Assessment Glossary - ncassessmentmanual
advertisement
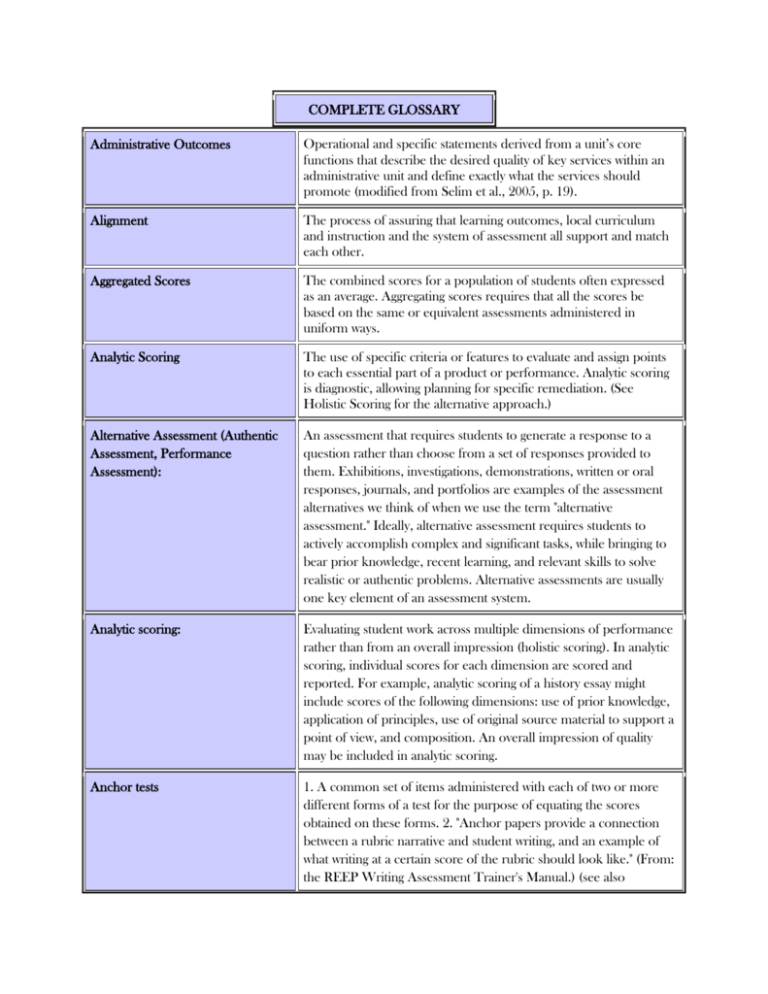
COMPLETE GLOSSARY Administrative Outcomes Operational and specific statements derived from a unit’s core functions that describe the desired quality of key services within an administrative unit and define exactly what the services should promote (modified from Selim et al., 2005, p. 19). Alignment The process of assuring that learning outcomes, local curriculum and instruction and the system of assessment all support and match each other. Aggregated Scores The combined scores for a population of students often expressed as an average. Aggregating scores requires that all the scores be based on the same or equivalent assessments administered in uniform ways. Analytic Scoring The use of specific criteria or features to evaluate and assign points to each essential part of a product or performance. Analytic scoring is diagnostic, allowing planning for specific remediation. (See Holistic Scoring for the alternative approach.) Alternative Assessment (Authentic Assessment, Performance Assessment): An assessment that requires students to generate a response to a question rather than choose from a set of responses provided to them. Exhibitions, investigations, demonstrations, written or oral responses, journals, and portfolios are examples of the assessment alternatives we think of when we use the term "alternative assessment." Ideally, alternative assessment requires students to actively accomplish complex and significant tasks, while bringing to bear prior knowledge, recent learning, and relevant skills to solve realistic or authentic problems. Alternative assessments are usually one key element of an assessment system. Analytic scoring: Evaluating student work across multiple dimensions of performance rather than from an overall impression (holistic scoring). In analytic scoring, individual scores for each dimension are scored and reported. For example, analytic scoring of a history essay might include scores of the following dimensions: use of prior knowledge, application of principles, use of original source material to support a point of view, and composition. An overall impression of quality may be included in analytic scoring. Anchor tests 1. A common set of items administered with each of two or more different forms of a test for the purpose of equating the scores obtained on these forms. 2. "Anchor papers provide a connection between a rubric narrative and student writing, and an example of what writing at a certain score of the rubric should look like." (From: the REEP Writing Assessment Trainer's Manual.) (see also Benchmark tasks; Benchmarking.) Annotated Rubric The notes from an assessment development group, often after a field test and initial scoring, which explain the meaning of criteria or distinctions between the criteria on a rubric. Annotation is an important tool to increase scoring reliability and to train others to score consistently. Assessment Any systematic method of obtaining information from tests and other sources, used to draw inferences about characteristics of people, objects, or programs; the process of gathering, describing, or quantifying information about performance; an exercise-such as a written test, portfolio, or experiment-that seeks to measure a student's skills or knowledge in a subject area. Also, a systematic and ongoing process of gathering and interpreting information to discover if programs/services are meeting intended outcomes/objectives and then using the information to enhance the programs/services (adapted from Virginia Commonwealth University, 2002 & Marchese, 1987). Authentic A characteristic of assessments that have a high degree of similarity to tasks performed in the real world. The more authentic the assessment, the less inference required to predict student success after graduation. Unit Effectiveness Handbook Page 82 Authentic assessment (alternative assessment, performance assessment) Assessment is authentic when we directly examine student performance on worthy intellectual tasks.... Authentic assessments present the student with a full array of tasks that mirror the priorities and challenges found in the best instructional activities. Benchmark A detailed description of a specific level of student performance expected of students at particular ages, grades, or development levels. Benchmarks are often represented by samples of student work. A set of benchmarks can be used as "checkpoints" to monitor progress toward meeting performance goals within and across grade levels. In ABE, SPLs (Student Performance Levels) are examples of benchmarks; targets for instruction. Benchmark tasks Pieces of student work selected by a group of lead teachers as exemplifying a certain score level. (See also Anchor Test.) Benchmarking Comparing performances of people on the same task; raters use "anchors" to score student work, usually comparing the student performance to the "anchor"; benchmarking is a common practice in the business world. (See also Anchor Test.) Bias A situation that occurs in testing when items systematically measure differently for different ethnic, gender, or age groups. Test developers reduce bias by analyzing item data separately for each group, then identifying and discarding items that appear to be biased. Competency: A group of characteristics, native