Grade 7 Science Pacing Guide 2012
advertisement

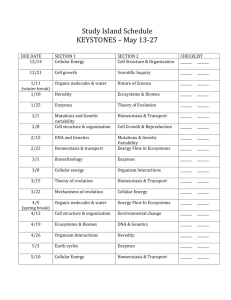
Grade 7 Science Pacing Guide 2012-13 SOL STRAND LS.1 Scientific Investigation Unit 1: Scientific Investigations - Independent and dependent variables - Constants and control - Metric measurement (length, volume, temperature, time, & mass) LS. 2 a-d LS. 3 a-b LS. 5 a-b Life Systems - Compare and contrast plant and animal cells - Identify the roles of cell organelles - Differentiate between mitosis and meiosis - Distinguish between active transport, passive transport (diffusion), and osmosis - Identify the raw materials and products of photosynthesis and cellular respiration LS. 12 a-f Life Systems Unit 2A: Cell Studies -Cell Theory -Cell parts -Cell organization Unit 2B: Part II – Cell Processes - Mitosis - Meiosis - Active/passive transport (diffusion) - Osmosis - Photosynthesis - Cellular Respiration Unit 3: Genetics - Role of DNA - Function of genes & chromosomes - Genotypes & phenotypes - Dominate & recessive traits - Homozygous vs. heterozygous - Genetic engineering - Historical contributions by notable scientists Unit 1, 2 &3 PMMS: week 12-13 LS. 13 a-c Earth & Space Systems - Investigate and understand the relationship b/t mutations, adaptations, natural selection, and extinction - Discuss how environmental influences can affect adaptation and change LS. 4 a-d Life Systems Unit 4: Adaptation Over Time -5 pieces of evidences for evolution - Organisms change over time through mutation, variation, adaptation, and natural selection - Understanding fossil evidence - Extinction - Contribution of Darwin Unit 5: Classification - 7 levels of classification - Dichotomous key - Binomial Nomenclature -History of classification - Six kingdoms survey - Survey of Invertebrates/Vertebrates Pre-test Benchmark #1 CONTENT SKILLS All units PMMS, SKMS & NFMS: week 1-2 Plan and Conduct Investigations - Identify variables - Collect data using the metric system - Organize data into charts and graphs and interpret that data - Discuss sources of experimental error - Understand how genotypes influence phenotypes - Use Punnett squares to predict possible reproductive outcomes - Distinguish b/t dominant & recessive traits - Distinguish b/t genotype & phenotype - Discuss applications of genetic engineering, positive and negative SKMS & NFMS: week 7-8, 25-26 - Classify organisms based on meaningful similarities - Use a dichotomous key to identify an organism - Analyze similarities and differences between organism groups Benchmark #2 Post-test LS. 5 d LS.6 b,d LS. 7 a,b LS.8 a-e LS. 9 c LS. 10 a-c Ecosystems LS. 6 a,c LS. 9 a-b Ecosystems LS. 11 a-e Ecosystems Unit 1-5 PMMS: week 27-28 Unit 6A: Ecology: Structures and Interactions in Ecosystems - Biotic & a-biotic factors - Interactions within a population (competition, cooperation, social hierarchy, territorial imperative) - Interactions among populations of a community (predator/prey, symbiotic relationships) - Organism responses to environmental stressors (phototropism, hibernation, dormancy) Unit 6B: Ecosystems and Biomes - Land biomes - Water biomes - Water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles - Ecological succession Unit 6C : Human Influences on the Ecosystem -Relationships between ecosystems and human activity (positive and negative) - Diagram food chains and food webs - Illustrate the flow of energy through a food chain - Draw and interpret an energy pyramid - Identify biotic and a-biotic components of an environment - Discuss examples of competition, cooperation, social hierarchy, territorial imperative - Identify predator-prey relationships - Distinguish between the 3 types of symbiosis - Identify individual responses to environmental stressors SKMS & NFMS: week 14-15, 30-31 All Units PMMS, SKMS & NFMS: week 35-36 - Compare/contrast the different biomes in terms of temperature, precipitation, vegetation, and species. - Distinguish between a biome and an ecosystem. - Explain/illustrate nature’s cycles - Describe ecological succession for a temperate forest biome Students will investigate and understand the effect of the following on ecosystems: - Food production and harvest - Change in habitat size, quality, and structure - Change in species competition - Population disturbances and factors that threaten species survival - Environmental issues including water supply and quality, air quality, energy production, and waste management