Revision Test
advertisement
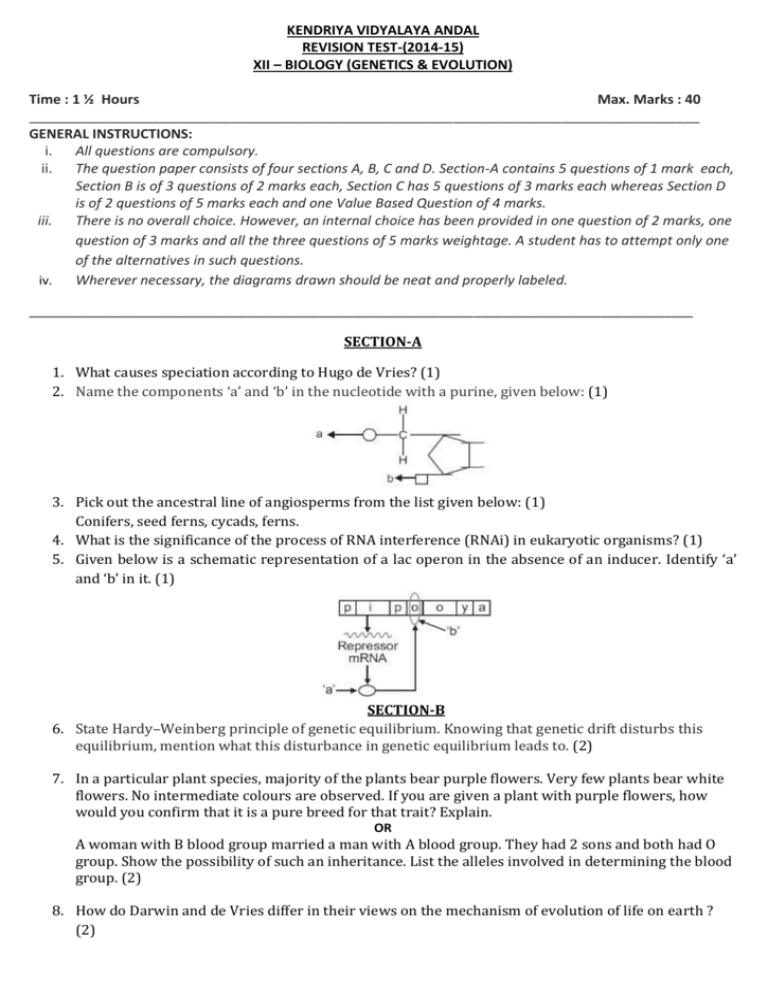
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA ANDAL REVISION TEST-(2014-15) XII – BIOLOGY (GENETICS & EVOLUTION) Time : 1 ½ Hours Max. Marks : 40 _______________________________________________________________________________________ GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS: i. All questions are compulsory. ii. The question paper consists of four sections A, B, C and D. Section-A contains 5 questions of 1 mark each, Section B is of 3 questions of 2 marks each, Section C has 5 questions of 3 marks each whereas Section D is of 2 questions of 5 marks each and one Value Based Question of 4 marks. iii. There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of 2 marks, one question of 3 marks and all the three questions of 5 marks weightage. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions. iv. Wherever necessary, the diagrams drawn should be neat and properly labeled. ______________________________________________________________________________________________ SECTION-A 1. What causes speciation according to Hugo de Vries? (1) 2. Name the components ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the nucleotide with a purine, given below: (1) 3. Pick out the ancestral line of angiosperms from the list given below: (1) Conifers, seed ferns, cycads, ferns. 4. What is the significance of the process of RNA interference (RNAi) in eukaryotic organisms? (1) 5. Given below is a schematic representation of a lac operon in the absence of an inducer. Identify ‘a’ and ‘b’ in it. (1) SECTION-B 6. State Hardy–Weinberg principle of genetic equilibrium. Knowing that genetic drift disturbs this equilibrium, mention what this disturbance in genetic equilibrium leads to. (2) 7. In a particular plant species, majority of the plants bear purple flowers. Very few plants bear white flowers. No intermediate colours are observed. If you are given a plant with purple flowers, how would you confirm that it is a pure breed for that trait? Explain. OR A woman with B blood group married a man with A blood group. They had 2 sons and both had O group. Show the possibility of such an inheritance. List the alleles involved in determining the blood group. (2) 8. How do Darwin and de Vries differ in their views on the mechanism of evolution of life on earth ? (2) SECTION-C 9. (a) One of the codons on mRNA is AUG. Draw the structure of tRNA adapter molecule for this codon. (b) Name the RNA polymerase that transcribes tRNA in eukaryotes. (c) What is unique about the amino acid this tRNA binds with? (3) 10. Study the pedigree chart given below showing the inheritance pattern of a human trait and answer the questions that follow: (1x3=3) (a) Give the genotype of the parents shown in generation I and of the son and daughter shown in generation II. (b) Give the genotype of the daughters shown in generation III. (c) Is the trait sex-linked or autosomal? Justify your answer. 11. Study the figure given below and answer the following questions: a. Write your observations on the variations seen in the Darwin’s finches shown above. (1) b. How did Darwin explain the existence of different varieties of finches on Galapagos Islands? (2) 12. Observe the given figure carefully and answer the questions that follow: a. What is this diagram representing? (1) b. Name the parts a, b and c. (1) c. In the eukaryotes, the DNA molecules are organised within the nulceus. How is the DNA molecule organised in a bacterial cell in absence of a nucleus? (1) 13. (a) Draw a schematic representation of the structure of a transcription unit and show the following in it: (3) a. Direction in which the transcription occurs b. Polarity of the two strands involved c. Template strand & Terminator gene (b) Mention the function of promoter gene in transcription. OR (a) In human genome which one of the chromosomes has the most genes and which one has the fewest? (b) Scientists have identified about 1.4 million single nucleotide polymorphs in human genome. How is the information of their existence going to help the scientists? VBQ (4 marks) Ravi was rushed to a nearby hospital after an accident which caused a lot of blood loss. The hospital failed to supply O negative blood for transfusion. Rahman who was attending a patient learned about the situation and agreed to donate blood being of the same blood group. Ravi’s mother initially refused but was later convinced by Ravi’s sister. a) What values do you find in Ravi’s sister and Rahman? b) Why can’t O positive blood be transfused into Ravi’s body? c) What is the genetic basis of blood group inheritance? SECTION-D 14. (a) How did Griffith explain the transformation of R strain (non-virulent) bacteria into S strain (virulent)? (b) Explain how MacLeod, McCarty and Avery determined the biochemical nature of the molecule responsible for transforming R strain bacteria into S strain bacteria. (5) OR (a) You are given tall pea plants with yellow seeds whose genotypes are unknown. How would you find the genotype of these plants? Explain with the help of cross. (b) Identify a, b and c in the table given below: 15. (a) What did Meselson and Stahl observe when (i) they cultured E. coli in a medium containing 15NH4Cl for a few generations and centrifuged the content? (ii) they transferred one such bacterium to the normal medium of NH4Cl and cultured for 2 generations? (b) What did Meselson and Stahl conclude from this experiment? Explain with the help of diagrams. (c) Which is the first genetic material? Give reasons in support of your answer. (5) OR A true breeding pea plant, homozygous for inflated and green pods is crossed with another pea plant with constricted and yellow pods (ffgg). (i) Work out the cross to show the phenotypes and genotypes of F1 and F2 generations. Give the phenotype ratio of F2 generation. (ii) List the laws of Mendel which can be derived from such a cross. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..