Cell Growth and Replication notes `15
advertisement
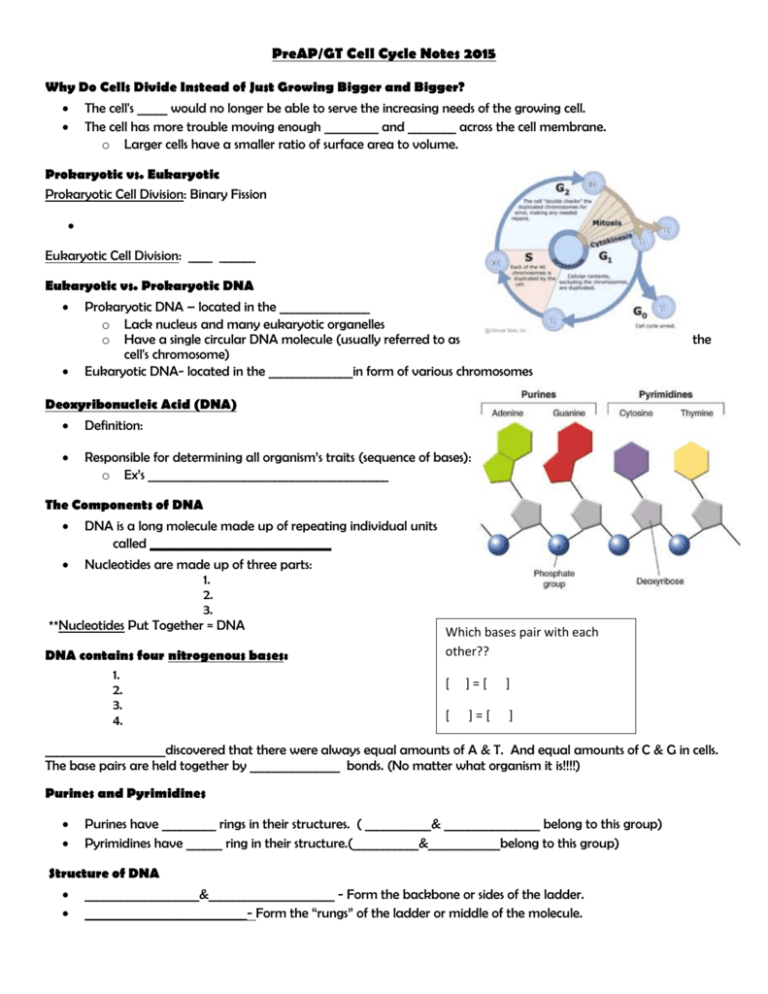
PreAP/GT Cell Cycle Notes 2015 Why Do Cells Divide Instead of Just Growing Bigger and Bigger? The cell's _____ would no longer be able to serve the increasing needs of the growing cell. The cell has more trouble moving enough _________ and ________ across the cell membrane. o Larger cells have a smaller ratio of surface area to volume. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cell Division: Binary Fission Eukaryotic Cell Division: ____ ______ Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic DNA Prokaryotic DNA – located in the _______________ o Lack nucleus and many eukaryotic organelles o Have a single circular DNA molecule (usually referred to as cell's chromosome) Eukaryotic DNA- located in the ______________in form of various chromosomes the Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition: Responsible for determining all organism’s traits (sequence of bases): o Ex’s ________________________________________ The Components of DNA DNA is a long molecule made up of repeating individual units called ___________________________ Nucleotides are made up of three parts: 1. 2. 3. **Nucleotides Put Together = DNA DNA contains four nitrogenous bases: 1. 2. 3. 4. Which bases pair with each other?? [ ]=[ ] [ ]=[ ] ____________________discovered that there were always equal amounts of A & T. And equal amounts of C & G in cells. The base pairs are held together by _______________ bonds. (No matter what organism it is!!!!) Purines and Pyrimidines Purines have _________ rings in their structures. ( ___________& ________________ belong to this group) Pyrimidines have ______ ring in their structure.(___________&____________belong to this group) Structure of DNA ___________________&_____________________ - Form the backbone or sides of the ladder. ___________________________- Form the “rungs” of the ladder or middle of the molecule. Shape of DNA: DNA looks like a “twisted ladder” called a _________________________. Discovering DNA 1. _______________________________ - Used X-ray diffraction; Showed the X-shaped pattern of DNA (helix shape) 2. ____________________ and _____________________ – Two scientists that discovered the double helix shape in 1953 You Try It! What is the complimentary DNA strand if the original DNA strand is AGTCTA? ______________________ Chromosomes _________________________ - Very long, continuous single piece of DNA, contains many genes _________________ - Sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait In eukaryotic cells, the genetic information that is passed on from one generation of cells to the next is carried by chromosomes. The cells of every organism have _________________________________________ o The cells of fruit flies have 8 chromosomes. o Human cells have __________ chromosomes. o Carrot cells have 18 chromosomes. Chromosomes are not visible in most cells except during _______________________. Well before cell division, each chromosome is ___________________ (During the S Phase of Interphase). DNA molecules are surprisingly long: 4, 639, 221 base pairs in E. coli At the beginning of cell division, however, the chromosomes condense into compact, visible structures; they are folded and tightly packed to fit within the cell. Each chromosome consists of two identical “sister” _______________________. o When the cell divides, the “sister” chromatids separate from each other. o One chromatid goes to each of the two new cells. Each pair of chromatids is attached at an area called the ________________________. If a meerkat’s parent skin cell contained 34 chromosomes; after cell division how many chromosomes would each of the meerkat’s daughter skin cells