Learning Objectives
advertisement

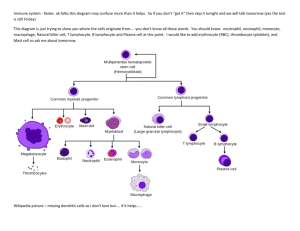
Guided Lecture Notes, Chapter 15, Innate and Adaptive Immunity Learning Objective 1. Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. (Refer to Figure 15-1.) Using examples, explain why innate/natural/native immunity is the immune system’s first line of defense. (Refer to PowerPoint slide 4.) Discuss why this type of immunity is more general. Using examples, explain why adaptive/acquired immunity elicits a specific, later response than innate immunity. (Refer to PowerPoint slide 5.) Learning Objective 2. State the origin of cells of the immune system in terms of myeloid or lymphoid origin. Describe the characteristics, origin, and role or monocytes/macrophages, granulocytes, and dendritic cells. Briefly describe the characteristics, origin, and role of natural killer cells, B lymphocytes, and T lymphocytes. Learning Objective 3. Identify the tissues that contribute to immunity. List central lymphoid organs and peripheral lymphoid organs and explain the function of each. (Refer to Figures 15-2 and 15-3.) Learning Objective 4. Describe the roles of cytokines, chemokines, and colonystimulating factors in the immune response Define cytokine and explain their role in the immune response. (Refer to PowerPoint slide 22.) Using examples, describe the function/effects of various cytokines. (Refer to Table 15-1.) Explain how chemokines and colony-stimulating factors contribute to immunity. Learning Objective 5. Explain how phagocytic neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells contribute to innate immunity. Explain the role of NK cells. (Refer to Figure 15-4.) Learning Objective 6. Describe the process of pathogen recognition and relate it to innate immunity. Explain the functioning of toll-like receptors. (Refer to Table 15-2.) Describe the relationship between pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Learning Objective 7. Describe the function of the complement system. Explain how the complement system elicits the inflammatory response, lyses foreign cells, and increases phagocytosis. (Refer to PowerPoint slide 30.) Describe the three pathways that activate the complement system. Learning Objective 8. List the substances and cells that participate in adaptive immunity. Explain the importance of antigens in eliciting the immune response. Define epitopes and haptens. (Refer to Figure 15-5.) Describe the cells that are involved in adaptive immunity. Learning Objective 9. Characterize the significance and function of major histocompatibility complex molecules (MHC). (Refer to PowerPoint slides 15–16 and Table 15-3.) Explain the role of MHC molecules in adaptive/acquired immunity. Describe the location and function of Class I MHC and Class II MHC molecules and discuss their relationship to HLA (human leukocytic antigens). (Refer to PowerPoint slides 15–16 and Figure 15-8.) Learning Objective 10. State the function of the five classes of immunoglobulins. Explain the role of B lymphocytes in humoral immunity. Identify the location and function of each immunoglobulin class (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE). (Refer to PowerPoint slide 28 and Table 15-4.) Differentiate between primary and secondary/memory phases of the humoral immune response. (Refer to PowerPoint slides 32–33 and Figure 15-11.) Learning Objective 11. Explain how helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells, and regulatory T cells contribute to cell-mediated immunity Explain how helper T cells regulate the immune system. (Refer to Figure 15-12.) Explain the function of cytotoxic T cells. (Refer to Figure 15-13.) Describe the role of regulatory T cells. Learning Objective 12. Compare passive and active immunity. Differentiate between active and passive immunity with regard to how each type of immunity is acquired, when immunity is achieved, and how long immunity lasts. (Refer to PowerPoint slides 34–36.) Learning Objective 13. Explain the transfer of passive immunity from mother to fetus and from mother to infant during breast-feeding. Describe how IgA is transferred in breast milk and explain the function of this antibody. (Refer to Figure 15-14.) Learning Objective 14. Describe changes in the immune response that occur with aging. Identify the reasons for declining immune function with age. Explain possible reasons for the increased incidence of autoimmune disease among the elderly.