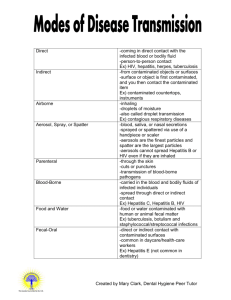
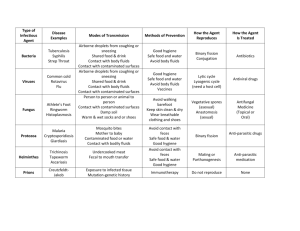
Exposure Control Plan
advertisement

NEW ENGLAND RESIDENTIAL SERVICES, INC. MANUAL FOR BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN FACILITY NAME: NEW ENGLAND RESIDENTIAL SERVICES, Inc. / NEW ENGLAND RESIDENTIAL SERVICES DATE OF PREPARATION: ORIGINAL 4/30/92 Katherine Grant LPN HSC REVISED 1/99 Katherine Grant, LPN HSC REVISED 2/20/99 CAROL A. CRISCI, RN CDDN REVISED 12/12/02 DDN Consulting Services, LLC REVISED 8/04 REVISED 1/2014 In accordance with the OSHA Blood borne Pathogens standard 29 CFR 1910.1030, the following exposure plan has been developed: 1. EXPOSURE DETERMINATION OSHA requires all employers to perform an exposure determination concerning which employees may occur occupational exposure. (Occupational exposure means reasonable anticipated skin, eye, mucous membrane, or parenteral contact with blood or other potentially infectious materials that may result from the performance of an employee’s duties. Other potentially infectious materials means (1) The following human body fluids: semen, vaginal secretions, cerebrospinal fluid, synovial fluid, pleural fluid, pericardial fluid, peritoneal fluid, amniotic fluid, saliva in dental procedures, any body fluid that is visibly contaminated with blood, and all body fluids in situations where it is difficult or impossible to differentiate between body fluids; (2) Any unfixed tissue or organ (other than intact skin) Occupational exposure is described as exposure to bodily fluids regardless of personal protective equipment. It should be assumed that all bodily fluid is infected even if the status of the individual is known. Infectious materials include blood and blood byproducts, semen and vaginal secretion and if blood is visible in feces, nasal secretions, sputum, sweat, tears, urine, emesis or saliva. A. The following is a list of all job classifications at our establishment in which all employees have occupational exposure:: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Direct Support Professionals House Managers Residential Directors Program Director Behavior Specialist Clinical Staff The following is a list of job classifications in which some employees at our establishment have occupational exposure: 1. Clerical Office Worker B. TASKS OR PROCEDURES WHERE EXPOSURE MAY OCCUR: 1. 2. 3. 4. Wound Care Dental Care Incontinent Care Menses Care 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. During a physical restraint During care of a client where potentially infectious material is present CPR First Aid Housekeeping Task Disposal of razors IMPLEMENTATION SCHEDULE AND METHOLOGY– OSHA requires that a plan also include a schedule and method of implementation for the various requirements of the standard. The following complies with this requirement. 1. 2. 3. 2. ENGINEERING CONTROLS A. All New England Residential Services facilities and programs, in addition to agency vehicles and staff vehicles used for work purposes must have personal protective equipment for employees at risk of exposure. Examples: a. gowns b. gloves c. goggles d. mask or face shields e. antiseptic towelettes f. CPR shield g. Red Biohazard bags B. All facilities must have puncture resistant containers for sharps if applicable (this can include, lancets, insulin syringes, disposable razors and razor blades). These containers shall be label or color-coded, leak proof on sides and bottom. These containers will be disposed of when they are two-thirds filled. C. Hand washing facilities must be available to all employees who incur exposure to potentially infectious material. See hand washing procedure. (Appendix) D. When provision of hand washing facilities is not feasible, antiseptic towelettes (Example: Purrell) should be utilized. If used, hands shall be washed with soap and water as soon as possible. E. If an employee incurs exposure to his/her skin or mucus membrane, then those areas shall be washed or flushed with water as appropriate as soon as feasible following contact. F. Needles, contaminated needles and other contaminated sharps will not be bent, recapped or broken. They shall be placed in appropriated sharp containers, as stated above. The container will be taped closed when full, double bagged and disposed of in the trash. The employer will ensure that employees are involved in the selection of effective engineering controls to improve employee’s acceptance of newer devices and to improve the quality of the selection process. G. 3. Universal Precautions: DEFINITION: Universal precaution is treating exposure to all bodily fluids as infectious even if the status is known to be otherwise. Universal precautions will be followed at all work sites. WORK AREA RESTRICTIONS A. C. C. In areas where contamination with infectious material may occur, employees are not to eat, drink, smoke, apply cosmetics, or lip balm, or handle contact lenses. Food and drink shall not be kept in refrigerators, freezers, shelves, cabinets, or countertops where blood or other potentially infectious materials are present (i.e. urine specimens cannot be placed in refrigerators utilized for food). Samples should be stored in a cooler with ice. All procedures will be conducted in a