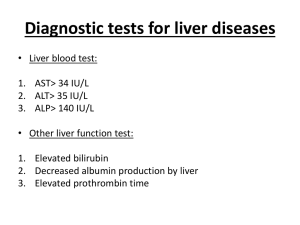
англ задачі49
advertisement

1. The patient has been in the hospital. The beginning of the disease was gradual: nausea, vomiting, dark urine, аcholic stools, yellowness of the skin and scleras. The liver is protruded by 3 cm. Jaundice was intensified on the 14th day of the disease. The liver diminished in sizes. Due to what complication of viral hepatitis, has the patient’s condition worsened? A. Hepatic encephlopathy * B. Meningitis C. Relapse of viral hepatitis D. Cholangitis E. Infectious-toxic shock 2. A 20 yr old woman with a 3-4 month history of bloody diarrhoea; stool examination negative for ova and parasites;stool cultures negative for clostridium,campylobacter and yersinia;normal small bowel series;oedema,hyperemia and ulceration of the rectum and sigmoid colon seen on sigmoidoscopic examination.Select the most likely Diagnosis: A. Ulcerative colitis * B. Gastroenteritis C. Carcinoid syndrome D. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome E. Granulomatous colitis 3. A 36yr. Old alcoholic patient has cirrhosis and pancreatic insufficiency due to recurrent pancreatitis. He complaints of nightblindness, decreased ability to taste food, and dry skin with hyperpigmentation. These complaints suggest deficiency of: A. Zinc * B. Copper C. Selenium D. Chromium E. Manganese 4. A 47 year old man presents to his physician with progressive abdominal swelling.On examination he is found to have ascites and a tender,enlarged liver.If the patient describes a chronic course associated with wasting and low grade fever,the diffrential diagnosis should include everything EXCEPT: A. Chronic Pancreatitis * B. Tuberculosis C. Cirrhosis with hepatocellular carcinoma D. Hepatitis E. Alcoholic liver disease with cirrhosis 5. A 45yr. Old man is admitted with his 3rd episode of upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage. He had 2 prior ulcer operation. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is suspected. All the following would support your suspicions EXCEPT: A. Supression of hypergastrinaemia by secretin given IV * B. A fasting gastrin level of 450pg/ml. C. Post operative notes detailling ulcers in the duodenum and jejunum D. Liver metastasis on CT scan E. A history of diarrhoea 6. A 60yr. Old woman, mother of 6 children, developed sudden onset of upper abdominal pain radiating to the back, associated with nausea, vomitting, fever and chills. Subsequently, she noticed yellow discoloration of her sclera and skin. On physical examination the patient was found to be febrile with temp.of 38.9C, along with right upper quadrant tenderness.Most likely Diagnosis: A. Choledocholithiasis * B. Benign biliary stricture C. Malibnant biliary stricture D. Carcinoma of the head of the pancreas E. Choledochal cyst 7. The family doctor diagnosed in a patient an acute bleeding of an intestine. What is professional tactics of the doctor in this situation? A. The urgent hospitalisation in sergical departmewnt. * B. To inject intravenously the aminocapronic acid. C. The urgent hospitalization in therapeutic department. D. A day time hospital. E. A hospital at home. 8. An elderly man presents with severe epigastric pain radiating to the right hypochondrium. The pain has been worsening over the past day and a half and goes through to his back and shoulders. The patient feels sick and has vomited several times. He is jaundiced. Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C * Gallstones Pancreatitis 9. An elderly woman presents with painless jaundice and weight loss. On physical examination you find the gallbladder to be enlarged. Choose the single most likely diagnosis Gallstones Crohn's disease Duodenal ulcer Duodenitis * Carcinoma head of pancreas 10. An elderly woman presents with painless jaundice and weight loss. On physical examination you find the gallbladder to be enlarged. She enjoys smoking and drinking. Choose the single most likely investigation from the list of options above * Carcinoma head of pancreas Reflux