or acquired, which indicate an individual's ability to acquire skills in a given area. Competency-based assessment (criterion-referenced assessment) Measures an individual's performance against a predetermined standard of acceptable performance. Progress is based on actual performance rather than on how well learners perform in comparison to others; usually still given under classroom conditions. CASAS and BEST are examples of competency-based assessments. Constructed response item An exercise for which examinees must create their own responses or products (performance assessment) rather than choose a response from an enumerated set (multiple choice). Constructivist theory Posits that people build new information onto pre-existing notions and modify their understanding in light of new data. In the process, their ideas gain in complexity and power. Constructivist theorists dismiss the idea that students learn by absorbing information through lectures or repeated rote practice. For example, EFF embraces a school of constructivism, which invites learners to create their own meaning and achieve their own goals by interacting actively with objects and information and by linking new materials to existing cognitive structures. Content standards Broadly stated expectations of what students should know and be able to do in particular subjects and (grade) levels. Content standards define for teachers, schools, students, and the community not only the expected student skills and knowledge, but what programs should teach. For example, in Equipped for the Future (EFF), there are 16 content standards or skills, each containing key aspects which are essential for being able to apply the skills to real tasks or activities. "Read With Understanding," then, entails: determining the reading purpose, selecting reading strategies appropriate to that purpose, monitoring comprehension and adjusting reading strategies, analyzing the information and reflecting on its underlying meaning, and integrating it with prior knowledge to address reading purpose. In Massachusetts' Curriculum Frameworks, each of the disciplines contains its own set of broader standards (The Massachusetts Common Core of Learning), as well as its own set of strands. The strands in English Language Arts (ELA) then, are reading, writing, oral communication, and critical thinking. Under reading, there are six levels of standards around symbol mastery, phonology and decoding, word recognition, and comprehension. Core Concepts (ACLS) The core concept of each framework articulates why the subject matter is important in the lives of the adult learner. The core concepts underlie the goals, the principles, knowledge, and skills the adult learner needs to have ownership of the subject matter. Countable Outcomes (ACLS) Results that can be quantified; all measures of student outcomes except learning gains, including executive function skills, and affective-related measures. Learning gains are gains in speaking, listening, reading, writing, and numeracy. Executive function skills include problem-solving, critical thinking, and metacognition. Affective-related measures include self-esteem, self confidence, and interpersonal communication. Examples of Countable Outcomes include: number of people who get jobs, number of people who register to vote, number of people who achieve a GED. Course-Level Assessment Assessment to determine the extent to which a specific course is achieving its learning goals. (For comparison, see Program Assessment and Institutional Assessment.) Criterion-Referenced Test A measurement of achievement of specific criteria stated as levels of mastery. The focus is performance of an individual as measured against a standard or criteria rather than against performance of others who take the same test. See Standardized, Norm‐referenced Tests. Unit Effectiveness Handbook Page 83 Creaming The process of focusing on participants who are easy to serve, with the possible consequence of neglecting those participants who are most in need of services. Criteria Guidelines, rules, characteristics, or dimensions that are used to judge the quality of student performance. Criteria indicate what we value in student responses, products or performances. They may be holistic, analytic, general, or specific. Scoring rubrics are based on criteria and define what the criteria mean and how they are used. Criterion-referenced assessment (competency-based assessment) An assessment where an individual's performance is compared to a specific learning objective or performance standard and not to the performance of other students. Criterion-referenced assessment tells us how well students are performing on specific goals or standards rather that just telling how their performance compares to a norm group of students nationally or locally. In criterion-referenced assessments, it is possible that none, or all, of the examinees will reach a particular goal or performance standard. Criterion-referenced tests Tests that assess a learner's achievement against an absolute standard or criterion of performance (rather than against a norming group). Curriculum (ACLS) All of the instruction, services, and activities provided for students through formal schooling including but not limited to: content, teaching methods and practices, instructional materials and guides, the physical learning