manner, which will minimize the potential of splashing, spraying, splattering or generating droplets of blood or other infectious material. Procedure for handling contaminated material must be followed. A. Contaminated equipment shall be decontaminated as necessary, unless the decontamination is not feasible. Review Section 5 – Housekeeping Practices 4. B. Proper disposal of contaminated material, examples: menses pads, diapers etc. (i.e., double bagged, but not biohazards) Review Section 5 – Housekeeping Practices C. Specimens of blood are collected and removed by outside lab. D. Labeling or color coding is required when specimen containers leave the facility, (i.e. urine specimen cups) PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT (PPE) All PPE shall be provided without cost to the employees. The equipment will be chosen based on the anticipated exposure to blood or other potentially infectious material. It will only be considered appropriate if infectious material can not pass through and reach the clothing, skin, eyes, mouth or other mucous membrane under normal conditions of use and for the duration of time that the equipment will be worn. Infectious contamination will be addressed as per procedure. a. b. c. c. Disposable gloves should be worn at all times when contact with blood or other bodily fluids fluids is anticipated, and when handling or touching contaminated items or surfaces. (Disposable)Gloves are to be disposed of after each use. They are not to be washed or decontaminated. Employees hands should be washed immediately upon removal of disposable gloves. Utility gloves may be washed or decontaminated if the glove barrier is not compromised. They will be replaced when they are cracked, peeling, torn, punctured or deteriorating. Gloves are to be worn for the following procedures and others as needed: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. d. e. f. Tooth brushing Toileting Wound care Incontinence care Vomiting/Diarrhea Laundry Housekeeping Any procedure/task that present exposure to Blood or OPIM Gowns or plastic aprons are indicated if blood splattering is likely. These situations are not routine. An example may be, but not limited to, if a client is bleeding profusely and needs to be restrained for emergency care. Masks in combination with eye protection devices such as goggles or mask/shields combination are required to be worn whenever splashes, spray splatter or droplets of blood or other infectious material may generate contamination of the eyes, mouth or nose. Mouth pieces, resuscitation bags or pocket masks/CPR shields for CPR usage. All PPE will be replaced as needed to maintain their effectiveness by NEW ENGLAND RESIDENTIAL SERVICES at no cost to the employee. All PPE, which is contaminated, will be removed immediately and double bagged in plastic bags. All equipment will be removed prior to leaving the work area. A kit containing a CPR shield, gloves and antiseptic towelettes should also be in each house and vehicle. 5. HOUSEKEEPING PRACTICES A. All facilities are to maintained on a daily cleaning schedule and on an as needed basis for immediate clean up of infectious material. It should be cleaned up immediately or as soon as feasible with disinfectant solution such as 1:10 dilution of bleach and water or appropriate disinfectant. B. All waste receptacles, pails and hampers shall be inspected and decontaminated on a weekly basis. A separate receptacle shall be used to dispose of any contaminated articles. The receptacle shall be lined with a plastic bag and covered. Prior to disposal, the bag should be placed in a second bag and sealed. C. Broken glassware which may be contaminated shall not be picked up directly with the hands. It should be picked up with brush and dust pan, tongs or forceps. D. Labels required by OSHA shall include the following legend: BIOHAZARD Regulated waste means liquid or semi-liquid blood or other potentially infectious material; contaminated items that would release blood or other potentially infectious materials in a liquid or semi-liquid state, if compressed. (Items that are caked with dried blood or other potentially infectious materials and are capable of releasing these materials during handling it, contaminated sharps.) Red bags or red containers may be substituted for labels. 6. 7. 8. LAUNDRY PROCEDURES A. Laundry contaminated with blood or other potentially infectious material shall be handled as little as possible and shall be laundered as soon as feasible. B. Any employee who has contact with contaminated laundry should wear protective gloves and other appropriate personal protective equipment. HEPATITIS B VACCINE A. All employees identified as having a risk of exposure will be offered the hepatitis B series at no cost. The series will be (made available) offered within 10 days of their initial assignment to any work that involves the potential for occupational exposure. B. Employees who decline the vaccination will sign a waiver ( see attached ) C. Employees who decline the vaccine initially may request the vaccine at a later time at no cost to them. D. The fact sheet and waiver will be distributed and reviewed at New Employee Orientation. POST EXPOSURE EVALUATION AND FOLLOW UP If an employee incurs an exposure incident, it should be reported to the supervisor and the nurse. The nurse will initiate and coordinate the record of exposure. The records will be maintained by the Human Resource Coordinator. A. All employees who incur an exposure will be offered post exposure evaluation and follow-up in accordance with OSHA standards. (Refer Form Occupational Exposure Evaluation. Team Report). According to Connecticut Public Act 89-246 1. The employee must file a report of significant exposure within 24 hours. 