Supplementary table 1: Distribution of infections according to ECDC
advertisement

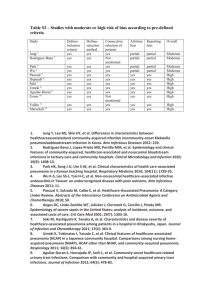
Supplementary table 1: Distribution of infections according to ECDC classification criteria Type of infection ECDC-class according to [15] n % Bloodstream C-CVC3 (n=13), S-DIG4 (n=10), S-PUL5 (n=7), S76 35.5% 1 6 7 8 9 infection SSI (n=4), S-SST (n=3) S-UTI (n=8), S-OTH (n=8), S-UO10 (n=23) Respiratory tract PN111 (n=4), PN312 (n=7), PN413 (n=4), PN514 58 27.1% 2 15 16 infection (n=39), LRI-Bron (n=2), LRI-Lung (n=2), Gastrointestinal GI-CDI17 (n=3), GI-GE18 (n=3), GI-GIT19 (n=7), 31 14.5% 2 20 21 system infections GI-IAB (n=16), EENT-ORAL (n=2), Urinary tract UTI-A22 (n=12), UTI-B23 (n=12) 24 11.2% 2 infection Others2 SYS-CESP24(n=4), SYS-DI25 (n=4), SSI-S26(n=6), 25 11.7% 27 28 CVS-Card (n=2), CVS-Endo (n=1), CVSVasc29(n=1), SST-Skin30 (n=3), SST-ST31 (n=1), CRI1-CVC32(n=1), CNS-IC33 (n=1), CNSMEN34(n=1) Total 214 100% 1 2 3 = blood culture positive = blood culture negative, = blood stream infection (BSI), related to central vascular catheter; 4= BSI, secondary digestive tract infection; 5= BSI, secondary to pulmonary infection; 6= BSI, secondary to surgical site infection; 7= BSI, secondary to skin and soft tissue infection; 8= BSI, secondary to urinary tract infection; 9= BSI, secondary to another infection; 10= BSI, (confirmed) unknown origin; 11= pneumonia, positive quantitative culture from minimally contaminated lower respiratory tract specimen; 12= pneumonia, microbiological diagnosis by alternative microbiology method; 13= pneumonia, positive sputum culture or nonquantitative culture from lower respiratory tract specimen; 14= pneumonia, clinical signs of pneumonia without positive microbiology; bronchitis, tracheobronchitis, bronchiolitis, tracheitis, without evidence of pneumonia; 15= LRI, other infections of the lower respiratory tract; 16= lower respiratory tract infection, other than pneumonia (LRI);17= gastrointestinal system infections (GI) clostridium difficile infection; 18= GI, gastroenteritis (excluding CDI); 19= GI, gastrointestinal tract (oesophagus, stomach, small and large bowel, and rectum), excluding GE, CDI; 20= GI, intra-abdominal, not specified elsewhere; 21= eye, ear, nose or mouth infection (EENT), oral cavity (mouth, tongue, or gums); 22= urinary tract infection (UTI), microbiologically confirmed symptomatic UTI; 23= UTI, not microbiologically confirmed symptomatic UTI; 24= systemic infections (SYS), clinical sepsis in adults and children; 25= SYS, disseminated infection; 26= surgical site infection (SSI), superficial; 27= cardiovascular system infection (CVS), myocarditis or pericarditis; 28= CVS, endocarditis; 29= CVS, arterial or venous infection; 30= skin and soft tissue infections (SST), skin; 31= SST, soft tissue (necrotizing fasciitis, infectious gangrene, necrotizing cellulitis, infectious myositis, lymphadenitis, or lymphangitis); 32= central vascular catheter-related infection (CRI), general CVC-related infection (no positive blood culture); 33= central nervous system infection (CNS), intracranial infection; 34= CNS, meningitis or ventriculitis. Supplementary Figure 1: *In one case, the pathogen (Enterococcus faecium) responded to the empirical therapy (ampicillin-sulbactam) even though the wild-type species is resistant. **In six cases, the wild-type species of the detected pathogen is resistant to the given empirical therapy, but therapy was not tested.