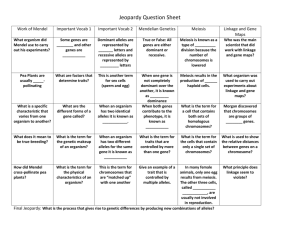
Genetics & Evolution Quiz: Inheritance, Speciation

Formative quiz – 10.2
1.
In some plants, the gene that codes for flower colour is controlled by more than one gene.
R – Red flowers
RB – Blue flowers rr/bb – White flowers a.
What is the name of this type of inheritance? (When more than one gene influences the phenotype? (1 point) b.
A plant with blue flowers (RRBB) was crossed with a white flowered plant (rrbb). What are the phenotypes and genotypes for the F1 generation? (2) c.
If the F1 plants are allowed to reproduce, what gametes will they produce? (1) d.
Using the gametes from your answer in part c, what are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for the next generation? Use a punnet square as part of your answer (5)
2.
When grey-bodied, long-winged Drosophila were crossed with blackbodied, vestigial-wing flies the F1 generation was found to contain:
407 grey-bodied, long-winged flies
396 black-bodied, vestigial-winged flies
75 black-bodied, long-winged flies
69 grey-bodied, vestigial-winged flies a.
State the name of a cross involving two genes (1) b.
Identify the recombinants (1)
The F1 generation does not follow Mendel’s Law of independent assortment. c.
State the expected ratio for a test cross that follows Mendel’s Law of independent assortment (1) d.
Explain how the observed ratio could have arisen (draw a punnet square to illustrate this), include a key to explain the symbols representing the alleles. (5)
3.
The table shows frequencies of ABO blood groups in three populations that do not breed with each other.
Population Frequency (%)
Andamanese
(India)
Navajo (N.
America)
O
9
73
A
60
27
B
23
0
AB
9
0
Kalmyk
(Mongolia)
26 23 41 11 a.
Compare the frequencies of the I A , I B and I alleles in the three populations (5) b.
Suggest two reasons for the difference (2) c.
Suggest two processes that could cause the blood group frequencies to change in a population (2)
d.
State the term used for all the alleles in an interbreeding population (1)
4.
In the species Allium schoenoprasum (chives) many adult plants have 16 chromosomes and many have 32. Smaller numbers of plants have 24 chromosomes. a.
The plants with 16 and 24 chromosomes are reproductively isolated, even when growing close together. Explain what could cause this isolation (4) b.
State two other causes of reproductive isolation (2) c.
Discuss whether the plants with 16 and 32 chromosomes are separate species (4)
Formative quiz – 10.3
1.
Define the term ‘gene pool’ (1)
2.
Define the term ‘speciation’ (1)
3.
Describe the difference between temporal, behavioural and geographic isolation (3)
4.
What is meant by the term ‘punctuated equilibrium’? (1)
5.