2. A test for HIV/HBV infectivity shall be drawn within 72 hours if the employee chooses. The blood sample will be kept for 90 days per OSHA standards, in case the employee decides to have the test. If the decision is made prior to the 90 days, the blood test is negative, and the source person consents, the source person’s blood will be tested. If the source person refuses to consent or disclosure, the following is needed. B. A statement that the person who was the source of exposure refused to consent to testing or disclosure or is deceased. C. A statement of exposure evaluation from the MD, and reason for the determination that exposure has occurred. D. A statement that if results are knows the worker would be able to take meaningful immediate action as defined in subsection 19A 5891J (Included in the information packet) which could not otherwise be taken. E. The employee will be offered post exposure prophylaxis in accordance with the current recommendations of the U.S. Public Health Services. F. G. Counseling shall be provided concerning necessary precautions to be followed. Information will be given on what potential illness to be alert for and to report to the appropriate personnel. The following persons have been designated to assure that the policy outlined here is effectively carried out, as well as to maintain records related to this policy: H. 9. Executive Director Program Director Residential Directors House Managers Human Resource Coordinator Nurse Consultant BBP exposures incidents are recorded on the OSHA log as “privacy case”, (if they meet the criteria for recording), and then recorded in the separate “sharps injury log”. INTERACTION WITH HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS A. B. C. New England Residential Services will ensure that the Health Care Professionals are provided with 1. A copy of the regulations 2. A description of the exposed employee’s duties as they relate to the exposure incident. 3. Documentation of the route of exposure and the circumstances under which the exposure occurred. The Health Care Professional shall provide a written evaluation of: 1. When the employee is sent to obtain the Hepatitis B series 2. Whenever the employee is sent to a health care professional following an exposure incident The Health Care Professional shall be instructed to limit their opinion to: 1. If Hepatitis vaccine is indicated 2. That the employee is informed of the results of the evaluation 3. That the employee has been told of any medical conditions resulting from exposure to blood or other potentially infectious material which require further treatment. 4. All other findings or diagnosis shall remain confidential and should not be included in the written report **(Note: The written opinion to the employer is not to reference any personal medical information) 10. TRAINING All employees will receive annual retraining in this area. Training will be conducted by the Nurse, trained staff, through use of a video and/or testing, as appropriate. Training Records shall be maintained for three (3) years from the date which training occurred. The records will be maintained in the office of the Human Resource Coordinator and will include the date of training sessions, content or summary of sessions, names and qualifications of person conducting training and names/job title of all persons attending training sessions. Training will consist of the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. The OSHA standards for blood borne pathogens Knowledge of access to the regulatory text Epidemiology and symptomology of blood borne diseases Mode of transmission of blood borne disease Exposure Control plan i.e. points of the plan lines of responsibility, how the plan is the plan is implemented and knowledge of how to access the plan. Procedures that might cause exposure to blood or infectious material in the work site An explanation of the use of and limitations of control methods that may prevent or reduce exposure including universal precaution, engineering controls, work practices and personal protective equipment PPE availability/How to select appropriate attire and how to dispose of contaminated PPE 9. 10. 11. 