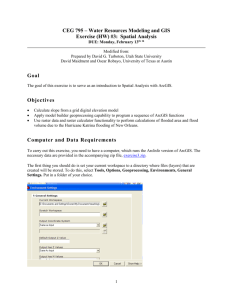
Appendix 1: Geomorphometric attributes used in the present study
advertisement

Appendix 1: Geomorphometric attributes used in the present study, definition and significance
Attribute
Definition
Estimation method
Elevation
Height above mean seal level or local reference at a given point in the earth’s surface
Directly measured from DEM
Slope
Rate of change of elevation; 𝑆𝑙𝑜𝑝𝑒 = arctan √(𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 )2 + (𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦)2 , where z is the altitude and x
and y are the coordinate axes.
Slope function of Surface
Analysis; Spatial Analyst
(ArcGIS 9.3)
Aspect function of Surface
Aspect
Compass direction of steepest downhill slope; 𝐴𝑠𝑝𝑒𝑐𝑡 = arctan [(𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦)⁄(𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 )]
Analysis; Spatial Analyst
(ArcGIS 9.3)
Rate of change of slope; 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑓𝑖𝑙𝑒 𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒 =
Profile curvature
Plan curvature
2
curvature
Relative relief
Slope-length and –
steepness (LS)
factor
2
Curvature function of Surface
2
− { [(𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 ) (𝛿 𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 )] + [2 (𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 ) (𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦) (𝛿 𝑧 ⁄𝛿𝑥𝛿𝑦)] + [(𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦
)2
2
2
(𝛿 𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦 )] } /
Analysis; Spatial Analyst
{ [(𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 )2 + (𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦)2 ] √[1 + (𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 )2 + (𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦)2 ]3 }
(ArcGIS 9.3)
Rate of change of aspect; 𝑃𝑙𝑎𝑛 𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒 =
Curvature function of Surface
− { [(𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦)2 (𝛿 2 𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 2 )] − [2 (𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 ) (𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦) (𝛿 2 𝑧 ⁄𝛿𝑥𝛿𝑦)] + [(𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 )2 (𝛿 2 𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦 2 )] } /
Analysis; Spatial Analyst
{ [(𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥
Tangential
2
)2
+ (𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦 ] √1 + [(𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑥 )2 + (𝛿𝑧⁄𝛿𝑦)2 ] }
)2
Product of plan curvature and the sine of the slope angle
𝑅𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑟𝑒𝑙𝑖𝑒𝑓 = (𝐻 − ℎ)⁄𝐴, where H and h are the maximum and minimum elevations and A is
area
(ArcGIS 9.3)
Raster calculator; Spatial
Analyst (ArcGIS 9.3)
Range function of
Neighbourhood Statistics;
Spatial Analyst (ArcGIS 9.3)
𝐿𝑆 𝐹𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 = (𝑛 + 1) × (𝐴𝑠 ⁄22.13)𝑛 × (𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝛽 ⁄0.0896)𝑚 , where n = 0.4, m = 1.3, As is specific
Hydrologic Analysis tool;
catchment area and is slope in degrees.
Terrain Analysis (Saga 2.0.8)
Terrain ruggedness
index (TRI)
Surface area ratio
(Rsa)
Topographic
wetness index (TWI)
𝑇𝑅𝐼 = √∑(𝑥𝑖𝑗 − 𝑥00 )2 , where xij is the elevation of each neighbour cell to cell (0,0)
Ratio of surface area to the planimetric area
𝑇𝑊𝐼 = 𝑙𝑛 (𝐴𝑠 ⁄tan 𝛽 ), where As is specific catchment area and is slope in degrees.
Morphometric Analysis tool;
Terrain Analysis (Saga 2.0.8)
Surface area Analysis tool;
Extension of ArcGIS 9.3
Hydrologic Analysis tool;
Terrain Analysis (Saga 2.0.8)
Hypsometric
̅ − ℎ)⁄(𝐻 − ℎ), where 𝐻
̅ is the weighted mean elevation, H and h are the maximum and
𝐼ℎ𝑦𝑝 = (𝐻
Morphometric Analysis tool;
integral (Ihyp)
minimum elevations.
Terrain Analysis (Saga 2.0.8)
(Langbein, 1947; Strahler, 1952; Beven and Kirkby, 1979; Zevenbergen and Thorne, 1987; Moore et al., 1992; Florinsky, 1998; Riley et al., 1999; Gallant
and Wilson, 2000; Jenness, 2009, 2012)