contain? _________________________ S-Phase: DNA Replication Before a cell divides, it duplicates its DNA via a process called ___________________________ Occurs during ______________________ of cell division Ensures that each resulting cell will have a complete _______________ set of DNA molecules Result: Two identical DNA molecules (each DNA molecule has one original strand and one new strand) How DNA Replication Occurs Step 1: o Helicase, an enzyme, ______________________________________ o Hydrogen bonds between ____________________ are broken o Result = 2 separated strands of DNA Step 2: A replication fork is formed. Step 3: Free floating nucleotides pair up with complimentary bases o Each strand of DNA serves as a template, or model, for the new strand o DNA Polymerase – Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Cell Cycle - Series of events that cells go through as they grow and replicate. o Interphase - Period of the cell cycle between cell divisions (consists of _________________ phases) o M Phase – (division of the cell nucleus) (division of the cytoplasm) o There are 3 “__________________________” that allow the cells to continue moving through the cell cycle. Regulating the Cell Cycle Not all cells move through the cell cycle at the same rate. Cell growth and cell division are controlled. ______________________ are proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle in ___________________. If cells are placed in a petri dish containing nutrient broth (provides food for the cells): o Cells will grow until they form a thin layer covering the bottom of the dish. o Then, the cells stop growing, when they come into ______________________________ with other cells. If cells are removed from the center of the dish: o The cells bordering the open space will begin dividing until they have filled the empty space. This occurs in an injury as well: o o If a cut in the skin or a break in a bone occurs, cells at the edges of the injury are stimulated to divide rapidly. When the healing process nears completion, the rate of cell division slows down. Cancer Cancer – o Cancer cell divide ____________________________________ and form masses of cells (tumors) o Cancer cells may spread throughout the body: o Disrupts normal activities and causes serious medical problems or even death o There are many reasons that cells can divide and grow out of control: Exposure to environmental causes: Nutritional deficiencies; genetic causes; some infections Cell Cycle (2 phase)- Interphase G1 Phase – o G1 Checkpoint S Phase – G2 Phase – o G2 Checkpoint Cell Cycle – M Phase (cell division) Cell Division – M Phase –Mitosis (division of the cell nucleus) Cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm) o Before cell division occurs, the cell replicates, or copies, all of its DNA. o Each daughter cell gets one complete set of genetic information. Asexual Reproduction Reproduction by Mitosis is classified as asexual, since the cells produced by mitosis are: Asexual Reproduction - Reproduction without the fusion of gametes; not necessary to have ______ parents o Examples include: Four Phases of Mitosis 1. _________________________(chromosomes visible/centrioles; nuclear envelope disappears) 2. _________________________ (microtubles line the chromosomes up in middle of cell ) 3. __________________________ (sister chromatids separate to opposite ends of cell) 4. __________________________ (chromosomes condense back to chromatin and nuclear envelope reappears) (Four phases are followed by _____________________________) Cytokinesis - Usually occurs at the same time as ________________. It is the division of the _____________ Animal Cells: _________ __________ Plant Cells: _________ __________









