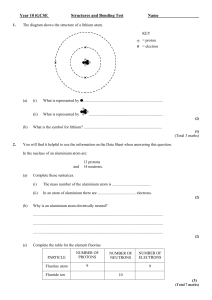
The final examination paper in chemistry for basic school graduates
advertisement
The final examination paper in chemistry for basic school graduates Nazarbayev Intellectual school in Astana Paper 1(45min) : 30 multiple-choice questions on the chemistry core.Paper 1 is made up of multiplechoice questions that test knowledge of the core only for students. The questions are designed to be short, one- or two-stage problems that address objectives 1 and 2. No marks are deducted for incorrect responses. Calculators are not permitted, but students are expected to carry out simple calculations. 1.An atom of any element must contain equal numbers of the following: A. electrons, neutrons and protons B. electrons and protons C. neutrons and protons D. electrons and neutrons (Total 1 mark) 2. Two of the subatomic particles that make up an atom are the proton and the electron. What are the electrical charges on a proton and an electron? Proton Electron A neutral negative B positive negative C negative positive D neutral positive (Total 1 mark) 3. The structure of an atom is defined by two numbers: the proton number and the nucleon number. What is the electronic structure of an atom with proton (atomic) number 5 and nucleon (mass) number 11? A 2,8,1 B 3,2 C 2,3 D 1,8,2 (Total 1 mark) 4. Cadmium is an element that has several isotopes. One of these isotopes is 112 48Cd. Which particle is another isotope of cadmium? Protons Neutrons A 48 62 B 48 112 C 112 48 D 62 48 (Total 1 mark) 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains one electron. D. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses two electrons. (Total 1 mark) 6. The boiling point of a substance is linked to the type of bonding present in the substance. Two elements X and Y combine to form a liquid with the relatively low boiling point of 120 °C. Which of the lines in the following table is correct? Type of element Type of bonding X Y A metal metal covalent B non-metal non-metal ionic C non-metal non-metal covalent D metal non-metal ionic (Total 1 mark) 7. Which is the best description of ionic bonding? A. The electrostatic attraction between positively charged nuclei and an electron pair B. The electrostatic attraction between positive ions and delocalized negative ions C. The electrostatic attraction between positive ions and delocalized electrons D. The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions (Total 1 mark) 8. Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon and has the formula CH4. Н | Н - С- Н | Н What is the total number of the electrons involved in the bonding in this molecule? A 10 B2 C8 D4 (Total 1 mark) 9. How many hydrogen atoms are contained in one mole of ethanol, C2H5OH? A. 5 B. 6 C. 1.0×1023 D. 3.6×1024 (Total 1 mark) 10. What amount (in moles) is present in 2.0 g of sodium hydroxide, NaOH? A. 0.050 B. 0.10 C. 20 D. 80 (Total 1 mark) 11. Which compound has the empirical formula with the greatest mass? A. C2H6 B. C4H10 C. C5H10 D. C6H6 (Total 1 mark) 12. A hydrocarbon contains 90% by mass of carbon. What is its empirical formula? A. CH2 B. C3H4 C. C7H10 D. C9H10 (Total 1 mark) 13. 3.0 dm3 of sulfur dioxide is reacted with 2.0 dm3 of oxygen according to the equation below. 2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g) What volume of sulfur trioxide (in dm3) is formed? (Assume the reaction goes to completion and all gases are measured at the same temperature and pressure.) A. 5.0 B. 4.0 C. 3.0 D. 2.0 (Total 1 mark) 14. What volume of 0.500 mol dm–3 sulfuric acid solution is required to react completely with 10.0 g of calcium carbonate according to the equation below? CaCO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) CaSO4(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) A. 100 cm3 C. 200 cm3 300 cm3 D. 400 cm3 B. (Total 1 mark) 15. A reaction occurring in the extraction of lead from its ore can be represented by this unbalanced equation: __PbS __O2 → __ PbO __ SO 2 When the equation is balanced using the smallest possible whole numbers, what is the coefficient for O2? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 (Total 1 mark) 16. When the equation above is balanced, what is the coefficient for oxygen? __C2H2(g) + __O2(g) → __ CO2(g) + __ H2O(g) A. 2 B. C. D. 3 4 5 (Total 1 mark) 17. A hydrocarbon contains 90% by mass of carbon. What is its empirical formula? A. CH2 B. C3H4 C. C7H10 D. C9H10 (Total 1 mark) 18. The percentage by mass of the elements in a compound is C = 72%, H = 12%, O = 16%. What is the mole ratio of C:H in the empirical formula of this compound? A. 1 : 1 B. 1 : 2 C. 1 : 6 D. 6 : 1 (Total 1 mark) 19. Which sample has the least number of atoms? A. 1 mol of H2SO4 B. 1 mol of CH3COOH C. 2 mol of H2O2 D. 2 mol of NH3 (Total 1 mark) 20. Which of the following contains the