CPUSH Unit 10 Review Game: The 1920s and 1930s
advertisement

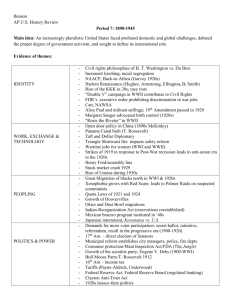
Boom to Bust REVIEW Game: The 1920s & 1930s 1. Explain ONE of the following quotes from the 1920s: (a) President Harding’s promised of a “return to normalcy” OR (b) President Calvin Coolidge’s statement that the “business of America is business.” 2. Two part question: (a) Why were prices so cheap on consumer goods in the 1920s? (b) How did companies in the 1920s help Americans buy goods that they could not afford? 3. Why was the 1920 census (which counts U.S. population, where people live, what jobs people have, etc.) so shocking to many Americans? (What did the 1920 census reveal about America that had never happened before?) 4. Two part question (a) What was the celebration of African-American culture through new artistic, literary, and musical forms? and (b) Name 1 famous member of this movement. 5. Two part question: (a) What was the “Lost Generation”? and (b) What was “Tin Pan Alley”? 6. Both the 18th and 19th Amendments were ratified in 1920 and had a great impact on the decade. What did these two amendments do? 7. Name 3 ways “flappers” expressed their independence in the 1920s 8. Two part question: (a) Name 2 reasons sports boomed in the 1920s and (b) Name 2 sports heroes of the 1920s. 9. Two part question: (a) What was the most popular form of media in the 1920s? (b) What is a “talkie”? 10. What mass-produced consumer good became the #1 industry of the 1920s? 11. Who became a celebrity for making the first solo flight across the Atlantic Ocean in 1927? 12. Rural Americans saw a lot of things in cities that they thought were “un-American.” Name 3 things rural Americans reacted against in the 1920s. 13. What was the Volstead Act? 14. Define each of the following terms (a) bootlegger, (b) rum runner, (c) speakeasy 15. Name two negative effects of Prohibition 16. Who were Nicola Sacco and Bartolomeo Vanzetti? 17. Two part question: (a) In 1921 and 1924 congress passed laws that created immigration quotas. What is an immigration quota? And (b) Which immigrants were effect by quotas? 18. The Ku Klux Klan believed in “100% Americanism.” Name 3 groups who the KKK attacked. 19. Why was John Scopes arrested in Dayton, Tennessee in 1925? 20. Name 3 ways the 1920s were different from the era before World War I 21.Pick any THREE of the following problems and explain how each contributed to the outbreak of the Great Depression in October 1929: (a) weak industries, (b) over-production/under-consumption, (c) farming, (d) uneven distribution of wealth, or (e) on margin buying. 22.Why was “Black Tuesday” (October 29, 1929) such an important date in American history? 23.How did bank failures contribute to the Great Depression? 24.What is “consumer confidence” and how did it make the Great Depression last so long? 25.Name 2 reasons for the Dust Bowl of the 1930s 26.Two part question: What is (a) a Hooverville? and (b) an Okie? 27.What did President Herbert mean by “rugged individualism”? 28.What were the “three R’s” of President Franklin Roosevelt’s New Deal program and what does each “R” mean? 29. Two part question: What is the (a) New Deal and (b) the 100 Days? 30.What was the first action FDR took as president to address the Great Depression? 31.What was the name of FDR’s radio communications to the American people about his plan to fight the depression? 32.Multiple choice: Which New Deal recovery program helped farmers by offering government subsidies so farmers would not produce as much food (thus lowering the supply and increasing price of crops)? (a) Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) (b) Works Progress Administration (WPA) (c) Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA) 33.Multiple choice: Which New Deal relief program gave jobs to young men, aged 18-25, to plant trees and build roads and parks? (a) Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) (b) Works Progress Administration (WPA) (c) Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA) 34.Multiple choice: Which was the largest job-creation program of the New Deal, creating jobs for 10 million Americans including artists, musicians, construction, teachers, doctors, etc.? (a) Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) (b) Works Progress Administration (WPA) (c) Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA) 35.Multiple choice: Which New Deal reform regulated the stock market? (a) Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) (b) Securities and Exchange Committee (SEC) (c) Social Security Administration (SSA) 36.Multiple choice: Which New Deal reform protected American from future bank failures? (a) Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) (b) Securities and Exchange Committee (SEC) (c) Social Security Administration (SSA) 37.Multiple choice: Which New Deal reform offered pensions for elderly Americans and welfare for single mothers and the disabled? (a) Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) (b) Securities and Exchange Committee (SEC) (c) Social Security Administration (SSA) 38.Name two goals of the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA): 39.One of the most popular critics of Franklin Roosevelt and the New Deal was Huey Long. What was Long’s plan to fight the depression? 