Stem Cells Basics Worksheet (NIH Document) Name: Directions
advertisement

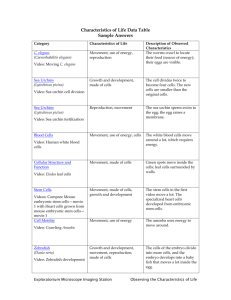
Stem Cells Basics Worksheet (NIH Document) Name:______________ Directions: Complete the following questions using complete sentences. 1. What two important characteristics distinguish stem cells from other cells? Define the following: 2. Pluripotent Cells: 3. Blastocyst: 4. Somatic Stem Cells: 5. In Vitro Fertilization: 6. What is meant by using stem cells for “drug screening”? 7. Where are embryonic stem cells harvested from? 8. What is an embryonic stem cell line? 9. Are adult or embryonic stem cells believed to be less likely to initiate rejection after transplantation? 10. What are your thoughts on stem cell research so far? 1. What two important characteristics distinguish stem cells from other cells? First, they are unspecialized cells capable of renewing themselves through cell division, sometimes after long periods of inactivity. Second, under certain physiologic or experimental conditions, they can be induced to become tissue- or organ-specific cells with special functions. Define the following: 2. Pluripotent Cells: Stem cells that can become any type of cell. 3. Blastocyst: A 3-5 day old embryo 4. Somatic Stem Cells: Non-embryonic adult stem cells. 5. In Vitro Fertilization: A technique that unites the egg and sperm in a lab instead of the female body. 6. What is meant by using stem cells for “drug screening”? To test a drug’s effect on the human body and organs without needing to use live animals or humans. 7. Where are embryonic stem cells harvested from? Embryonic stem cells, as their name suggests, are derived from embryos. Most embryonic stem cells are derived from embryos that develop from eggs that have been fertilized in vitro—in an in vitro fertilization clinic—and then donated for research purposes with informed consent of the donors. They are not derived from eggs fertilized in a woman's body. 8. What is an embryonic stem cell line? Embryonic stem cells that have proliferated in cell culture for for a prolonged period of time without differentiating, are pluripotent, and have not developed genetic abnormalities are referred to as an embryonic stem cell line. 9. Are adult or embryonic stem cells believed to be less likely to initiate rejection after transplantation? Embryonic 10. What are your thoughts on stem cell research so far?