Cell Membrane Structure & Function: Notes
advertisement

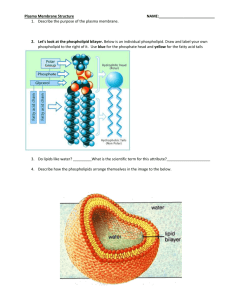
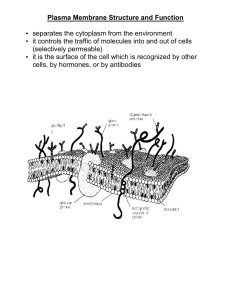
Cell Membrane: Structure and function Plasma (Cell) Membrane: Flexible boundary of a cell that separates a cell from its surroundings. Regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection and support. This is called SELECTIVE PERMEABILITY Some molecules are allowed to pass through plasma membrane at any time. Other molecules are only allowed at certain times or in limited amounts. Some molecules are never allowed. Structure of the Plasma Membrane The organization of all these structures is called the fluid mosaic model Plasma membrane contains: Protein molecules that are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer Carbohydrate molecules are attached to many of the proteins Phospholipid Bilayer Double-layered sheet that makes up nearly all plasma membranes. o Phospholipid Lipids with hydrophobic (hates water) tails and hydrophilic (water lover) heads that form two layers in the membrane. Made up of glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and a phosphate group. Membrane Proteins Proteins that can send or receive signals from nearby cells. Cholesterol A hydrophobic lipid molecule that changes the fluidity of the membrane. Transport or Channel Proteins Proteins that help carry substances across the membrane or allow molecules to pass through a channel. Glycolipid Lipids with carbohydrate chains that serve as cell recognition markers. Glycoprotein Proteins with carbohydrate chain that cans serve as cell recognition markers and can help neighboring cells interact or stick to each other. Cytoskeleton Filaments Long protein chains that help the cell hold its shape. Organelles and other larger molecules can travel along these chains like super highways in the cell.