11. An explanation of the basic procedure to be followed in the event of exposure Labeling procedure for contaminated receptacle The Hepatitis B vaccine including efficacy, safety, and benefits of being vaccinated RECORD KEEPING All records (regarding Hepatitis vaccine, Post exposure incidents ) required by OSHA standards will be maintained in (separated, locked files at ) the office of the Human Resource Coordinator. In accordance with 29CFR1910.20.AGENCY will maintain records for 30 years for employees with occupational exposure incidents. The record will contain: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Name Social Security Number A copy of the employee Hep B vaccination status including the date of vaccine Medical records relative to the employee’s ability to receive the vaccine A copy of all examinations, medical testing and follow-ups A copy of the Health Care Professional’s written opinion in cases of exposure A copy of the information given to the Health Care Professional New England Residential Services will ensure that these records are kept confidential and are not disclosed without written consent from the employee except as required by law. All records will be maintained in compliance with Connecticut State Regulation Section 19a-581590. They will be maintained by the Human Resource Coordinator. DATES All provisions required by the standard will be implemented by: 1. May 24, 1992 This exposure Control Plan 2. June 4, 1992 Information and training record keeping 3. July 6, 1992 Engineering and work Practice controls. PPE, Housekeeping, Hep B vaccine, post exposure evaluation and follow-up. OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS PRACTICE: All significant exposure to client blood or other body fluid shall be considered serious and shall be reported. SIGNIFICANT EXPOSURE IS DEFINED AS: 1. A parental exposure such as a needle stick 2. Mucous membrane exposure such as splash to the eye or mouth 3. Cutaneous exposure involving large amounts of blood or body fluids, and prolonged contact especially when skin is chapped, abraded or affected with dermatitis EXAMPLES OF WHAT MAY CONSTITUE SIGNIFICANT EXPOSURE 1. Helping an individual who has had an accident and is bleeding 2. Helping to clean up bloody wounds 3. Changing bed linens after an individual has hemorrhaged or experienced extensive bleeding. 4. Changing a dressing that is covered with blood that has oozed from a wound 5. Emptying bedpans containing bloody urine or stool with visible blood 6. Helping a client with personal care – tooth brushing oral hygiene 7. Assisting lab personnel to draw blood by holding an individual’s hand/arm and blood spurts 8. ALL BODY FLUIDS, BLOOD, STOOL, URINE, SALIVA, VAGINAL SECRETIONS, WOUND DRAINAGE, etc. ARE CONSIDERED CONTAMINATED PROCEDURE: 1. Immediately after exposure by needle stick or cut, wash site well with soap and water. After splash to mucous membranes, rinse thoroughly with water 2. Complete incident report form NOTE: if an employee, all documentation will go into his/her file. 3. Exposures must be reported to the Director or House Manager assigned to the site at which the exposure occurred immediately. This person shall initiate the Occupational Exposure Evaluation 4. 5. 6. Team Report. Refer employee to the nearest designated Occupational Health Center. The employee must receive treatment and evaluation within 24 hours. All known exposures shall be investigated by the Safety Committee to establish the conditions surrounding the exposure and to improve training, work practices, or protective equipment to prevent a recurrence. The consulting nurse in each house will routinely check all incident reports and forward any with suspected occupational exposure incidences to designated OSHA representative who will in turn notify the employee as soon as possible in order to review the report and the following: A. B. C. D. 7. Was there a significant exposure to Blood Borne pathogens? (the nurse will review the incident report and decide) If yes, was procedure followed? (New England Residential Services post-exposure incident report) Check with employee as to Hepatitis B status Follow procedure for HIV significant exposure check list if applicable Exposure reports for Blood Borne Pathogens shall be kept confidential to protect the privacy of the injured. Only these persons with a need to know will be permitted access to such incident reports. Completed exposure report forms shall be maintained separately from the employee personnel records, reports of significant exposure will be maintained for the duration of employment up to 30 years. CLEANING UP SPILLS AND DECONTAMINATION OF BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS PRACTICE: It is the practice of NEW ENGLAND RESIDENTIAL SERVICES that all spills or splashes of blood or other body fluids be cleaned up and the spill or splash area decontaminated as soon as possible. This is to minimize the danger of environmental contamination and the possible spread of blood borne infections to employees and residents. This is to also prevent exposure to the AIDS, HIV and Hepatitis B viruses or other blood borne infections through contact with blood or body fluids. EQUIPMENT AND SUPPLIES NEEDED 1. Non sterile gloves (exam or heavy duty) 2. Spray bottle of disinfectant (1 part bleach to 10 parts water)(Appropriated disinfectant) 3. Cloth or paper towel 4. Double plastic bag 5. Mask, goggles and impervious isolation gown (as appropriate to the situation) 6. Forceps, tongs or brush and dustpan (as applicable if picking up Broken glass) 7. Other items as appropriate or as may be needed PROCEDURE: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Assemble necessary equipment and supplies Put on non-sterile exam gloves or heavy duty gloves