Active Transport
advertisement

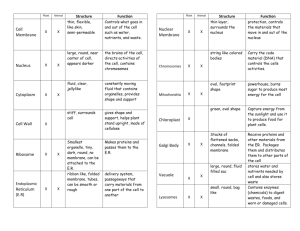
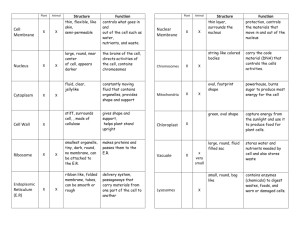
Cells: the building blocks of life!!! What is a cell? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Cells: An Overview Generalized There are trillions of cells in the human body Of those trillions, there are over 200 different kinds that vary in size, shape and function Despite all their differences, all human cells have 3 main parts _____________________________________– the outer layer of the cell _____________________________________ – fluid inside the cells. Contains organelles ______________________________________ – the control center of the cell The Plasma Membrane…What is it? The outer layer of the cell. Think of it as the _________________________________ for the cell It is a _________________________________________________ that is selective about what can enter or leave the cell Separates the body’s 2 main fluid compartments o __________________________________ – fluid inside the cell o __________________________________- fluid outside and in between the cells The Plasma Membrane: Structure Phospholipids: ______ Glycolipids: _______ Cholesterol:_______ Double layer membrane primarily made of ______________________________ The polar _______________ are attracted to water (hydrophilic) so they lie on the inner and outer surface of the membrane ***remember intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid = water The nonpolar _______________avoid the fluid (hydrophobic) and line up in the center of the membrane Glycolipids Lipid with an attached _________________________________ Found only in the outer surface of the plasma membrane Combine with other glycolipids to make ______________________ (sugar coating) Glycocalyx o o o Fuzzy, sticky carbohydrate-rich area surrounding the cell Every cell has a _________________________________ of sugars in its glycocalyx; therefore, the glycocalyx provides a very specific biological marker for ______________________________ Essentially I.D. tags for the cell to cell recognition **This is why sperm know to fertilize an egg and not a blood cell!!! Cholesterol It’s not the devil! O Wedges between ___________________________________________________ O _________________________ the membrane Membrane Proteins Integral Proteins Peripheral Proteins 3 factors bind cells together 1. Glycoproteins in the glycocalyx act as an adhesive 2. Wavy contours of membranes fit together in a tongue and groove fashion 3. Special membrane junctions are formed Special Membrane Junctions: Tight Junction o __________________________________ junction helps prevent molecules from passing through the extracellular space between adjacent cells Desmosomes o ______________________________ junctions scattered like rivets along the sides of adjacent cells that prevent ________________________ o Button like plaque on cytoplasmic side held together by thin linker proteins (cadherins) on the cellular side o Thicker protein filaments “lock” together with the plaque on the opposite side to anchor them together o Strong yet flexible junctions Gap Junctions o Allow chemical substances to pass between adjacent cells o Connected to other cells by a hollow cylinders ( ______________________) o Ions, sugars, and other small molecules pass through these channels Membrane Transport The plasma membrane is a _____________________________________________ membrane that allows nutrients to enter the cell while keeping unwanted elements out of the cell as well as ridding itself of toxic waste products. Interstitial Fluid (the cellular super highway) o Fluid between the cells that contains nutrients such as vitamins, sugars and amino acids, hormones and neurotransmitters, and waste products Passive Transport o o o o Simple diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Filtration Active Transport o Solute Pumping o Vesicular Transport Exocytosis Endocytosis (phagocytosis) o Bulk Phase Endocytosis o Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis Passive Transport Diffusion o o The tendency of molecules or ions to scatter ____________________ throughout the environment Molecules move from areas of _______________ concentration to ________________ concentration Simple Diffusion o o Substances that are nonpolar and lipid soluble (oxygen, carbon dioxide, fat-soluble vitamins, and alcohol) diffuse directly through the lipid bilayer However, polar and charged particles can selectively pass through channel protein pores if they are small enough Facilitated Diffusion o o Certain molecules (glucose and other simple sugars) are too ________________________ to dissolve in the lipid bilayer and too large to pass through membrane channels so they must be helped across ___________________________________________ in the plasma membrane allow entrance to the cell bypassing the non- polar portion of the cell by engulfing then releasing the molecule into the cell Osmosis o o The diffusion of a ______________________, such as water through a selectively permeable membrane Occurs whenever the water concentration differs on the two sides of the membrane ***Even though water is highly polar, it passes easily through the lipid bilayer**** Tonicity Osmotic imbalances cause cells to shrink or swell until the solute concentration on both sides of the plasma membrane is the same, or the membrane is stretched to its breaking point Tonicity is the ability of a solution to change the tone or shape of cells by altering their internal water volume Isotonic solutions with the same concentration of ________________________________ as the cells Cells retain ______________________________shape and have no loss or gain of ________________ Hypertonic Solutions with ________________________concentration of solutes than the cell Cells in a hypertonic solutions lose water and _________________________________ (crenate) Hypotonic Solutions with a ______________________________ concentration of solutes than the cell Cells in a hypotonic solution __________________ water and ____________________and sometimes burst (lyse) Filtration The process that forces water and solutes through a membrane or capillary wall by fluid, or hydrostatic, pressure. Pushes solute containing fluid from a higher pressure area to a lower pressure area. Not selective, only blood cells and protein molecules too large to pass through the membrane pores are held back Active Transport Similar to ___________________________________diffusion in that it needs carrier proteins that combine with the transported substances. Solute pumping move ___________________________ “uphill” against their concentration gradients Vesicular Transport The transport of large particles and macromolecules across the plasma membrane The substance or cell product to be released is 1st enclosed in a membranous sac called a vesicle 2 types of vesicular transport _______________________________ - movement of substances from the cell interior to the extracellular space Moves materials out of the cell Material is carried in a membranous vesicle Vesicle migrates to plasma membrane Vesicle combines with plasma membrane Material is emptied to the outside __________________________________ – movement of substances from the extracellular space into the cell Extracellular substances are engulfed by being enclosed in a membranous vesicle Types of endocytosis o o o Phagocytosis—cell _______________________‖ Pinocytosis—cell ________________________‖ Receptor mediated The Cytoplasm The “stuff” between the plasma membrane and the nucleus Forms the foundation of the cell and contains the ________________________________ “Little organs” The Organelles The “machinery” of the cell Each organelle “little organ” has a specific job in the cell to maintain the life of the cell Mitochondria The “power plants” of a cell providing most of its __________________________________ Carbohydrate, lipid and protein molecules are broken down here and the energy is used to form molecules of __________________ Complex organelles that contain their own __________, ___________, and ribosomes and are able to ______________________________themselves Ribosomes Made of protein and RNA, these are the site of ____________________________________ (production) Some are free floating in the cytoplasm and others are attached to membranes forming ___________________________________ Rough ER Ribbons of membrane studded with _________________________________, which make all the proteins secreted from the cells Manufactures the ___________________________ proteins and ________________________________ that form the plasma membrane –considered a “membrane factory” Once made, proteins are enclosed in _____________________________ for transport to the ____________________________________________ where they are further processed Golgi Aparatus Made of stacked, flattened membranous sacs with many tiny vesicles that pinch of for “shipping proteins. Main function is to ________________________________________________________ the proteins and lipids made by the rough ER. --See figure 3.20 on page 86 “Packages” are shipped 1 of 3 ways o Vesicle is destined for _________________________________ o Vesicle is to become part of the __________________________________________________ o Vesicles becomes a ________________________________ Lysosomes Vesicles produced by the ______________________________________ that contain digestive enzymes Function as a cell’s “demolition crew”by o Digesting particles taken in by phagocytosis (esp. bacteria, viruses, and toxins) o Geting rid of worn-out or non-functioning organelles o Performing metabolic functions such as glycogen breakdown and release o Breaking down non-useful tissues such as the webbing between the fingers and toes of a developing fetus o Breaking down bone to release Calcium ions into the blood Peroxisomes Membranous sacs containing powerful _____________________________ (oxidases and catalases) which detoxify harmful substances and neutralize free radicals Especially numerous in the _______________________ and _________________________ cells which are very active in detoxification Free Radicals- normal byproducts of cellular metabolism that can have harmful effects on cells if allowed to accumulate The Cytoskeleton The “cell skeleton” – it is a network of _________________ running through the ___________________ Supports cell structure and aids in cell movement 3 types of rods from smallest to larges o Microfilaments o Intermediate filaments o microtubules Microtubules Cylindrical structures made of tubulin proteins ___________________________the cell and give it __________________________ Involved in intracellular and cellular ______________________________ Form the ________________________________ Centrioles Paired cylindrical bodies each composed of ______________ triplets of microtubules Organize a microtubule network during ___________________________ to form the spindle and asters Form the bases of ___________________________ and ________________________ Cilia Whip-like cellular extensions on the surface of certain cells Example: cells that line the respiratory tract have cilia that propel mucus laden with bacteria and dust particles upward away from the lungs Flagella Long tail-like projection formed by centrioles Example: sperm which have one flagellum used for movement NOTE: Cilia propel other substances across the cell’s surface whereas the flagella propels the cell itself Microvilli “Little Shaggy Hairs” Tiny finger like extensions of the plasma membrane Increase the plasma membrane ______________________________________ tremendously The Nucleus The ____________________________________________________ of the cell Has 3 regions or structures o The nuclear envelope o Nucleoli o Chromatin Most cells only have 1 nucleus but some are ___________________________________ – having more than 1 nucleus (ex. Skeletal muscles) All human cells except ______________________________________ have at least 1 nucleus. RBC’s are the only anucleate cells therefore cannot reproduce and only live for 3-4 months in the blood stream The Nuclear Envelope Surrounds the _______________________ in a double layer membrane barrier separated by a fluid filled space The outer membrane is connected with the rough ER of the cytoplasm and studded with ribosomes & pores Nucleoli Spherical bodies found within the ____________________________ Produce ________________________________________ molecules for the creation of _________________________________ Chromatin Uncoiled _____________________________________ consisting of DNA and histone protein molecules _______________________________ is responsible for packing long DNA molecules in a compact, orderly way Cell Division Cells must reproduce if an organism is to grow and repair damaged tissues During cell reproduction, a cell divides its genes equally and then splits into 2 identical cells Cell division involves 2 major events o Mitosis- when the chromatin in the nucleus combine into chromasomes and are equally divided between the 2 forming cells o Cytokinesis – separation of the cytoplasm to produce 2 daughter cells. Each daughter cell has the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell