A Glimpse of the Multiple Intelligence Theory
advertisement

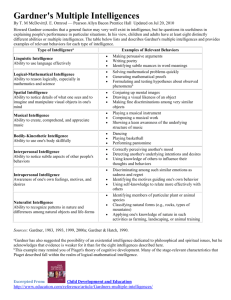
Name: Vincent Zachary Subject: Freshmen English 102 Professor: Teddy Chocos Date: 3/13/2013 A Glimpse of the Multiple Intelligence Theory Born in 1943, Howard Gardner, Hobbs Professor of Cognition and Education at the Harvard Graduate School of Education, redefined the way intelligence is being perceived in this world. His contributions towards the field of education earned him many outstanding accolades such as receiving the MacArthur Foundation award in 1981 and the Grawemeyer Award in Education in 1990, being the first American ever to receive it. Acting as co-director of Harvard’s Project Zero, which aim is to improve the standards of education in schools by putting the elements of creativity into effect in terms of how students think and solve problems, he formulated one of the most famous theories regarding human intelligence in the modern age; it is known as the Multiple Intelligence Theory. The Multiple Intelligence Theory first came to light from his published book, Frames of Mind. In the book, he argued against the generalized perception of intelligence, which is based the measurements set by the IQ (Intelligence Quotient) test, a test formulated by a French psychologist named Alfred Binet. The results of an IQ test will signify the level of basic intelligence a person inherently possesses. Gardner begged to differ with this famous method of intelligence measurement, and he supported his objections with several insights. One of it was based on the fact that IQ results may be the decisive factor for a person in terms of succeeding in schools, but not a contributing factor towards successes in life. The second insight was established by his research of the human brain. He found that certain parts of the brain control the functionality of the mind, and this discovery led him to believe that intelligence is not restricted to one singular form; it is in fact dispersed into several. The purpose of the Multiple Intelligence Theory was not formed to disprove Binet’s theory. Rather, its aim is to enhance it, shedding the singularity of intelligence and pluralize it into multiple intelligences, and Gardner did so by introducing seven forms of intelligences (Musical, Bodily-Kinesthetic, Logical-Mathematical, Linguistic, Spatial, Interpersonal and Intrapersonal). These intelligences were selected based on strict criteria, both biological and cultural, and only those which pass that particular criteria are recognised under the theory. Factual evidences and real-life examples pertaining to their respective intelligences were given. Under the category of Musical Intelligence, he introduced world renowned violinist Yehudi Menuhin, who was a child prodigy. First he gave a background of how Menuhin was exposed to violin music, along with his remarkably fast progress in becoming an international performer. Gardner explained how his musical intelligence was triggered before he even played the violin, suggesting that his strong response towards hearing violin music for the first time and incredible advancement in violin when he underwent training was the act of musical intelligence. Gardner also gave factual information on why musical intelligence made the criteria. He explained that established parts of the brain are biologically linked to the perception and production of music. Although his theory defined intelligence in several forms, these intelligences work together as a whole system. Although this may seem contradictory, Gardner aims to establish his point that human intelligence are not restricted to standardized tests alone. The theory established the unique attributes a single person has, for her or she may possess several intelligences, which allows the person to have a personalised identity, which is of utmost importance for every human being to know his or her strengths and weaknesses