Use forceps, tongs or brush and dustpan to pick up broken glass Wipe up the spill or splash with a cloth or a paper towel Discard the saturated paper towel into the plastic bag Spray the spill or splash with the disinfectant solution until the contaminated area is wet. Wipe up the disinfectant solution with a paper towel. Repeat as necessary until the spill or splashes are dry. Discard the contaminated cleaning paper towel into the plastic bag Spray disinfectant solution onto the discarded paper towel inside the plastic bag Remove gloves and place them into the plastic bag Tie the bag. If the outside of the plastic bag becomes contaminated with blood, place the contaminated bag into a clean plastic bag Place the plastic bag into a second plastic bag and dispose of in the trash WASH HANDS NOTE: On a small spill area and skin surface, a 70% isopropyl alcohol pledge may be used to disinfect the area NOTE: Surfaces and equipment contaminated with spills or splashes of blood or body fluids must be cleaned up as soon as practical. SEPARATING AND STORAGE OF MEDICAL WASTES In the event of a large amount of contaminated waste, bodily fluids containing infectious material or blood soaked bandage material, a red bio-hazard bag will be used for cleanup. It will be stored in a separate location from other trash and disposed of by a licensed facility according to state regulations. PRACTICE: Medical wastes stored for treatment, disposal, or pickup shall be protected in accordance with established policies and procedures. Medical waste will be separated from general waste in accordance with current federal and state guidelines. PROCEDURE: 1. Medical waste in Red Biohazard bags may not be discarded with general trash 2. Should general trash be placed in containers with medical waste, the trash will be handled as regulated medical waste 3. Medical waste generated will be separated (to the extent practical) (e.g. blood soaked bandages, tubing, gauze pads, and swabs) 4. It shall be the responsibility of all employees to discard waste into appropriate receptacles 5. Medical waste must be discarded into designated containers (e.g. red bag or container marked with “BIOHAZARD“symbol) 6. Should medical wastes storage containers become full, the facility coordinator will notify the administrator to arrange for pick up. 7. It is the responsibility of the agency to monitor the medical waste storage to ensure that medical wastes are treated, disposed of, or picked up by the authorized vendor on a timely basis. BIOHAZARD LABELING PRACTICE: It is the practice of NEW ENGLAND RESIDENTIAL SERVICES that (regulated waste) material contaminated with blood, body fluids, or other potentially infections material must be identified by a ‘BIOHAZARD’ label when red bagging is not used. PROCEDURE: 1. When red bagging is not used all waste containing blood, body fluids or other potentially infectious materials must be identified by a BIOHAZARD label. 2. Biohazard labels shall be used as a means to prevent accidental injury or illness to employees who are exposed to hazardous or potentially hazardous conditions, equipment, or operations which are out of the ordinary, unexpected, or not readily apparent. Note: When red bagging or red containers are not used, labels shall be used. 3. Warning labels will be affixed to containers of regulated waste, refrigerators containing blood or other potentially infectious material, and other containers used to store, transport or ship blood or other potentially infections materials. 4. Bags or other receptacles containing articles contaminated with potentially infections material (such as dressing to a wound which are soaked, dripping saturated, dried or caked), including contaminated disposable items, shall be labeled or otherwise identified. The labels shall have the single word BIOHAZARD or the biological hazard symbol. Note: If the outside of the bag is contaminated with body fluids, a second outer bag shall be used. 5. If tags are not used, red bagging or red containers shall be used as a means of identification of contaminated materials. HEPATITIS B FACT SHEET 1. The disease: Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. It can be caused by a virus, bacteria, chemical agents or poisons. There are several type of infectious hepatitis (A, B, non-A and non-B), which are caused by a virus. The institutionalized mentally retarded population was once identified as a high risk group. Screening and vaccinations were done in the 1980’s. At the time of screening some people were identified as carriers of the disease. The mentally retarded population is at no more of a risk of contracting the disease but due to institutionalization were more apt to be exposed to the disease. people with mental retardation living in the community are at no higher risk than the general population. Hepatitis B strikes about 200,000 persons each year in the U.S.A. It is usually spread by contact with infected blood, or blood products. It is spread by sharing IV drug needles, sexual relations, transfusions, contaminated needles which might be used in ear piercing or tattooing. It is spread by person to person, or by person to environment to person such as someone cleaning up blood from the environment. It is not spread through casual contact, or by the air. The occupational risk of contracting hepatitis B from an infected person lies primarily from the contact with blood or blood products, although safety procedures have been established for use when working with any body fluids such as blood, urine, feces, semen, or saliva. 