environment, assessment and evaluation, time organization, leadership, and controls. Curriculum includes planned, overt topics of instruction as well as unseen elements such as norms and values taught by the school and through classroom interactions between the teacher and learner, hidden social messages imbedded in the curriculum materials themselves, and the material that is not included in the overt or planned curriculum. Curriculum Framework (ACLS) A curriculum framework is a document outlining content strands and learning standards for a given subject area. The Massachusetts CFs are grounded in an understanding of how adult students learn, and they address the question "What do adult learners need to know and be able to do to function successfully in their roles of parent/family member, worker, and citizen?" Curriculum frameworks provide a structure from which lessons and curricula can be organized and presented to the student. The specific knowledge and skills taught in the classroom are based on student needs and objectives as identified by the teacher and students. By providing examples of learning activities and successful instructional strategies, the frameworks link statewide learning standards found within the framework to educational practices developed at the classroom level. The process of developing standards-based assessments using the frameworks is intended to produce consistency in learning standards among ABE programs across the state. Curriculum Mapping A matrix showing the coverage of each program learning outcome in each course. It may also indicate the level of emphasis of each outcome in each course (from Bridgewater State College, n. d. as Course Mapping). Cut Score The number of points needed which represents the criteria for successful completion of an assessment task, such as eight out of 10, or the percent that must be attained to be determined as successful in performing an assessment task (e.g., 80%). Cut score also refers to the critical point for dividing scores into two groups in reference to some criterion. It is possible to set multiple cut scores from differing criterion (e.g., meets, does not meet and exceeds). Cut score A specified point on a score scale, such that scores at or above that point are interpreted or acted upon differently from scores below that point. (See also Performance Standard.) Direct Assessment Method of gauging student achievement of learning outcomes through evaluation of student work products (Bridgewater State College, n. d.). For comparison, see Indirect Assessment. Equipped for the Future A customer-driven, standards-based, collaborative initiative of the National Institute for Literacy. EFF's large goal is to align the components of the nation's adult learning system to focus on the range of skills and knowledge that adults need to achieve their primary purposes for learning. EFF has been instrumental in shifting approaches for adult literacy education from an emphasis on replicating K-12 education to one that uses research-based standards to prepare adults to meet their real-world goals. Evaluation When used for most educational settings, evaluation means to measure, compare, and judge the quality of student work, schools, or a specific educational program. Exemplar Actual samples of student work that illustrate the essential characteristics of work typical of exemplary student work at the top scoring level on a scoring rubric. Several exemplars are desirable to promote creativity so that students see multiple products/performances are possible. Embedded Assessment Methods A method in which evidence of student learning outcomes for the program is obtained from assignments in particular courses in the curriculum (Bridgewater State College, n. d.). Expectation An estimate of the percent of students who will meet the defined standard for a learning outcome. Unit Effectiveness Handbook Page 84 Feasibility/Reasonableness A characteristic of scoring criteria ensuring that the judging of student work is appropriate for the conditions within which the task was completed. Formative assessment Assessment that provides feedback to the teacher for the purpose of improving instruction. Generative Skills The term EFF gives to the skills or knowledge that their research revealed to be core to the performance of a wide range of tasks carried out in multiple roles. The Generative Skills are durable over time in face of changes in technology, work process, and societal demands. They cross functions and serve as the foundation for effective adaptation to changes in role requirements. Goals The general aims or purposes of a program and its curriculum. Effective goals are broadly stated, meaningful, achievable and assessable. Goals provide a framework for determining the more specific educational objectives of a program, and should be consistent with program and institutional mission. Grade Level Equivalent (GLE) The school grade level for a given population for which a given score is the median score in that population. For example, if a test was administered during the month of October to a norming group of sixth grade students and the median scale score obtained was 475, then the grade equivalent for a scale score of 475 on that test would be set at 6.1 - 6 representing Grade 6 and .1 representing the month of October (September is taken as the beginning