Ratios Unit Plan Math 6th
advertisement

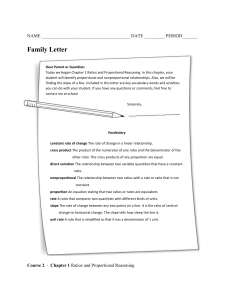
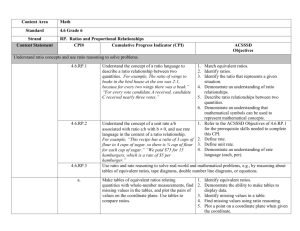
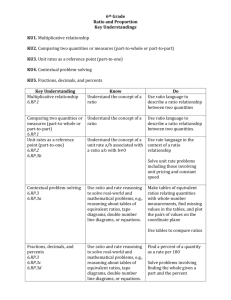
6th Subject/Grade or Course: Math Major (m) Common Core cluster for the Unit: 6.RP Understand ratio concepts and use ratio reasoning to solve problems. 6.NS Compute fluently with multi-digit numbers and find common factors and multiples. SAXON LINK Lesson 10 Saxon course 2 Investigation I Saxon Course 2 Lesson 15, 16 Saxon Course 2 Lesson 36 Saxon Course 2 Lesson 46, 48, 50 Saxon Course 2 Common Core Cluster # from above: 6.RP 6.NS SAXON LINK Lessons 1-10 Saxon Course 2 Lesson 10 Saxon course 2 Investigation I Saxon Course 2 Lesson 15, 16 Saxon Course 2 1 MATHEMATICS Unit Name: Ratios and Proportions Supporting and Additional (s/a) Common Core Standards for the Unit: 6.RP.1. Understand the concept of ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities. 6.RP.2. Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b ≠ 0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship. 6.RP.3a-d. Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. 6.NS.4. Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. Common Core Supporting / Additional (s/a) Standards # from above: 6.RP.1 6.RP.2 6.RP.3a-d 6.NS.4 Pacing: 6 weeks Bridging Common Core Standards from Previous Grade(s): 5.NF Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions. 5.NF Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions. 5.G Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real world and mathematical problems. Common Core Bridging Standards from Previous Grade(s)# from above: 5.NF.1 5.NF.2 5.NF.1 5.NF.2a-b 5.NF.3a-b 5.NF.4 5.NF.5a-c 5.G.1 5.G.2 MATHEMATICS Subject/Grade or Course: Math Unit Name: Ratios and Proportions Pacing: 6 weeks Structure of Math / Overarching Understanding(s): Essential Questions: Use reasoning with ratios and rates to solve real-world and How can reasoning with ratios and rates help solve real-world mathematical problems. and mathematical problems? Teacher Note: How are ratios and percents alike? How are they different? o Relationships between fractions, decimals, and percents are How do you determine a unit rate given a table of values? developed in this unit. Students learn how these forms are What are the differences between converting measurements in related to one another and make decisions about when to use the metric and standard measurement systems? each form. Given the quantity and price of two objects, how can you o Understanding and applying the relationships between determine which one is the better buy? fractions, decimals, and percents, students will solve real How are fractions, decimals, and percents related? world problems such as unit rate, measurement conversions, How are common factors and multiples applied to solve realconstant rate, and comparison of quantities. world scenarios? o Fractions are viewed as rates, ratios, or parts of a proportion How can I use multiplication and division to solve ratio and to provide underpinnings needed in seventh grade for work rate problems? with proportional reasoning. What is the difference between a ratio and a rate? How can I use tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations to compare rates of change? STUDENT-FRIENDLY LEARNING TARGET STATEMENTS MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Learning Targets 6.RP.1 Understand MP.4 Model with mathematics. the concept of ratio MP.6 Attend to precision. and use ratio MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. language to describe Compare and contrast the properties of ratios and fractions. a ratio relationship o I understand that ratios compare part to part and fractions do not. between two Create a variety of models to show ratios in real-world settings. quantities. o I can model real world ratios using appropriate symbols. Create examples of ratios and explain their meaning. o I can create examples of ratios in context. SAXON LINK: o I can explain the meaning and context of any ratio. SAXON Course 2 Apply the use of ratios to real-world situations. Section 1 o I can translate a ratio into a real world problem. Use ratio language to describe a comparison of two quantities which can be written as a to b, a/b, or a:b. 6th 2 MATHEMATICS Subject/Grade or Course: Math Unit Name: Ratios and Proportions o I can describe ratios and their symbols using correct vocabulary. o I can select the correct symbols to express ratios three ways. o I can compare two quantities using a ratio. 6th 6.RP.2 Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b ≠ 0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship. SAXON LINK: Saxon 8/7 and course 2 Section 1 3 MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. MP.4 Model with mathematics. MP.6 Attend to precision. MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. Create unit rates to name the amount of either quantity, in terms of the other quantity. o I can write a unit rate. o I can describe the relationship between the two quantities in a unit rate. Demonstrate understanding of unit rate. o I can illustrate a unit rate using multiple models. o I can explain unit rates using appropriate vocabulary. Interpret the relationship between unit rates and ratios. o I understand that all ratios can be expressed as unit rates. o I can model the relationship between the unit rate and a ratio. Generate ratios for a variety of unit rates. o I can increase and decrease unit rates to provide solutions for real-world situations. Pacing: 6 weeks MATHEMATICS Subject/Grade or Course: Math Unit Name: Ratios and Proportions Pacing: 6 weeks 6.RP.3.a Make tables MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. of equivalent ratios MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. relating quantities MP.3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. with whole number MP.4 Model with mathematics. measurements, find MP.5 Use appropriate tools strategically. missing values in the MP.6 Attend to precision. tables, and plot the MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. pairs of values on the Create table of equivalent ratios using real-world examples. coordinate plane. Use o I understand that all ratios in a ratio table are equivalent. tables to compare o I understand that every ratio has an infinite number of equivalent ratios. ratios o I can create a ratio table using real-world examples. SAXON LINK: Find missing values within a ratio table. Saxon 7/6 o I can apply previous ratio knowledge to find missing values in a table. L 105 Compare ratios using tables. L 41 o I can expand ratio tables to compare ratios. L 43 o I can describe the multiplicative value of ratios. Plot pairs of values from a ratio table on a coordinate plane. o I can plot pairs on a coordinate plane from a ratio table. 6.RP.3.b Solve unit MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. rate problems MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. including those MP.3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. involving unit MP.4 Model with mathematics. pricing and constant MP.5 Use appropriate tools strategically. speed. For example, MP.6 Attend to precision. if it took 7 hours to MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. mow 4 lawns, then at MP.8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. that rate, how many Construct and reason about real-world problems involving unit pricing and constant speed. lawns could be o I can construct models to solve real-world problems involving unit price and constant speed. mowed in 35 hours? o I can evaluate and determine accuracy of a solution. At what rate were o I can provide evidence to defend my solution. lawns being mowed? Solve unit rate problems involving unit pricing. o I can transfer my unit rate knowledge to solve problems containing unit price. SAXON LINK: Solve unit rate problems involving constant speed. Investigation 1 6th 4 MATHEMATICS Subject/Grade or Course: Math Unit Name: Ratios and Proportions o I can calculate constant speed using unit rates. Saxon 8/7 6th 6.RP.3.c Find a percent of a quantity as a rate per 100 (e.g., 30% of a quantity means 30/100 times the quantity); solve problems involving finding the whole, given a part and the percent. SAXON LINK SAXON 8/7 LESSON 15 LESSON 36 SAXON 7/6 Lesson 105 5 Pacing: 6 weeks MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. MP.3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. MP.4 Model with mathematics. MP.5 Use appropriate tools strategically. MP.6 Attend to precision. MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. MP.8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Construct models of equivalent fractions, decimals, and percents. o I can model equivalent fractions, decimals, and percents. Convert decimals to percentages. o I can provide