40.Why were many Americans critical of FDR’s New Deal by 1935? 41.In 1937, the U.S. Supreme Court declared many of the New Deal programs unconstitutional. FDR by trying to “pack the court.” What is “court packing”? 42.Which New Deal reform guaranteed union workers the right to strike and collectively bargain as well as outlawed company practices that discouraged union membership? 43.For the 1st time in American history, FDR decided to get America out of a depression by active government spending, even if the government did not have the money to spend. What is the concept called when the government goes into debt to stimulate the economy? 44.Why did the depression finally come to an end in the 1940s? 45.Name 2 groups of Americans that joined the “Democratic Coalition” (Democratic voting bloc) and became very loyal to the Democratic Party because of FDR’s New Deal efforts? 46.During the depression, who was most responsible for bring attention to the inequalities and racism suffered by African American and the inequalities that women faced in the 1930s? 47.Name 1 major difference between the approaches taken by President Herbert Hoover and President Franklin Roosevelt to combat the depression? 48.Name two New Deal programs that offered relief to Americans during the depression 49.Name two New Deal programs that created long-lasting reforms during the depression 50.Why were Social Security and the Tennessee Valley Authority criticized as “socialistic”? CPUSH Unit 10 Review Game: The 1920s and 1930s THE ANSWERS 1. (a) “Return to normalcy”: Return to isolationism/neutrality, rejected the League of Nations, never signed the Treaty of Versailles; (b) “Business of America is business”: The gov’t should not control the economy; a return to “pro-business” policies to promote economic growth; low taxes; No new progressive reforms 2. (a) Mass production/assembly line production made goods cheap; (b) Available credit (installment plans) also advertising encouraged Americans to buy 3. The census revealed that more Americans lived in urban areas than in rural areas. 4. (a) Harlem Renaissance (b) Langston Hughes (author), Louis Armstrong (musician), Duke Ellington (musician), Ella Fitzgerald (entertainer), etc. 5. (a) Authors like Ernest Hemingway, F Scott Fitzgerald, and TS Eliot who rejected American consumerism and conformity in the 1920s. (b) A musical production center that released 90% of American popular music including jazz, ragtime, and dance music. 6. 18th Amendment created Prohibition; 19th Amendment gave women the right to vote 7. Women voted, danced, wore short hair and dresses, smoked, drank, had causal unchaperoned dates with boys, worked jobs, danced in clubs, expressed their sexuality 8. (a) Americans had more leisure time, more money to spend, radio broadcasted sporting events; (b) Babe Ruth (baseball), Jack Dempsey (boxing), Red Grange (football), Gertrude Ederle (1st woman to swim the English Channel), Bobby Jones (golf) 9. (a) Radio; (b) a movie with sound, like The Jazz Singer 10. Cars 11. Charles Lindbergh 12. Immigration, non-Protestants (Catholics and Jews). Communists, socialists, anarchists, drinking, scientific ideas like evolution, flappers, the Harlem Renaissance. 13. This law enforced the 18th Amendment and made it illegal to sell, manufacture, or transport alcohol during Prohibition. 14. (a) Someone who made alcohol, (b) someone who smuggled alcohol, (c) secret nightclubs 15. Smuggling increased, bootlegging/moonshining increased, organized crime increased, violence increased, mob bosses paid off politicians and police 16. Two Italian immigrants and anarchists who were accused of murder. Sacco and Vanzetti were executed even though there was not much evidence. 