxygen rich atmosphere? (Which in turn allowed the rise of eukaryotes) a. Hyperthermophiles b. Cyanobacteria c. Halophiles d. Protezoa 8. Gram Postive bacteria have a ______ peptidoglycan cell wall. a. Thin b. Thick 9. A process whereby an organism receives genetic material from another organism without being the offspring of that organism is called what? a. Sexual Reproduction Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu b. Pollination c. Fertilization d. Horizontal Gene Transfer 10. This helps bacteria hold together to form colonies, helps aquatic species float, and forms a protective capsule, what is it? a. Biofilm b. Magnetosome c. Mucilage (glycocalxy) d. Cell Wall 11. Bacteria and Archaea reproduce asexually by a process known as what? a. Look Mom no Hands! b. Binary Fisson c. Pili d. Cilia 12. The process where new genetic material in a prokaryotic cell is altered by the uptake of foreign DNA from the cell’s surrounding is called what? a. Transformation b. Transduction c. Conjugation d. Endospore 13. Metabolism varies with respect to oxygen in prokaryotes, so which of the following requires oxygen for surivial. a. Obligate Aerobes b. Facultative Anaerobes c. Obligate Anaerobes d. Aerotolerant Anaerobes 14. Cyanobacteria and other prokaryotes can metabolize nitrogen, these cyanobacteria are referred to as what? a. Diazotrophs b. Chemoautroph c. Halophiles d. Eudicots 15. The process of using bacteria as a way to clean stuff (for example an oil spill) is called? a. Bioremediation b. Bacteria Attack! c. Antibiotics d. GMO’s 16. The Earth’s first eukaryotes were ______. a. Diazotrophs b. Protists c. Flagellas d. Euphylss 17. There are 4 types of Protist nutrition, off the following which describes Phagotrophs? a. Ingestive heteroptrophs (uses phagocytosis) b. Uptake of small organic molecules c. Photosynthetic protist d. Photosynthetic and phagotrophic 18. Dinoflagellates can “bloom” on the surface of water when conditions are right, causes which of the following? a. Scum b. Red Tides c. Moss d. Endospores 19. Which Protists are in the same eukaryotic supergroup as land plants? a. Green Algae b. Red Algae c. Red and Green Algae d. Dinoflagellates 20. Charophyceans share several key traits with land plants, which is not true? a. Both share a distinctive type of cytokinesis b. Both have intercellular connections known as plasmodesmata c. Both reproduce by means of an egg and sperm d. Tyler is both their favorite SI Leader! 21. Where is a bacterial cell's DNA found? a. Mitochondria b. Nucleus c. Peroxisome d. Nucleoid region e. Capsule 22. Gram-___________ bacteria have many lipopolysaccharides on their cell wall, meaning they are ___________ resistant to antibiotics which prevent peptidoglycan cross-linking. a. Negative…more b. Negative…less c. Positive…less d. Positive…more 23. Prokaryotes can either make their own energy, which are called __________________, or get energy from outside sources, called __________________. 24. Gram positive bacteria have cell walls primarily composed of __________________. 25. Related families are grouped into the next-highest taxon called a: a. b. c. d. e. Class Phylum Order Genus Kingdom 26. What theory involves the idea that mitochondria were originally aerobic heterotrophic bacteria? a. Endosymbiotic theory b. Cell theory c. Germ theory d. Mitochondrial theory 27. Which domain are protists a member of? a. Bacteria b. Prokaryotes c. Archaea d. Eukaryotes e. Both a and b 28. What are believed to have originally been bacteria before endosymbiosis occurred? a. Ribosomes b. Chloroplasts c. Mitochondria d. Golgi Apparatus e. Both a and b are correct f. both b and c are correct 29. Which of the following is not an alveolate? a. Dinoflagellates b. Diatoms (they are stramenophiles) c. Apicomplexans d. Ciliates 30. What protist spins in the water, can be bioluminescent, and is responsible for “red tides”? a. Red algae b. Brown algae c. Dinoflagellates d. Diatoms HOW TO STUDY FOR TEST 1. Review all powerpoints Write out outlines of each slide in notebook Study all tables and graphs on slides, study corresponding tables and graphs in the book Study pictures and know what they are (ex: if you see a picture of red blood cells and a purple worm-like protest among the cells, what is it a picture of?) 2. Use your book The best way to use the book is to study the pictures. Study all tables, pictures, and graphs that are on both power point and in the book. Read the summary of key concepts, if you don’t understand something, review it End of chapter questions 3. SI worksheets Get them all from the si website, get the answers in session or ask me before or after class Some Important Tables and Figures in book – not all of them, but the ones I thought would be the most important. p.460- History of life on earth p. 529- Differences between eukaryotes, bacteria, and archaea p. 532- How to read a phylogenetic tree p. 533- monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic figure p. 383- Fig 18.14 Binary fission p. 382- Fig 18.12 Plasmids p. 384 Table 18.3 Gene transfer in bacteria cells p. 547 Fig 27.1 Note relationships between bacteria, archaea, and eukarya p.551 Fig 27.7 p.553 Fig 27.9 p.557 Table 27.2 p.568 Fig 28.5 – Eukaryotic supergroups p.570 Fig 28.8A- Euglena (a mixotroph!) p.570 fig 28.9 supergroup land plants and relatives p.573 fig 28.25 alveolata, stramenopila, and rhizaria relationship p.576 Table 28.1 Very useful table of Eukaryotic supergroups p. 571 Fig 28.12 – Endosymbiosis theory (know this well