the equivalent percentage given a decimal. Convert fractions to percentages. o I can provide the equivalent percentage given a fraction. Explain the relationship between fractions, decimals, and percents. o I can create and justify a conjecture explaining the relationship between fractions, decimals, and percents. Find a percent of a quantity as a rate per 100 (e.g., 30% of a quantity means 30/100 or 0.3 times the quantity). o I can construct a model showing a percent using ratio concepts. Given a part and the percent, solve problems to find the whole. MATHEMATICS Subject/Grade or Course: Math Unit Name: Ratios and Proportions o I can use equivalent ratio knowledge to find the whole given the percent and the part. 6th 6.RP.3.d Use ratio reasoning to convert measurement units; manipulate and transform units appropriately when multiplying or dividing quantities. SAXON LINK SAXON 8/7 LESSON 15 LESSON 36 Lessons 81-85 6 Pacing: 6 weeks MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. MP.3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. MP.4 Model with mathematics. MP.5 Use appropriate tools strategically. MP.6 Attend to precision. MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. MP.8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Create a model to demonstrate equivalent units of measure. o I can construct a variety of models showing equivalency within measurement units. Use models to discover the mathematical operation to extend the pattern. o I can extend patterns using a model. o I can examine and analyze a pattern to determine the mathematical operation used. Explain a comparison between various equivalent units of measure as a ratio (12 inches = 1 foot, 12:1). o I can describe the relationship between equivalent units of measure and ratios. MATHEMATICS Subject/Grade or Course: Math Unit Name: Ratios and Proportions Pacing: 6 weeks 6.NS.4. Find the MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. greatest common MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. factor of two whole MP.3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. numbers less than or MP.5 Use appropriate tools strategically. equal to 100 and the MP.6 Attend to precision. least common MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. multiple of two MP.8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. whole numbers less Distinguish prime from composite numbers. than or equal to 12. o I can classify prime and composite numbers. Apply divisibility rules. SAXON LINK: o I can make and defend a conjecture involving divisibility rules. Saxon 8/7 o I can apply divisibility rules. Lesson 6, 21. 27 Decompose (break down) numbers into factors. o I can use divisibility rules to decompose numbers into factors. Saxon 7/6 o I can represent a number as the product of its factors. L 19, 20, 30 o I can find the prime factorization of a number using various models. Demonstrate the use of prime factorization to find common factors and multiples. o I can apply the concept of prime factorization to find common factors and multiples. Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100. o I can apply various strategies to find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers. Find the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. o I can apply various strategies to find the least common multiple of two whole numbers. Apply the distributive property to express any sum as a multiple of a GCF and the sum of two whole numbers. o I understand and can use the distributive property. o I can identify the greatest common factor using the distributive property. Assessment Tasks Claim #1/DOK 1, 2, 3, 4 (circle one): that Provide Claim #2/DOK 1, 2, 3, 4 (circle one): Evidence for Claims Claim #3/DOK 1, 2, 3, 4 (circle one): including DOK Claim #4/DOK 1, 2, 3, 4 (circle one): 6th Materials/Resources http://commoncoretools.files.wordpress.com/2012/02/ccss_progression_rp_67_2011_11_12_corrected.pdf http://schools.nyc.gov/NR/rdonlyres/A9F735CB-47E4-40F8-884FEA54D0AB5705/0/NYCDOEG6MathRatios_Final.pdf 7 MATHEMATICS Subject/Grade or Course: Math Unit Name: Ratios and Proportions Pacing: 6 weeks http://illustrativemathematics.org/standards/k8 Developing Essential Understanding of Ratios, Proportions & Proportional Reasoning Grades 6-8 NCTM 6th Teacher Notes 8 We did not have time to add assessment tasks within the claims. Please see the above resources for excellent examples.