2. The vaccine: NEW ENGLAND RESIDENTIAL SERVICES will pay for the series of three injections. A. Hepatitis B vaccine is manufactured from yeast and not blood plasma. You would receive three injections: one initial, one in a month and one six months from the initial injection. The injections are given in the upper arm in the deltoid muscle. The vaccine when introduced into the body stimulates the body to produce antibodies to protect you from contracting the disease. The vaccine produces protective immunity in about 90% of healthy persons. B. Testing for immunity after the vaccination is recommended and is paid for by NEW ENGLAND RESIDENTIAL SERVICES. C. How long does protection from Hepatitis B Vaccine Last? Studies indicate that immunological memory remains intact for at least 20 years among healthy vaccinated individuals who initiated Hepatitis B vaccination >6 months of age. The vaccine confers long-term protection against clinical illness and chronic Hepatitis B virus infection. Cellular immunity appears to persist even though antibody levels might become low or decline below detectable levels. 3. Side effects: The most common side effect observed following vaccination has been soreness at the site of injection, including redness, swelling and warmth. Also observed has been occasional fatigue, malaise, low grade fever, chills, irritability, nausea, headache, or dizziness. Anaphylactic reaction has never been documented but is possible as it is a parenteral injection. 4. Post Exposure: If you’ve been immunized and you are exposed, you probably will not need further treatment unless your antibody level is low. Then you will need further treatment. You will need to be tested and a booster dose will be given. Report any exposure incident to your supervisor immediately. A post exposure evaluation will be done. Know that there are at least five types of viral hepatitis Five types of viral hepatitis have been identified (see table below) They have similar clinical features, but vary significantly in modes of transmission, prevalence and outcome. DIFFERENT TYPES OF HEPATITS Types of Hepatitis Mode of Transmission Incubation Period Serological Tests A Fecal/Oral 15 to 50 days Available Complications Fulminant hepatitis relapse Fulminant hepatitis Chronic liver disease Cirrhosis Primary hepatocellular carcinoma B Parenteral/ Sexual/Perinatal 40 to 180 days Available C Parenteral 35 to 75 days Available Chronic liver disease Cirrhosis Primary hepatocellular carcinoma D Parenteral/ Sexual/Perinatal 21 to 49 days Available Chronic liver disease Fulminant hepatitis E Fecal/Oral 28 to 42 days Not Widely Available High mortality in pregnant women Fetal demise HANDWASHING - Appendix I CLEANLINESS IS THE BEST PROTECTION FROM DISEASE. EFFECTIVE PROTECTION KNOWN. HANDWASHING IS THE MOST WHEN TO WASH HANDS: PERSONNEL MUST WASH HANDS 1) Before assisting with personal care of individuals 2) Before and after contact with the face and mouth of individuals 3) After personal use of the toilet 4) After blowing or wiping the nose 5) Before eating, smoking or drinking 6) On completion of duty 7) Before preparing food, unloading the dishwasher, and setting the table 8) After doing the laundry 9) When coming on duty 10) Whenever hands are soiled PROCEDURE FOR EMPLOYEE SIGNIFICANT EXPOSURE INCIDENTS (CHECK EACH ITEM THEN PROCEED) QUESTIONS Date Yes No Did the Did the employee feel he/she was put at significant risk for contracting blood borne diseases? 1. Was the House Manager, Director or Human Resource Coordinator notified? 2. Was the NEW ENGLAND RESIDENTIAL SERVICES employee injury report completed? 3. Did the Employee Health representative meet with the employee w/i 48 hours? A. Was the employee willing to have baseline blood drawn w/I 72 H? B. Did the E.H. rep advise the employee regarding requirements if the employee is requesting that the source individual be tested? C. Did the E.H. rep. assist the employee in arranging for baseline test and was the appointment made? D. Did the E.H. rep. initiate the process of informed consent between the physician, individual and guardian, if applicable? 4. Have the employee test results been obtained? Are results negative? 5. Has informed consent been obtained? In the above situation all criteria have been met to have the source individual tested for HIV status. The individual will be tested and the results will be shared with the employee, ensuring confidentiality as outlined by law. The physician will share results with the individual and/or guardian. 