oesophagitis Acute pancreatitis Chronic pancreatitis Duodenal ulcer 11.A patient complains of feeling heaviness behind his breast bone, periodical sensation of food stoppage, dysphagy. During the X-ray examination barium contrast revealed a single saccular outpouching of anterodextral esophagus wall with regular contours and rigidly outlined neck. What is the most probable diagnosis? A. Hiatal hernia B. Esophageal diverticulum * C. Varix dilatation of esophageal veins D. Cancer of esophagus E. Esophageal polyp 12.A patient suffers from chronic recurrent pancreatitis with evident disturbance of exocrinous function. After intake of rich spicy food and spirits his stool becomes fatty. Reduced production of what factor is the most probable cause of steatorrhea? A. Acidity of gastric juice B. Tripsin C. Amylase D. Lipase * E. Alkaline phosphatase 13.A 38 y.o. woman was hospitalized to the surgical unit with acute abdominal pain irradiating to the spine and vomiting. On laparocentesis hemmorhagic fluid is obtained. What disease is suspected? A. Acute enterocolitis B. Acute pancreatitis * C. Acute appendicitis D. Renal colic E. Perforative gastric ulcer 14.A patient is 65 y.o. He has been a smoker for 40 years. Hew has lost 10 kg during the last 3 months. Complains of pain in the epigastric area after taking meals, diarrhea, jaundice. Physical examination revealed enlarged, painless gallbladder. Feces are light-coloured and clay-like. Blood analysis revealed increased level of whole and direct bilirubin, alkaline phosphotase and glutaminepyruvate transferase. Clinical urine analysis showed positive bilirubin reaction and negative urobilinogene reaction. Where is the initial process that caused these changes? A. In pancreas * B. In gallbladder C. In common bile duct D. In liver E. In duodenum 15.A 50 y.o. woman for 1 year complained of attacks of right subcostal pain after fatty meal. Last week the attacks have repeated every day and become more painful. What diagnostic study would you recommend? A. Blood cell count B. Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder * C. Liver function tests D. X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract E. Ultrasound study of the pancreas 16.A 75 y.o. man has acute pain in the paraumbilical region accompanied by vomiting and feeling of abdominal swelling in approximately 30 minutes after meals. He lost 10 kg during the last months because he doesn't eat in order to avoid pain. Abdomen examination reveals no changes in the periods between pain attacks. Above the right femoral artery a murmur can be auscultated, peripheral pulsation in the lower extrimities is weak. X-ray examination of stomach and colonoscopy reealed no changes. What is the leading factor of this pathogenesis? A. Inflammation B. Ischemia * C. Psychogenic changes D. Neoplastic process E. Transient obstruction 17.Medical examination of a man revealed "geographic tongue". This microsymptom is the evidence of the following vitamin deficiency: A. Vitamin C B. Vitamin D C. Vitamin PP D. Vitamin A E. Vitamins of B group * 18.A 45 y.o. man complains of having intensive pain in the epigastric region 1,5-2 hours later after food intake. He has been suffering from ulcer for 11 years. Objectively: t0- 36,50С, RR- 16/min, Ps- 70 bpm, AP- 120/80 mm Hg. On palpation: local painfulness in the right epigastric region. What parameters of intragastric Ph-meter in the region of stomach body are the most typical for this patient's disease? A. рН = 5,0-6,0 B. рН = 6,0-7,0 C. рН = 3,0-4,0 D. рН = 4,0-5,0 E. рН = 1,0-2,0 * 19.A man with liver cirrhosis complained of nasal bleedings, right subcostal pain, weakness, nausea. On physical examination: jaundice, hemorrhagic rash, enlarged liver span (of 14 cm), liver edge irregular. What is the cause of hemorrhagic syndrome in this patient? A. Decreased liver production of procoagulants. * B. As a consequence of DIC. C. Thrombocytopenia. D. As a result of portal hypertension. E. K and C hypovitaminosis. 