of the school year and equals .0). Grade level norms Interpreting scores on a test in reference to the average performance of children at each grade level. For example, in ABE, standardized tests are frequently used that have been normed on children in the elementary, middle, and secondary school grades; thus, an ability of 4.8 would be assigned to an adult reading at about the same level as a child in her 8th month of the 4th grade, for example. While the grade level score is based on the performance of children in the school grades, the interpretation of the score should be based on the performance of adults on the test. The TABE and the ABLE provide norms for adults in ABE programs that permit test users to interpret scores both in grade levels and in relation to adult performance on the tests. Guiding Principles (ACLS) Underlying tenets or assumptions that describe effective learning, teaching and assessment within each subject area. Habits of Mind (ACLS) A fluid and life-long approach to learning that involves reflection, inquiry, and action. It is an approach that favors uncovering concepts rather than covering content. They encourage the learner to think about how they acquire knowledge. High-stakes test A test used to provide results that have important, direct consequences for examinees, programs, or institutions involved in the testing. For example, MCAS (K-12) is considered a high-stakes test because children who do not pass the examination do not receive a high school diploma, regardless of their performance in other areas of their school education. Holistic scoring Evaluating student work in which the score is based on an overall impression of student performance rather than multiple dimensions of performance (analytic scoring). Impacts Changes that occur in the family, community, and larger society as a consequence of participation in adult literacy education. Indicators Measures used to track performance over time. Accountability systems commonly use input indicators (provide information about the capacity of the system and its programs); process indicators (track participation in programs to see whether different educational approaches produce different results); output indicators (short-term measures of results); outcome indicators (long-term measures of outcomes and impacts). Indirect Assessment Assessment that deduces student achievement of learning outcomes through students’ reported perception of their own learning. May also be the opinions or thoughts of others about student knowledge, skills, attitudes, learning experiences, and perceptions. Examples of indirect measures include student surveys about instruction; focus groups; alumni surveys; employer surveys (modified from Community College of Aurora, n. d., California Polytechnic State University, n. d., & Bridgewater State College, n. d.0). For comparison, see Direct Assessment. Indirect Measure of Learning Outcome Students or others report their perception of how well a given learning outcome has been achieved (California Polytechnic State University, n.d.). Institutional Assessment Assessment to determine the extent to which a college or university is achieving its mission. (For comparison, see Course‐level assessment and Program Assessment.) Inter-rater reliability The consistency with which two or more judges rate the work or performance of test takers. Item response theory (IRT) A method for scaling individual items for difficulty in such a way that an item has a known probability of being correctly completed by an adult of a given ability level. Iterative A term used in research to refer to the repetition of a cycle of processes with an eye toward moving ever more closely toward desired results. In EFF for example, the term is used to describe how EFF has progressively refined the concepts and components of EFF through research, feedback from customers (learners, practitioners, stakeholders, and policymakers), incorporation of research developments in related areas, further feedback from customers, etc., in an effort to be responsive and credible to their constituents. Learning Outcomes (ACLS) Learning outcomes describe the learning mastered in behavioral terms at specific levels. In other words, what the learner will be able to do. Learning Standards (ACLS) Learning standards define in a general sense the skills and abilities to be mastered by students in each strand at clearly articulated levels of proficiency. Map A chart that summarizes the major elements of a system and shows the relationships between the parts of a system. Materials-based assessment Evaluation of learners on the basis of tests following the completion of a particular set of curriculum materials. A commercial text and its accompanying workbook is an example of this type of assessment. Measurement Process of quantifying any human attribute pertinent to education without necessarily making judgements or interpretations. Methods of Assessment Tests and procedures used to measure student performance in meeting the standards for a learning outcome. These assessments must relate to a learning outcome, identify a particular kind of evidence to be evaluated, define exercises that elicit that evidence and describe systematic scoring procedures. Methods of assessment are classified as either forced choice/short answer or complex generated (performance-based) response. Metacognition Refers to an individual's ability to think about his/her own thinking and to monitor his/her own learning. Metacognition is integral to a learner's ability to actively partner in his or her own learning and facilitates transfer of learning to other contexts. National Education Goal 6 One of the national education goals created by the 50 governors at an education summit in 1989. Goal 6 is the only goal directly related to adult learning and is often referred to as the Adult Literacy and Lifelong Learning Goal. Goal 6 reads, "Every adult American will be literate and will possess the knowledge and skills necessary to compete in a global economy and exercise the rights and responsibilities of citizenship." National Adult Literacy Survey (NALS) A national survey reported in 1993, which provided a profile of the literacy skills of the United States' adult population. The results revealed that more than 40% of all American adults have literacy levels at Levels 1 or 2 (out of five), below the level required to secure jobs at good wages. National Institute for Literacy (NIFL) An independent federal organization created by the National Literacy Act of 1991 to serve as a focal point for public and private activities that support the development of high-quality regional, state, and national literacy services. One of NIFL's primary activities is promoting adult literacy system reform through Equipped for the Future (EFF). National Reporting System (NRS) An outcome-based reporting system for the state-administered, federally funded adult education program required by Title II of the Workforce Investment Act. The goals of the NRS were to establish a national accountability system for education programs by identifying measures for national reporting and their definitions, establishing methods for data collection, developing software standards for reporting to the U.S. Department of Education, and developing training materials and activities on NRS requirements and procedures. Norm-referenced assessment An assessment where student performance or performances are compared to that or those of a larger group. Usually the larger group or "norm group" is a national sample representing a wide and diverse cross-section of students. Students, schools, districts, and even states are compared or rank-ordered in relation to the norm group. The purpose of a norm-referenced assessment is usually to sort students and not to measure achievement towards some criterion of performance. Norm-referenced test An objective test that is standardized on a group of individuals whose performance is evaluated in relation to the performance of others; contrasted with criterion-referenced test. Most standardized achievement tests are referred to as norm-referenced. Norms A performance standard that is established by a reference group and that describes average or typical performance. Usually norms are determined by testing a representative group and then calculating the group's test performance. Objective Precise statement that specifies the performance or behavior a student is to demonstrate relative to a knowledge or skill. Objectives typically relate to lessons or units, not "big ideas" such as described by an outcome. Opportunity to learn (OTL) A standard that provides students with the teachers, materials, facilities, and instructional experiences that will enable them to achieve high standards. Opportunity to learn is what takes place in classrooms that enables students to acquire the knowledge and skills that are expected. OTL can include what is taught, how it is taught, by whom, and with what resources. Outcomes Changes in learners, such as learning gains in reading and writing, promotions at work, or increased self-confidence that occur as a direct result of their participation in adult literacy education; knowledge, attitudes, skills, etc., that the student or learner acquires as a result of a learning experience. Participatory assessment (alternative assessment, authentic assessment, performance-based assessment) A process for examining performance that views literacy as practices and critical reflection; requires the use of a broad range of strategies in assessment; and provides an active role for learners in the assessment process. Performance accountability A means of judging policies and programs by measuring their outcomes or results against agreed upon standards. A performance accountability system provides the framework for measuring outcomes - not merely processes or workloads. Performance assessment (alternative assessment, authentic assessment, participatory assessment) Performance assessment is a form of testing that requires students to perform a task rather than select an answer from a ready-made list. Performance assessment is an activity that requires students to construct a response, create a product, or perform a demonstration. Usually there are multiple ways that an examinee can approach a performance assessment and more than one correct answer. Performance Based Assessments A methodology requiring reasoning about recurring issues, problems and concepts that apply in both academic and practical situations. Students Unit Effectiveness Handbook Page 87 actively engage in generating complex responses requiring integration of knowledge and strategies, not just use of isolated facts and skills. See Complex Generated Response. Performance standards A statement or description of a set of operational tasks exemplifying a level of performance associated with a more general content standard; the statement may be used to guide judgements about the location of a cut score on a score scale; the term often implies a desired level of performance. 