6. B Safety Committee or designee convenes the exposure evaluation team. Committee determine if significant exposure has occurred Committee determines of all steps of the procedure as outlined in the law have been followed of the law. In the above situation all criteria have been met to have the individual tested without informed consent. The individual will be tested and the results will be shared with the employee, ensuring confidentiality as outlined by law. The physician will share results with the individual and/ or guardian. Signature: Date completed CONSENT FOR HIV TEST I have been informed that my blood will be tested in order to detect whether or not I have antibodies and or antigens in my blood to the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). I understand that the test is performed by withdrawing blood and using a substance to test the blood. I have been informed that the test is new and its accuracy and reliability are still uncertain and that the test results, may in some cases indicate that a person has antibodies and or antigens to the virus when the person does not (false positive), or that it may fail to detect that a person has antibodies to the virus when the person has the antibodies (false negative) I understand that in order to diagnose AIDS, other means must be used in conjunction with this blood test. I have been informed that if I have any questions in regards to the nature of the blood test, its expected benefits, the risks and alternative tests. I may ask those questions before I decide to consent to the blood test. I understand the results are confidential and will only be released to those health care practitioners directly responsible for my care and treatment and to no others, as required by law. I further understand that no additional release of the results will be made without my written authorization. By my signature below I acknowledge that I have been given all the information I desire concerning the blood test and the release of the results and have had all my questions answered. Further, I acknowledge that I have given consent for the performance of a blood test to detect antibodies to the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Signed: If signed by other than the patient indicate relationship Date: Witness: ___________________________________ INFORMED CONSENT TO AIDS-VIRUS (HIV) ANTIBODY TEST I have read all of this form or it has been read to me and I have discussed it with my doctor or test counselor. I have been told about the nature of HIV, AIDS and HIV-related illness and have been told about how the virus may be passed from one person to another. I agree to take the HIV antibody test. _____________________________________ Name of the person to be tested _________________ Date of Birth _____________________________________ Signature of the person to be tested Or person authorized to consent for person _________________ Date If someone other than the person to be tested has signed, state the name and address of the person signing and the relationship to the person to be tested. If necessary explain why the person to be tested did not sign. I have provided to the person who signed this form an explanation of the nature of the disease HIV, AIDS, and HIV related illness, information about behaviors known to pose risk for transmission of HIV infection and have discussed and answered any questions about the information covered in the form. _____________________________________ Name of the physician or test counselor _____________________________________ Signature of physician or test counselor OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE EVALUATION TEAM REPORT Name of Employee: Date Reported ______________ Name of source individual: Significant exposure: Yes _________ NO _________ Date of exposure ____________ Accident and incident report attached: Yes _________ No __________ Explanation of incident: Plan of Correction Follow up: _____________________________________ Signature of Employee ___________________________ Date _____________________________________ Signature of Supervisor ___________________________ Date _____________________________________ Signature of Human Resource Coordinator ____________________________ Date Cc: File: Human resources WAIVER TO AIDS-VIRUS (HIV) ANTIBODY TESTING I have read all of this form or it has been read to me and I’ve discussed it with my doctor or test counselor. I have been told about the nature of HIV and HIV related illness and have been told about how the virus may be passed from one person to another. I refuse to take the HIV antibody test ________________________________________ Name of person refusing the test _______________________ Date of birth ________________________________________ Signature of the person refusing test _______________________ Date If someone other than the person to be tested has signed, state the name and address of the person signing and the relationship to the person to be tested. If necessary explain why the person to be tested did not sign. I have provided to the person who signed this form an explanation of the nature of the disease HIV, AIDS, and HIV related illness. Information about behaviors know to pose risk for transmission of HIV infection and have discussed and answered any questions about the information covered in the form. _____________________________________ Name of the physician or test counselor _____________________________________ Signature of physician or test counselor OSHA Annual Sign Off by Administration I have reviewed the Control plan and it is current and up to date with practice. NAME SIGNATURE DATE