20.A 45-year-old man for 1 month has complained of epigastric and right subcostal aching pain, pruritus, indigestion, dark color of the urine and acholic stool, fever, and significant weight loss. On exam: jaundice, presence of Curvuasier’s sign. US scan did not reveal stones in the gallbladder and choledochus. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Cancer of the pancreas head * B. Gallbladder stones C. Chronic pancreatitis D. Chronic cholangitis E. Chronic hepatitis 21.A 22-year-old woman complained of right subcostal aching pain, nausea, and decreased appetite. She fell ill 2 months after appendectomy when jaundice appeared. She was treated in an infectious hospital. 1 year later above mentioned symptoms developed. On exam: the subicteric sclerae, enlarged firm liver. Your preliminary diagnosis A. Chronic viral hepatitis * B. Calculous cholecystitis C. Gilbert’s disease D. Acute viral hepatitis E. Chronic cholangitis 22.A 50 -year-old woman for 1 year complained of attacks of right subcostal pain after fatty meal. Last week the attacks have repeated every day and become more painful. What diagnostic study would you recommend? A. Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder * B. Liver function tests C. X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract D. Ultrasound study of the pancreas E. Blood cell count 23.A 27 -year-old man complained of aching epigastric pain just after meal, heartburn, and nausea. Stomach endoscopy revealed a large amount of mucus, hyperemia and edema of mucous membrane in gastric fundus with areas of atrophy. Establish the diagnosis. A. Chronic type A gastritis * B. Chronic type B gastritis C. Peptic ulcer of the stomach D. Chronic type C gastritis E. Menetrier’s disease 24.A 39 -year-old woman complained of squeezed epigastric pain 1 hour after meal and heartburn. She had been ill for 2 years. On palpation, there was moderate tenderness in pyloroduodenal area. Antral gastritis was revealed on gastroscopy. What study can establish genesis of the disease? A. Revealing of Helicobacter infection in gastric mucosa * B. Detection of autoantibodies in the serum C. Gastrin level in blood D. Examination of stomach secretion E. Examination of stomach motor function 25.A patient, aged 48, complains of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, itching of the skin. Repeatedly he had been treated in infectious diseases hospital due to icterus and itch. Objectively: meteorism, ascitis, dilation of abdominal wall veins, protruded navel, spleen enlargement. Diagnosis is: A. Liver cirrhosis * B. Cancer of the liver C. Cancer of the head of pancreas D. Gallstones E. Viral hepatitis B 26.A 27-year-old man complains of pains in epigastrium which are relieved by food intake. EGDFS shows antral erosive gastritis, biopsy of antral mucous presents Hеlicobacter Pylori. Diagnosis is: A. Gastritis of type B * B. Gastritis of A type C. Reflux - gastritis D. Menetrier's gastritis E. Rigid antral gastritis 27.In the development of the inflammation processes glucocorticoids reduce the level of a certain most important active enzyme. It results also in the reducing of the synthesis of prostaglandins and leukotrienes which has a key-role in the development of the inflammation processes. Give the exact term of this enzyme. A. Phospholipase A2 * B. Arachidonic acid C. Lipoxygenasе D. Cyclooxygenase – 1 E. Cyclooxygenase – 2 28.The patient has been in the hospital. The beginning of the disease was gradual: nausea, vomiting, dark urine, аcholic stools, yellowness of the skin and scleras. The liver is protruded by 3 cm. Jaundice was intensified on the 14th day of the disease. The liver diminished in sizes. Due to what complication of viral hepatitis, has the patient’s condition worsened? F. Hepatic encephlopathy * G. Meningitis H. Relapse of viral hepatitis I. Cholangitis J. Infectious-toxic shock 29.A 20 yr old woman with a 3-4 month history of bloody diarrhoea; stool examination negative for ova and parasites;stool cultures negative for clostridium,campylobacter and yersinia;normal small bowel series;oedema,hyperemia and ulceration of the rectum and sigmoid colon seen on sigmoidoscopic examination.Select the most likely Diagnosis: F. Ulcerative colitis * G. Gastroenteritis H. Carcinoid syndrome I. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome J. Granulomatous colitis 30.A 36yr. Old alcoholic patient has cirrhosis and pancreatic insufficiency due to recurrent pancreatitis. He complaints of nightblindness, decreased ability to taste food, and dry skin with hyperpigmentation. These complaints suggest deficiency of: F. Zinc * G. Copper H. Selenium I. Chromium J. Manganese 31.A 47 year old man presents to his physician with progressive abdominal swelling.On examination he is found to have ascites and a tender,enlarged liver.If the patient describes a chronic course associated with wasting and low grade fever,the diffrential diagnosis should include everything EXCEPT: F. Chronic Pancreatitis * G. Tuberculosis H. Cirrhosis with hepatocellular carcinoma I. Hepatitis J. Alcoholic liver disease with cirrhosis 32.A 45yr. Old man is admitted with his 3rd episode of upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage. He had 2 prior ulcer operation. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is suspected. All the following would support your suspicions EXCEPT: F. Supression of hypergastrinaemia by secretin given IV * G. A fasting gastrin level of 450pg/ml. H. Post operative notes detailling ulcers in the duodenum and jejunum I. Liver metastasis on CT scan J. A history of diarrhoea 33.A 60yr. Old woman, mother of 6 children, developed sudden onset of upper abdominal pain radiating to the back, associated with nausea, vomitting, fever and chills. Subsequently, she noticed yellow discoloration of her sclera and skin. On physical examination the patient was found to be febrile with temp.of 38.9C, along with right upper quadrant tenderness.Most likely Diagnosis: F. Choledocholithiasis * G. Benign biliary stricture H. Malibnant biliary stricture I. Carcinoma of the head of the pancreas J. Choledochal cyst 34.The family doctor diagnosed in a patient an acute bleeding of an intestine. What is professional tactics of the doctor in this situation? F. The urgent hospitalisation in sergical departmewnt. * G. To inject intravenously the aminocapronic acid. H. The urgent hospitalization in therapeutic department. I. A day time hospital. J. A hospital at home. 35. A 39 year-old womam has jaundice. Blood examination shows total serum bilirubin 127 mcmol/L, direct bilirubin 120 mcmol/L and alkaline phosphatase 2,8. The Diagnosis is: A. Viral hepatitis B. Chronic active hepatitis C. Haemolytic jaundice D. Hemolytic anemia E.* Obstructive jaundice 36. A 45 year-old male presents with jaundice. Total bilirubin is 93 mcmol/L, direct is 81 mcmol/L, alkaline phosphatase 3,2. units. Diagnosis is: A. Viral hepatitis B. Chronic active hepatitis C. Hemolytic jaundice D. Hemolytic anemia E.* Obstructive jaundice 37. A 30-year man presented with fever, nausea and jaundice of 6 days duration. The biochemical tests revealed a bilirubin of 35 mcmol/L (conjugated 15,9 mcmol/L), AST 0.99, ALT- 1.07. The serological tests showed presence of HBs Ag, IgM anti-HBc and Hbe Ag. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Chronic hepatitis B infection with high infectivity. B. Chronic hepatitis infection with low infectivity. C. Acute hepatitis B infection with low infectivity D. None of above E.* Acute hepatitis B infection with high infectivity. 38. A 39-yr-old man presents with acute abdominal pain that radiates through to the back. The pain is severe and causes him to feel sick and vomit repeatedly. On physical examination you find the abdomen to be tender. His serum amylase is five times greater than normal. Choose the single most likely diagnosis A. Gastric atrophy B. Non-ulcer dyspepsia C. Basal pneumonia D. None of above E.