2. Explicit definitions of what students must do to demonstrate proficiency at a specific level on the content standards; for example, in Massachusetts' Curriculum Frameworks in the area of 'reading', there are six levels for each of four standards. Under the standard "comprehension", performance can range from "develop vocabulary" to "interpret charts & graphs" to "recognize a variety of genres & styles." Pilot A large‐scale administration of an assessment, usually with several classes of students if not all students in a program. The purpose of the pilot is to detect any flaws in the assessment before the assessment is considered "done" and is fully implemented. See Field Test for contrast. Performance task A carefully planned activity that requires learners to address all the components of performance of a standard in a way that is meaningful and authentic. Performance tasks can be used for both instructional and assessment purposes. Portfolio assessment A portfolio is a collection of work, usually drawn from students' classroom work. A portfolio becomes a portfolio assessment when (1) the assessment purpose is defined; (2) criteria or methods are made clear for determining what is put into the portfolio, by whom, and when; and (3) criteria for assessing either the collection or individual pieces of work are identified and used to make judgments about performance. Portfolios can be designed to assess student progress, effort, and/or achievement, and encourage students to reflect on their learning. Proficiency Level The equivalent of a cut score (on a forced‐choice assessment) but for a performance/complex assessment. The proficiency level for a performance assessment is set by determining the required performance criteria (such as the required level on a rubric) for a specific grade level. Such a proficiency level could be achievement of all the criteria required for a scoring level, or it could be a set number of points achieved by combining scores for each feature on the rubric. Program Assessment Assessment to determine the extent to which students in a departmental program can demonstrate the learning outcomes for the program. For comparison, see Course‐level Assessment and Institutional Assessment. Program Review The process of evaluating the quality and effectiveness of a program (University of Texas at Arlington, 1998). Prompt In a narrow sense, a prompt is a statement to which a student responds in an assessment, often a reading passage, picture, chart or other form of information. In the fullest sense, a prompt is the directions that ask the student to undertake a task. Prompts should include the context of the situation, the problem to be solved, the role the student takes, and the audience for the product or performance. Quality program indicator A variable reflecting effective and efficient program performance; distinguished from a measure (data used to determine the level of performance) and a performance standard (the level of acceptable performance in terms of a specific numeric criterion). Rationale Written statements providing the reasons for steps taken and choices made. Rating scales Values given to student performance. Subjective assessments are made on predetermined criteria for documenting where learners fall on a continuum of proficiency. Rating scales include numerical scales or descriptive scales. Raw Score The number of items that are answered correctly out of the total possible. Reliability How accurately a score will be reproduced if an individual is measured again. The degree to which the results of an assessment are dependable and consistently measure particular student knowledge and/or skills. Reliability is an indication of the consistency of scores across raters, over time, or across different tasks or items that measure the same thing. Thus, reliability may be expressed as (a) the relationship between test items intended to measure the same skill or knowledge (item reliability), (b) the relationship between two administrations of the same test to the same student or students (test/retest reliability), or (c) the degree of agreement between two or more raters (rater reliability). An unreliable assessment cannot be valid. Representativeness A factor of performance tasks and of scoring criteria ensuring that the task and criteria focus on the significant elements, concepts and strategies in the outcome(s) assessed. Rubrics Specific sets of criteria that clearly define for both student and teacher what a range of acceptable and unacceptable performance looks like. Criteria define descriptors of ability at each level of performance and assign values to each level. Levels referred to are proficiency levels which describe a continuum from excellent to unacceptable product. Scale scores A score to which raw scores are converted by numerical transformation (e.g., conversion of raw scores to percentile ranks or standard scores); units of a single, equal-interval scale that are applied across levels of a test; for example, on TABE 7 & 8, scale