greatest number of molecules? A. 1 g of CH3Cl B. 1 g of CH2Cl2 C. 1 g of CHCl3 D. 1 g of CCl4 (Total 1 mark) 21. Which property decreases down group 7 in the periodic table? A. atomic radius B. electronegativity C. ionic radius D. melting point (Total 1 mark) 22. Which pair would react together most vigorously? A. Li and Cl2 B. Li and Br2 C. K and Cl2 D. K and Br2 (Total 1 mark) 23. Which properties of period 3 elements increase from sodium to argon? I. II. III. A. B. C. D. Nuclear charge Atomic radius Electronegativity I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III (Total 1 mark) 24. Which property decreases down group 7 in the periodic table? A. atomic radius B. electronegativity C. ionic radius D. melting point (Total 1 mark) 25. The compounds Na2O, Al2O3 and SO2 respectively are A. acidic, amphoteric and basic. B. amphoteric, basic and acidic. C. basic, acidic and amphoteric. D. basic, amphoteric and acidic. (Total 1 mark) 26. Which oxides produce an acidic solution when added to water? I. SiO2 II. P4O6 III. SO2 A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III (Total 1 mark) 27. Which series is arranged in order of increasing radius? A. Ca2+ < Cl– < K+ B. K+ < Ca2+ < Cl– C. Ca2+ < K+ < Cl– D. Cl– < K+ < Ca2+ (Total 1 mark) 28. Which factors lead to an element having a low value of first ionization energy? I. large atomic radius II. high number of occupied energy levels III. high nuclear charge A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III (Total 1 mark) 29. Which statement concerning a chemical reaction at equilibrium is not correct? A. B. C. D. The concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. Equilibrium can be approached from both directions. The rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. All reaction stops. (Total 1 mark) 30. Which statements are correct for a reaction at equilibrium? I. The forward and reverse reactions both continue. II. The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. III. The concentrations of reactants and products are equal. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III (Total 1 mark) Paper 2 tests knowledge of the core only for students. The questions address objectives 1, 2 and 3 and the paper is divided into two sections. In section A, there is a data-based question that requires students to analyse a given set of data. The remainder of section A is made up of short-answer questions. In section B, students are required to answer one question from a choice of three. These extended-response questions may involve writing a number of paragraphs, solving a substantial problem, or carrying out a substantial piece of analysis or evaluation. A calculator is required for this paper. Section A: one data-based question and several short-answer questions on the core (all compulsory) 2.1. Oxidation and Reduction. (b) A chemistry teacher demonstrated the reaction between sodium and water to some students. What evidence is there that: 1 (b) (i) this reaction of refers to the redox? .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. (1 mark) 1 (b) (i i) Sodium is a reducing agent? .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. (1 mark) 1 (b) (i i) Hydrogen is an oxidizing agent? .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. (1 mark) 1 (b) (i i i) a gas was produced? .................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................. (1 mark) (Total 3 marks) 2.2. Electrolysis. Reactions at the electrodes A student investigated the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution. The student measured the volume of hydrogen gas produced in ten minutes. 2 (a) Sodium chloride does not conduct electricity when it is solid. Explain, in terms of ions, why sodium chloride solution conducts electricity. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... (1 mark) 2 (b) Chlorine is produced at the positive electrode. Why are chloride ions attracted to the positive electrode? ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... (1 mark) 2 (c)Hydrogen gas is produced at the negative electrode. Why are sodium ions attracted to the negative electrode? .......................................................................................................................................... . ........................................................................................................................................... (1 mark) (Total 3 marks) 2.3. Families alkanes A student carried out the transformation scheme: X Y C2H4 → C6H5Cl → C2H5OH (a) (i) The first step was the conversion of ethene to compound X, using chloroethane as the reagent and Ni as a catalyst. Write the equation for the reaction. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................... (2 marks) (ii)name the substance X, Y . ............................................................................................................................................................... (2 marks) (Total 4 marks) Section B: one extended-response question on the core (from a choice of three) 2.4 Families alkenes. Ethene, propene and but-2-ene are members of the alkene homologous series. 4(a) Describe three features of members of a homologous series. ……………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… (3 marks) 4(b) State and explain which compound has the highest boiling point. …….............................................................................................................................................. …………………………………………………………………………………………………… (3 marks) 4(c) Draw the structural formula and give the name of an alkene containing five carbon atoms. ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… (2 marks) 4(d) Write an equation for the reaction between but-2-ene and hydrogen bromide, showing the structure of the organic product. State the type of reaction occurring. ………………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (3 marks) (Total 11 marks) 2.5 Families alcohols 5(a) List two characteristics of a homologous serie alcohols ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) 5(b) Ethanol and butanol can be distinguished by their melting points. State and explain which of the two compounds will have a higher melting point. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) 5(c) Draw the three isomers containing the alcohol functional group of formula C4H9OH. …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………....... (2) (Total 5 marks) 2.6 Families carboxylic acids 6. Propene can be converted to propanoic acid in three steps: step1 step 2 step 3 propene → propan-1-ol → propanal → propanoic acid 6(a) State the type of reaction occurring in steps 2 and 3 and the reagents needed. Describe how the conditions of the reaction can be altered to obtain the maximum amount of propanal, and in a separate experiment, to obtain the maximum amount of propanoic acid. (5 marks) 6b) Identify the strongest type of intermolecular force present in each of the compounds propan-1-ol, propanal and propanoic acid. List these compounds in decreasing order of boiling point. (4 marks) (Total 9 marks) Paper3 tests knowledge of the options and addresses objectives 1, 2 and 3. Students are required to answer several short-answer questions in each of the two options studied. A calculator is required for this paper.mSeveral short-answer questions in each of the two options studied (all compulsory) 3.7Cracking 7. Industrial method oil refining is cracking. 7(a)Name what kinds of cracking you know? ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (2 marks) 7(b) Write the reactions of cracking of petroleum hydrocarbons and explain the features of these reactions ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (2 marks) 7(c) What kind of gas oil cracking is for isopropyl alcohol? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (1 marks) (Total 5 marks) 3.8Crude oil 8. All grades of aviation gasoline begin distilled at about 40 degrees Celsius and end distilled at or above 180 degrees. 8(a)What are they contain hydrocarbons - methane homologues: the lowest and the highest relative molecular mass. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (2 marks) 8(b) Write the structural formulas given you methane homologues ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (2 marks) (Total 4 marks) 3.9 Polymerization Supermarkets in the UK have been advised by the Government to stop giving plastic bags to customers. Plastic bags are made from a polymer. The polymer is made from ethene. The structural formula of ethene is shown. H H \ / C═ C / \ H H Ethene is made by cracking hydrocarbons. These hydrocarbons come from crude oil. 9 (a) Complete these sentences about ethane: (i) Ethene is a hydrocarbon because it contains only ..................................................... and...............................................................................................................................(2 marks) (ii) Ethene is unsaturated because it has a ............................................................................... bond. (1 marks) 9 (b) Tick (*) the name of the polymer formed when many ethene molecules join together. Name of polymer Tick (*) poly(chloroprene) poly(ethene) poly(propene) (1 mark) 9 (c) Suggest two reasons why supermarkets should stop giving plastic bags to customers. 1 ........................................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................................... 2 ........................................