Sample Exam (Exercpt)
advertisement

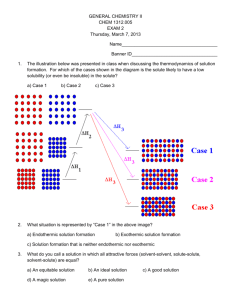
Part 3: Thermodynamic Factors Affecting Solution Formation 7. Dissolving one substance in another usually a) increases the entropy 8. c) leaves the entropy unchanged The formation of a solution is often accompanied by a change in enthalpy (ΔH). Shown below is the diagram presented in class when this topic was discussed. The 3 possible outcomes (with regard to enthalpy) have been labeled as Case 1, Case 2, and Case 3. Which of these corresponds to an endothermic solution formation process? a) Case 1 9. b) decreases the entropy b) Case 2 c) Case 3 In question 8, the solute would probably a) Have a high solubility in the solvent. A quite concentrated solution could be prepared. b) Have a low solubility, or maybe even be insoluble in the solvent. Only a dilute solution (if any) could be prepared. 10. In the diagram shown in question 8, which case corresponds to the formation of an ideal solution? a) Case 1 b) Case 2 c) Case 3 Part 4: Calculation of Solution Concentration Units 11. A salt water solution was prepared by dissolving 0.155 moles of NaCl in enough water to produce 75.8 mL of solution. What is the molarity of NaCl in this solution? a) 0.82 M 12. c) 2.58 M d) 3.45 M e) 4.98 M b) 1.87 m c) 3.06 m d) 4.22 m e) 5.71 m b) 1.22 m c) 1.97 m d) 3.18 m e) 4.16 m b) 0.195 c) 0.266 d) 0.402 e) 0.516 What is the mole fraction of ethylene glycol (CH2OHCHOHCH2OH or in condensed form, C3H8O3) in a solution prepared by dissolving 50.0 g of C3H8O3 in 70.0 g of water? Atomic weights: C 12.01 H 1.008 O 16.00 a) 0.123 17. b) 1.54 M What is the mole fraction of ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) in a solution prepared by dissolving 0.587 moles of C 2H5OH in 0.872 moles of water? a) 0.116 16. e) 3.16 M A potassium iodide solution was prepared by dissolving 134 g of KI in 194 g of water. What is the molality of KI in this solution? Atomic weights: K 39.10 I 126.90 a) 0.85 m 15. d) 2.96 A calcium chloride solution was prepared by dissolving 0.472 moles of CaCl2 in 511 g of water. What is the molality of CaCl2 in this solution? a) 0.92 m 14. c) 2.04 M An aqueous solution of KCl was prepared by dissolving 14.23 g of KCl in enough water to produce 124 mL of solution. What is the molarity of KCl in this solution? Atomic weights: K 39.10 Cl 35.45 a) 0.85 M 13. b) 1.38 M b) 0.218 c) 0.296 d) 0.415 e) 0.552 What is the mass percent of glucose (C6H12O6) in a solution prepared by dissolving 25.48 g of C6H12O6 in 84.77 g of water? a) 12.98% b) 23.11% c) 37.14% d) 51.02% e) 67.34% Part 5: Converting From One Concentration Unit to Another 18. What is the molality of a 1.47 M solution of KI in water? The density of this solution is 1.17 g/mL. Atomic weights: K 39.10 I 126.90 a) 1.02 m 19. c) 2.16 m d) 2.97 m e) 3.87 m What is the molarity of an 8.94 m solution of MgCl2 in water? The density of this solution is 1.37 g/mL. Atomic weights: Mg 24.31 Cl 35.45 a) 3.48 M 20. b) 1.59 m b) 4.77 M c) 6.62 M d) 9.73 M e) 12.56 M What is the mole fraction of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in a 9.43 m NaOH solution? Atomic weights: H 1.008 O 16.00 Na 22.99 a) 0.145 b) 0.258 c) 0.331 d) 0.519 e) 0.722 Part 6: Colligative Properties 21. What is the vapor pressure of a solution containing 12.35 g of naphthalene, C 10H8 (solute) dissolved in 100.00 g of hexane, C6H14 (solvent) at 25 oC? Assume that the naphthalene is a non-volatile, non-ionizing solute, and that the solution obeys Raoult’s law. At 25 oC, the vapor pressure of pure hexane is 151 torr. Atomic weights: C 12.01 H 1.008 a) 27 torr 22. b) 54 torr c) 75 torr d) 103 torr Deleted from test, due to an error on this question. Choose answer a for automatic credit. a) Choose a! e) 139 torr 23. Deleted from test due to an error. Choose answer a for automatic credit. a) Choose a! 24. Deleted from test due to an error. Choose answer a for automatic credit. a) Choose a! 25. An aqueous solution containing 35.9 g of an unknown non-volatile, non-ionizing compound (solute) dissolved in 150.0 g of water (solvent) was found to have a freezing point of -1.3 oC. What is the molecular weight of the unknown compound? Note that pure water has a freezing point of 0.0 oC, and the freezing point depression constant for water is 1.86 oC/m. a) 75.8 g/mol b) 122 g/mol c) 181 g/mol d) 256 g/mol e) 342 g/mol