scores are expressed as numbers that may range from 0 through 999. SCANS (Secretary's Commission on Necessary Skills) An initiative of the United States Department of Labor that identified the skills workers need to perform in the world of work and which made recommendations for changes in secondary education to facilitate the development of these skills. The SCANS report was published in 1991 and identified five competencies (allocating resources, working with others, using information, understanding systems, and using technology) and 3 foundational skill sets (basic skills, thinking skills, and personal qualities). Scoring Rubric A set of related scoring scales used for judging student work and awarding points to reflect the evaluation of the work. Selected response item An exercise for which examinees must choose a response from an enumerated set (multiple choice) rather than create their own responses or products (performance assessment). Standard error of measurement The difference between an observed score and the corresponding true score or proficiency; the standard deviation of an individual's observed scores from repeated administrations of a test or parallel forms of a test, under identical conditions. Because such data cannot generally be collected, the standard error of measurement is usually estimated from group data. Standardization A consistent set of procedures for designing, administering, and scoring an assessment. The purpose of standardization is to assure that all students are assessed under the same conditions so that their scores have the same meaning and are not influenced by differing conditions. Standardized procedures are very important when scores will be used to compare individuals or groups. Standardized testing A test designed to be given under specified, standard conditions to obtain a sample of learner behavior that can be used to make inferences about the learner's ability. Standardized testing allows results to be compared statistically to a standard such as a norm or criteria. If the test is not administered according to the standard conditions, the results are invalid. Standards The broadest of a family of terms referring to statements of expectations for student learning, including content standards, performance standards, Opportunity to Learn (OTL), and benchmarks. Standards-based reform A program of school improvement involving setting high standards for all students and a process for adapting instruction and assessment to make sure all students can achieve the standards. Strands (ACLS) A way of organizing what adult learners need to know and be able to do within core curriculum. Strands need not be taught sequentially or separately. They identify processes, themes, content, and skills. Student Learning Outcomes Operational statements of demonstrable knowledge or skill that students will possess upon completion of a program or course. For UEP purposes, these statements may be the student program competencies or more specific statements derived from the student program competencies. Student performance level (SPL) A standard description of a student's (ESOL) language ability at a given level in terms of speaking, listening, reading, writing, and the ability to communicate with a native speaker; a profile of skill levels for a student can thus be assigned and used for placement, instructional, or reporting purposes. Sufficiency A judgment on whether an assessment task is comprehensive enough to produce a sample of student work broad enough in depth relative to a body of knowledge or skill to be considered an adequate measure of whether the student has attained the knowledge or achieved the skill. For forced choice assessments, the number of items used to decide this is the crucial issue for sufficiency. Summative assessment A culminating assessment, which gives information on students' mastery of content, knowledge, or skills. Task A goal‐directed assessment activity or project, which prescribes that the student use their background knowledge and skill in a somewhat long-term process to solve complex problems or answer a multi‐faceted question. Triangulation A process of combining methodologies to strengthen the reliability of a design approach; when applied to alternative assessment, triangulation refers to the collection and comparison of data or information from three difference sources or perspectives. Validity The extent to which an assessment measures what it is supposed to measure and the extent to which inferences and actions made on the basis of test scores are appropriate and accurate. For example, if a student performs well on a reading test, how confident are we that that student is a good reader? A valid standards-based assessment is aligned with the standards intended to be measured, provides an accurate and reliable estimate of students' performance relative to the standard, and is fair. An assessment cannot be valid if it is not reliable. Weighting A method to combine the results of two or more assessments used in calculating the percent who meet the standard for a learning outcome. If some assessments are deemed more important due to the amount of time for completion or the number of items included in the assessment, etc. the cut‐scores on those assessments may be given greater consideration or weight in determining the overall performance level.