* Acute pancreatitis 39. A 45-years man presents with acute abdominal pain in the epigastrium. The pain radiates to the back between the scapulae. It is excruciating. The patient is nauseous and vomits repeatedly. Choose the single most likely diagnosis A. Gallstones B. Gastric ulcer C. Duodenal ulcer D. None of above E.* Acute pancreatitis 40. A 50-yr-old secretary is brought to you with jaundice, malaise and tender hepatomegaly. She has been drinking heavily for the past 2 weeks. Choose the single most likely diagnosis from the list of options above. A. Hepatoma B. Malabsorption C. Pancreatitis D. Peptic ulcer E.* Cirrhosis 41. A 47-yr-old alcoholic presents with weight loss, fever, ascites and pain in the right hypochondrium. Abdominal USG A. ws a focal lesion in a cirrhotic liver. Serum ?-FetoProtein is grossly elevated. Choose the single most likely diagnosis from the list of options above. B. C. D. E.* 42. Sclerosing cholangitis Primary biliary cirrhosis Wilson's disease Pancreatic carcinoma A 59 - year old man presents to his internist with jaundice. The patient is receiving no medication and his only symptomatic complaints is mild fatigue over the past 2 months. Physical examination is remarkable only for the presence of scleral icterus. The patient has no significant past medical history. Analysis of serum chemistry reveals the following: AST 0.58, ALT- 0.58. Total bilirubin: 81.7 mcmol/L Direct Bilirubin: 46 mcmol/L Alkaline phosphatase: 2,2. Which of the following is the next appropriate diagnostic A. step? biopsy Liver B. Total blood count C. Coprogram D. Diastase of urine E.* Ultrasound 43. A 51-yr-old man complains of chronic ill health. He presents with malaise, low grade fever and jaundice. His liver is large and tender and is jaundiced. Biopsy of the liver demonstrates piecemeal necrosis. His HbsAg is positive and HbE antigen is negative. Choose the single most likely management A. B. C. D. E.* Dexamethasone Metronidazole Laparotomy Tinidazole Interferon 44. A 43 year man complains of his appearance. His wife says his eyes are yellow. On physical examination you find mild hepatomegaly. His alkaline phosphatase, albumin and globulin are normal. He says he is a teetotaller. choose the single most likely diagnosis from the list of options above A. B. C. D. E.* 45. Hepatocellular carcinoma Cirrhosis Gallstones Pancreatitis Chronic persistent hepatitis A healthy young waiter complains of feeling unwell with nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea. He has a headache, fever and abdominal pain. On palpation you find the liver to be tender and enlarged. choose the single most likely diagnosis from the list of options above A. Leukaemia B. Cirrhosis C. Gallstones D. Pancreatitis E.* Hepatitis A 46. A 48-yr-old stockbroker presents with jaundice and physical exhaustion. His liver and spleen are enlarged and you notice he has spider naevi on both cheeks. He says he is a moderate drinker and that he has been unwell for more than a year now. A. Hepatitis B B. Hepatitis C C. Gallstones D. Pancreatitis E.* Chronic active hepatitis 47. A middle-aged social worker presents with abdominal pain and fever. She has been unwell for 2 weeks and feels she is getting worse rather than better. Her urine is dark and her stools are pale. She has tender lymph nodes and joint pain. choose the single most likely diagnosis from the list of options above A. B. C. D. E.* 48. A. B. C. Hepatitis A Cirrhosis Gallstones Pancreatitis Hepatitis B A 41-year man presents with dull, aching pain in the right hypochondrium, which he had for 3 weeks. Other complaints include impotence, arthritis, lethargy and weight loss. Choose the single most likely diagnosis from the list of options above. Sclerosing cholangitis Primary biliary cirrhosis Wilson's disease D. Pancreatic carcinoma E.* Haemochromatosis 49. A 39-yr-old man with known ulcerative colitis presented with progressive abdominal pain and itching. On examination he was jaundiced. Choose the single most likely diagnosis from the list of options above. A. Haemochromatosis B. Primary biliary cirrhosis C. Wilson's disease D. Pancreatic carcinoma E.* Sclerosing cholangitis