17. (a) These immigration laws created quotas that placed a maximum number of immigrants who were allowed to enter the USA. (b) Immigration laws favored Northern European immigrants (from England, Ireland, Germany) and discriminated against Southern and Eastern European immigrants (Italy, Austria, Russia, Poland) 18. African Americans, immigrants, Catholics, Jews, unions, socialists, anarchists 19. He taught evolution to his Biology class which violated the state anti-evolution law 20. Government: changed from progressive pro-business & laissez-faire Foreign policy: changed from imperialism isolationism Industry: changed from ROSE (railroads, oil steel, electricity) consumer goods People: Average income rose, women became more independent and could vote, blacks experienced a Harlem Renaissance; Immigration was restricted 21. (a) Railroads, steel, cotton textile, oil industries were all suffering during the 1920s; These industries began laying off employees well before the crash in October 1929. (b) Companies were making too many consumer goods and there were not enough buyers by the late 1920s (c) Farmers struggled in the 1920s because of the decline in demand for crops after World War I. Farmers had heavy debts and many lost their farms to the banks (foreclosure) (d) 70% of Americans were poor and were not able to spend much money in the 1920s. (e) “Buying on margin” 22. The stock market crashed sparking the Great Depression 23. The “run on the banks” led to a lack of funds and banks had to close; When banks failed, Americans lost their life’s savings; Money in banks was not insured 24. Confidence to spend money. Americans did not spend money which kept business unable to sell which meant there were few jobs 25. Over-farming in the Plains, heavy droughts, lack of trees, high winds, loose topsoil 26. (a) a group of shanties created by people who lost their homes; (b) A farmer (typically from Oklahoma) who moved to California because he lost his farm during the Dust Bowl. 27. This was Hoover’s initial response to the depression: People should work together to work their way out of the depression; He reassured Americans that good times would return; He rejected active gov’t intervention in the economy during the early years of the depression 28. (a) Relief—provide immediate assistance to the unemployment through relief checks and gov’t-created jobs; Recovery—stimulate the economy (especially farming and industry) in order to end the depression; Reform—create long-term solutions to economic problems in order to avoid future depressions 29. (a) FDR’s program to end the depression; (b) FDR’s first 3 months in office when Congress passed 15 New Deal laws to fight the depression 30. The bank holiday 31. Fireside chats 32. AAA 33. CCC 34. WPA 35. SEC 36. FDIC 37. Social Security 38. Provide cheap hydroelectric power to the South and create jobs for unemployed workers 39. His “Share the Wealth” plan would have taxed rich Americans. The very rich would have all money over $1 million taxed and every American would be given $2,500. 40. Since 1933, FDR spend billions of dollars (deficit spending) but the depression had not ended. Many Americans were worried about the size of gov’t, the expense of the New Deal, & how America would pay for it later. 41. FDR attempted to increase the number of justices from 9 to 15. According to the Constitution, the president can appoint whoever he wants to the Supreme Court (but the Senate has to approve). FDR hoped to add 6 more justices who supported the New Deal. The Senate rejected his court packing plan. 42. Wagner Act 43. Deficit spending 44. World War II led to total war, created factory jobs, stimulated industry and agriculture 45. Union members, African Americans, immigrants, & poor voters 46. FDR’s wife, Eleanor Roosevelt 47. Hoover believed in individual efforts while FDR believed the gov’t should take the lead; Hoover did not think it was the government’s responsibility to intervene in the economy while FDR did; Hoover believed in “rugged individualism” while FDR initiated the New Deal. 48. Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), Works Progress Administration (WPA), Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), Public Works Administration (PWA), Civil Works Administration (CWA) 49. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), Social Security, Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), Wagner Act 50. Both programs gave the gov’t control (over retirement, welfare programs, and electricity) rather than private companies. Anytime the gov’t provides a service that could be handled by businesses it is considered a threat to free enterprise (capitalism). Unit 10 Review: The 1920s & 1930s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 1st Place _____________________________________________ 2nd Place _____________________________________________ 3rd Place _____________________________________________ 4th Place _____________________________________________ Unit 10 Review: The 1920s & 1930s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 1st Place _____________________________________________ 2nd Place _____________________________________________ 3rd Place _____________________________________________ 4th Place _____________________________________________