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................................... (2 marks) 9(d) Determine the relative molecular weight polyethylene, if the degree of polymerization is 1000. (1 mark) (Total 7 marks) MARKSCHEME The final examination paper in chemistry for basic school graduates Nazarbayev Intellectual school in Astana Paper 1(45min) : 30 multiple-choice questions on the chemistry core.Paper 1 is made up of multiplechoice questions that test knowledge of the core only for students. The questions are designed to be short, one- or two-stage problems that address objectives 1 and 2. No marks are deducted for incorrect responses. Calculators are not permitted, but students are expected to carry out simple calculations. 1.An atom of any element must contain equal numbers of the following: A. electrons, neutrons and protons B. electrons and protons C. neutrons and protons D. electrons and neutrons (Total 1 mark) 2. Two of the subatomic particles that make up an atom are the proton and the electron. What are the electrical charges on a proton and an electron? Proton Electron A neutral negative B positive negative C negative positive D neutral positive (Total 1 mark) 3. The structure of an atom is defined by two numbers: the proton number and the nucleon number. What is the electronic structure of an atom with proton (atomic) number 5 and nucleon (mass) number 11? A 2,8,1 B 3,2 C 2,3 D 1,8,2 (Total 1 mark) 4. Cadmium is an element that has several isotopes. One of these isotopes is another isotope of cadmium? Protons Neutrons A 48 62 B 48 112 C 112 48 D 62 48 112 48Cd. Which particle is (Total 1 mark) 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains one electron. D. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses two electrons. (Total 1 mark) 6. The boiling point of a substance is linked to the type of bonding present in the substance. Two elements X and Y combine to form a liquid with the relatively low boiling point of 120 °C. Which of the lines in the following table is correct? Type of element Type bonding X Y A metal metal covalent B non-metal non-metal ionic C non-metal non-metal covalent D metal non-metal ionic of (Total 1 mark) 7. Which is the best description of ionic bonding? A. The electrostatic attraction between positively charged nuclei and an electron pair B. The electrostatic attraction between positive ions and delocalized negative ions C. The electrostatic attraction between positive ions and delocalized electrons D. The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions (Total 1 mark) 8. Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon and has the formula CH4. Н | Н - С- Н | Н What is the total number of the electrons involved in the bonding in this molecule? A 10 B2 C8 D4 (Total 1 mark) 9. How many hydrogen atoms are contained in one mole of ethanol, C2H5OH? A. 5 B. 6 C. 1.0×1023 D. 3.6×1024 (Total 1 mark) 10. What amount (in moles) is present in 2.0 g of sodium hydroxide, NaOH? A. 0.050 B. 0.10 C. 20 D. 80 (Total 1 mark) 11. Which compound has the empirical formula with the greatest mass? A. C2H6 B. C4H10 C. C5H10 D. C6H6 (Total 1 mark) 12. A hydrocarbon contains 90% by mass of carbon. What is its empirical formula? A. CH2 B. C3H4 C. C7H10 D. C9H10 (Total 1 mark) 13. 3.0 dm3 of sulfur dioxide is reacted with 2.0 dm3 of oxygen according to the equation below. 2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g) What volume of sulfur trioxide (in dm3) is formed? (Assume the reaction goes to completion and all gases are measured at the same temperature and pressure.) A. 5.0 B. 4.0 C. 3.0 D. 2.0 (Total 1 mark) 14. What volume of 0.500 mol dm–3 sulfuric acid solution is required to react completely with 10.0 g of calcium carbonate according to the equation below? CaCO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) → CaSO4(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) A. 100 cm3 B. C. 200 cm3 300 cm3 D. 400 cm3 (Total 1 mark) 15. A reaction occurring in the extraction of lead from its ore can be represented by this unbalanced equation: __PbS + __O2 →__ PbO + __ SO 2 When the equation is balanced using the smallest possible whole numbers, what is the coefficient for O2? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 (Total 1 mark) 16. When the equation above is balanced, what is the coefficient for oxygen? __C2H2(g) + __O2(g) → __ CO2(g) + __ H2O(g) A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5 (Total 1 mark) 17. A hydrocarbon contains 90% by mass of carbon. What is its empirical formula? A. CH2 B. C3H4 C. C7H10 D. C9H10 (Total 1 mark) 18. The percentage by mass of the elements in a compound is C = 72%, H = 12%, O = 16%. What is the mole ratio of C:H in the empirical formula of this compound? A. 1 : 1 B. 1 : 2 C. 1 : 6 D. 6 : 1 (Total 1 mark) 19. Which sample has the least number of atoms? A. 1 mol of H2SO4 B. 1 mol of CH3COOH C. 2 mol of H2O2 D. 2 mol of NH3 (Total 1 mark) 20. Which of the following contains the greatest number of molecules? A. 1 g of CH3Cl B. 1 g of CH2Cl2 C. 1 g of CHCl3 D. 1 g of CCl4 (Total 1 mark) 21. Which property decreases down group 7 in the periodic table? A. atomic radius B. electronegativity C. ionic radius D. melting point (Total 1 mark) 22. Which pair would react together most vigorously? A. Li and Cl2 B. Li and Br2 C. K and Cl2 D. K and Br2 (Total 1 mark) 23. Which properties of period 3 elements increase from sodium to argon? I. Nuclear charge II. Atomic radius III. Electronegativity A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III (Total 1 mark) 24. Which property decreases down group 7 in the periodic table? A. B. C. D. atomic radius electronegativity ionic radius melting point (Total 1 mark) 25. The compounds Na2O, Al2O3 and SO2 respectively are A. acidic, amphoteric and basic. B. amphoteric, basic and acidic. C. basic, acidic and amphoteric. D. basic, amphoteric and acidic. (Total 1 mark) 26. Which oxides produce an acidic solution when added to water? I. SiO2 II. P4O6 III. SO2 A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III (Total 1 mark) 27. Which series is arranged in order of increasing radius? A. Ca2+ < Cl– < K+ B. K+ < Ca2+ < Cl– C. Ca2+ < K+ < Cl– D. Cl– < K+ < Ca2+ (Total 1 mark) 28. Which factors lead to an element having a low value of first ionization energy? I. large atomic radius II. high number of occupied energy levels III. high nuclear charge A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III (Total 1 mark) 29. Which statement concerning a chemical reaction at equilibrium is not correct? A. The concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. B. Equilibrium can be approached from both directions. C. The rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. D. All reaction stops. (Total 1 mark) 30. Which statements are correct for a reaction at equilibrium? I. The forward and reverse reactions both continue. II. The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. III. The concentrations of reactants and products are equal. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III (Total 1 mark) Paper 2 tests knowledge of the core only for students. The questions address objectives 1, 2 and 3 and the paper is divided into two sections. In section A, there is a data-based question that requires students to analyse a given set of data. The remainder of section A is made up of short-answer questions. In section B, students are required to answer one question from a choice of three. These extended-response questions may involve writing a number of paragraphs, solving a substantial problem, or carrying out a substantial piece of analysis or evaluation. A calculator is required for this paper. Section A: one data-based question and several short-answer questions on the core (all compulsory) 2.1. Oxidation and Reduction. (b) A chemistry teacher demonstrated the reaction between sodium and water to some students. What evidence is there that: 1 (b) (i) this reaction of refers to the redox? to change the oxidation state of the atoms before and after reaction............................................. .....2Na0 +2H+2O-2 →2Na+O-2H+ +H02........................................................ (1 mark) 1 (b) (i i) Sodium is a reducing agent? ........Na0.-1e→Na+......................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................. (1 mark) 1 (b) (i i) Hydrogen is an oxidizing agent? .........H+ +..1e→H0....................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................. (1 mark) 1 (b) (i i i) a gas was produced? .............2H0→H2..................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................. (1 mark) (Total 3 marks) 2.2. Electrolysis. Reactions at the electrodes A student investigated the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution. The student measured the volume of hydrogen gas produced in ten minutes. 2 (a) Sodium chloride does not conduct electricity when it is solid. Explain, in terms of ions, why sodium chloride solution conducts electricity. ....... solution contains free sodium ions and chloride ions............................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... (1 mark) 2 (b) Chlorine is produced at the positive electrode. Why are chloride ions attracted to the positive electrode? ..... because chloride ions are negatively charged........................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... (1 mark) 2 (c)Hydrogen gas is produced at the negative electrode. Why are sodium ions attracted to the negative electrode? ............ sodium ions are positively charged....................................................................................... . ........................................................................................................................................... (1 mark) (Total 3 marks) 2.3. Families alkanes A student carried out the transformation scheme: X Y C2H4 → C6H5Cl → C2H5OH (a) (i) The first step was the conversion of ethene to compound X, using chloroethane as the reagent and Ni as a catalyst. Write the equation for the reaction. ...... C2H4 + HCl→ C2H5Cl....................................................................... ......C2H5Cl + NaOH→ C2H5OH +HCl....... (2 marks) (ii)name the substance X, Y . HCl hydrogen chloride............... NaOH sodium hydroxide (2 marks) (Total 4 marks) Section B: one extended-response question on the core (from a choice of three) 2.4 Families alkenes. Ethene, propene and but-2-ene are members of the alkene homologous series. 4(a) Describe three features of members of a homologous series. … …… same general formula/CnH2n; formulas of successive members differ by CH2; similar chemical properties/same functional group; gradation/gradual change in physical properties;………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… (3 marks) 4(b) State and explain which compound has the highest boiling point. …….............................................................................................................................................. Ethene<< propene<< but-2-ene Ethene lower/ propene higher; propene lower/ but-2-ene higher but-2-ene; Accept 2-butene. strongest intermolecular/van der Waals’ forces; largest (molecular) mass/size/surface area/area of contact;…………………………………………………………………………………………………… (3 marks) 4(c) Draw the structural formula and give the name of an alkene containing five carbon atoms. CH2CHCH2CH2CH3/CH3CHCHCH2CH3/any correct branched structure; Accept more detailed formula. pent-1-ene/pent-2-ene; 2 Name must match formula. Accept 1-pentene/2-pentene. ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. (2 marks) 4(d) Write an equation for the reaction between but-2-ene and hydrogen bromide, showing the structure of the organic product. State the type of reaction occurring. CH3-CH=CH-CH3 +HBr → CH3-CHBr-CH2-CH3 ………………………………………………………………………………………………. Award [1] for all molecular formulas correct and [1] for correct product structure. Award [1] for completely correct equation starting with but-1-ene. addition; ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (3 marks) (Total 11 marks) 2.6 Families alcohols 5(a) List two characteristics of a homologous serie alcohols ..................................................................................................................................... one general formula/same general formula; differ by CH2; similar chemical properties; gradual change in physical properties; ......................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) 5(b) Ethanol and butanol can be distinguished by their melting points. State and explain which of the two compounds will have a higher melting point. ..................................................................................................................................... ...........Ethanol << butanol Ethanol lower/ butanol higher due to larger mass of butanol /stronger Van der Waals’/dispersion forces ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) 5(c) Draw the three isomers containing the alcohol functional group of formula C4H9OH. ……… CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-OH …………………………………………………………………………………………….. CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. CH3-CH2-CHOH-CH3 …………………………………………………………………………………………....... (2) (Total 5 marks) 2.6 Families carboxylic acids 6. Propene can be converted to propanoic acid in three steps: step1 step 2 step 3 propene → propan-1-ol → propanal → propanoic acid 6(a) State the type of reaction occurring in steps 2 and 3 and the reagents needed. Describe how the conditions of the reaction can be altered to obtain the maximum amount of propanal, and in a separate experiment, to obtain the maximum amount of propanoic acid. Oxidation Oxidants - KMnO4, K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4, CuO, O2 + catalyst. The ease of oxidation of alcohols decreases in the series: ≥ primary secondary >> tertiary. Primary alcohols in the oxidation of aldehyde, which are then readily oxidized to carboxylic acids. (5 marks) 6b) Identify the strongest type of intermolecular force present in each of the compounds propan-1-ol, propanal and propanoic acid. List these compounds in decreasing order of boiling point. Consequence of the polarity of the O-H and the presence of the unshared electron pairs on the oxygen atom is the ability of hydroxy to form hydrogen bonds. The association of alcohol molecules. Association of molecules ROH This explains why even lower alcohols - a liquid with relatively high boiling point (bp. Methanol +64,5 ° C). In the transition from mono-to polyhydric alcohols or phenols boiling and melting sharply. Hydration Hydration of alcohol molecules molecules ROH Ability to dissolve in water decreases with the increase of the hydrocarbon radical and a polyhydric hydroxy-atom. Methanol, ethanol, propanol, isopropanol, ethylene glycol and glycerin mixed with water in any ratio. The solubility of phenol in water is limited. (4 marks) (Total 9 marks) Paper3 tests knowledge of the options and addresses objectives 1, 2 and 3. Students are required to answer several short-answer questions in each of the two options studied. A calculator is required for this paper.mSeveral short-answer questions in each of the two options studied (all compulsory) 3.7Cracking 7. Industrial method oil refining is cracking. 7(a)Name what kinds of cracking you know? Thermal and catalytic cracking. To the process used two methods: thermal cracking (when heated without air) and catalytic cracking (more moderate heating in the presence of a catalyst). ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (2 marks) 7(b) Write the reactions of cracking of petroleum hydrocarbons and explain the features of these reactions Cracking - the process of thermal decomposition of hydrocarbons, which is based on the cleavage reaction of the carbon chain of large molecules to form compounds with shorter chain. Thermal cracking. At a temperature of 450-700 ° C alkanes decompose due to the rupture of the C-C (stronger C-H bond at a temperature maintained) and form alkanes and alkenes with fewer carbon atoms.For example: C6H14 →C2H6 + C4H8 Catalytic cracking is carried out in the presence of catalysts (usually aluminum and silicon oxides) at 500 ° C and atmospheric pressure. This, along with breaking the molecules are isomerization and dehydrogenation: ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (2 marks) 7(c) What kind of gas oil cracking is for isopropyl alcohol? + H2O (кат.) CH3–CH2-CH3→ CH3–CH=CH2 → CH3CH(OH)CH3 -Н2 ………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (1 marks) (Total 5 marks) 3.8Crude oil 8. All grades of aviation gasoline begin distilled at about 40 degrees Celsius and end distilled at or above 180 degrees. 8(a)What are they contain hydrocarbons - methane homologues: the lowest and the highest relative molecular mass. С4Н10 the lowest С12Н26 and the highest relative molecular mass. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (2 marks) 8(b) Write the structural formulas given you methane homologues CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 CH3-(CH2)10-CH3 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (2 marks) (Total 4 marks) 3.9 Polymerization Supermarkets in the UK have been advised by the Government to stop giving plastic bags to customers. Plastic bags are made from a polymer. The polymer is made from ethene. The structural formula of ethene is shown. H H \ / C═ C / \ H H Ethene is made by cracking hydrocarbons. These hydrocarbons come from crude oil. 9 (a) Complete these sentences about ethane: (ii) Ethene is a hydrocarbon because it contains only . because it contains carbon and hydrogen С- саrbon.................................................... and... Н marks) (iii) hydrogen............................................................................................................................(2 Ethene is unsaturated because it has a contains a double bond, one pi bond, in a place which can break the coupling reaction ............................................................................... bond. (1 marks) 9 (b) Tick (*) the name of the polymer formed when many ethene molecules join together. Name of polymer Tick (*) poly(chloroprene) poly(ethene) + poly(propene) (1 mark) 9 (c) Suggest two reasons why supermarkets should stop giving plastic bags to customers. 1,2 .. Plastic in its composition has very strong links between the molecules, so it can not degrade normal terrestrial conditions. Let a thousand years will lie in the ground - it did not happen, at least in contrast to the same zheleza.Chto then remains? Burn? But it is very dangerous and harmful, because when heated plastic emits toxic substances such as hydrogen chloride (hydrochloric acid) and formaldehyde, which when inhaled can die in a few minutes. It remains only very expensive, recycled, which almost no one wants to do. Why, they think. All the same, until the day when the damage caused by us will tell, we will not live. Human selfishness, indifference to the future generations ... ...................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................................... (2 marks) 9(d) Determine the relative molecular weight polyethylene, if the degree of polymerization is 1000. 1000x28=28000 (1 mark) (Total 7 marks)