WHMIS - Safety Symbols
advertisement

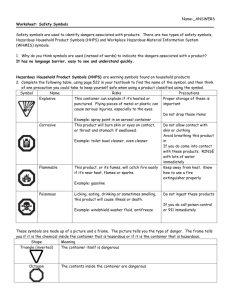
What is WHMIS? 1. WHMIS stands for Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System. 2. It is an information system implemented in 1988, which is designed to help students know more about safety and health hazards of materials that they use in the workplace. 3. WHMIS gives workers and employers key safety and handling information in the form of special labels, symbols, and Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) on potentially dangerous chemicals that are used on the job. 4. You will come across controlled products that fall under the WHMIS legislation at school (for example, the chemicals used in your science class or shop class), and at any workplace where chemicals are used. The purpose of a WHMIS symbol is to identify the product as controlled and to alert workers to the hazards and safe handling procedures of the product. However, WHMIS symbols are small and can only give limited information. The MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) gives more information. It informs you of the: Name of the chemical WHMIS hazard symbols Risks and precautions First Aid instructions Name and address of supplier WHMIS Symbols Symbol Class A Compressed Gas Examples: fire extinguishers, propane, chlorine, welding gases. Hazards and Safe Handling Measures - Is kept under pressure - Heat may cause to explode - Dropping may cause to explode - Keep container closed tightly and ensure valves are effective. Symbol Class B Flammable & Combustible Material Examples: propane, gasoline Hazards and Safe Handling Measures Includes any solid, liquid or gas that will burn. - May burn at relatively low temperatures - May burst into flame spontaneously when in contact with air - May release flammable gas when in contact with water - Keep away from heat or sources of ignition - Keep container tightly closed Class C Oxidizing Material Examples: Oxygen gas, hydrogen peroxide, bleach Oxidizers cause other substances to burn or continue to burn because they release oxygen. Oxidizers will not usually catch fire by themselves. - May cause a fire if it contacts combustibles such as wood. - Keep away from heat - Keep away from flammable and combustible materials Class D – Poisonous and Infectious Materials Class D1 Material Causing Immediate & Serious Toxic Effects Examples: hydrogen sulphide, strychnine, cyanide These materials are highly poisonous and immediately dangerous to life. - May be fatal or cause permanent damage if it enters the body through the skin, is inhaled or ingested. - Do not breath gas or vapours - Avoid skin contact - Wear suitable personal protective equipment Symbol Class D2 Material Causing Other Toxic Effects Examples: asbestos, saccharin, mercury Hazards and Safe Handling Measures Materials in this class are toxic, but their effects are not immediate but likely to harm you in some way. - May cause death if repeatedly exposed - May irritate eyes and skin and cause chemical allergies - May cause cancer, birth defects and sterility - Do not breath gas or vapours - Wear suitable personal protective equipment - Wash hands thoroughly after using these materials Class D3 Biohazardous Infectious Materials Examples: HIV, Hepatitis B, salmonella These materials are organisms (and the toxins of organisms) that cause disease in persons and animals. They are germs – bacteria, viruses, fungi, etc. - May cause serious illness and death - Keep containers tightly closed - Wear suitable protective equipment - Seek medical attention if you feel ill Class E Corrosive Examples: sulphuric acid, caustic soda, many cleaners and disinfectants These materials effects are permanent. Acids and bases are corrosive. - Causes severe eye and skin irritation upon contact - Tissue damage with extended exposure - May be harmful if inhaled/avoid skin contact - Use recommended respiratory protective equipment and other personal protective equipment Symbol Class F Dangerously Reactive Material Examples: benzoyl peroxide, epoxy resins. Hazards and Safe Handling Measures This includes a wide variety of chemicals that are potentially self-reactive. - It is very unstable - May react with water to release toxic or flammable gas - May explode if subjected to shock, friction or heat - Keep away from heat and water - Wear suitable protective clothing International Symbol Hazards • Not all products are controlled by the WHMIS legislation. You’ll see other symbols on products you commonly find around the house and garden, including cosmetics (like hairsprays), pesticides, and some household products (like oven cleaners). These products use the International Hazard Symbols you see below. Note: The border that surrounds each symbol signifies the danger level of the hazard • An octagon (same shape as a stop sign) indicates “DANGER” and represents the most dangerous hazard. • A diamond indicates “WARNING” and represents a moderate or medium hazard level. A warning diamond does not pose as extreme a risk as the danger octagon. • The upside-down triangle indicates “CAUTION” and represents the slightest or least hazard of the three borders. This does not make it hazardless! Use these products with caution. What is WHMIS? 1. WHMIS stands for _________________________________________________. 2. It is an information system implemented in 1988, which is designed to help students know more about safe ___________________________________ of materials that they use in the workplace. 3. WHMIS gives workers and employers key safety and handling information in the form of special labels, symbols, and ____________________________ (MSDS) on potentially dangerous chemicals that are used on the job. 4. You will come across controlled products that fall under the WHMIS legislation at school (for example, the chemicals used in your science class or shop class), and at any workplace where chemicals are used. The purpose of a WHMIS symbol is to identify the product as _____________ and to alert workers to the hazards and safe handling procedures of the product. However, WHMIS symbols are small and can only give limited information. The MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) gives more information. It informs you of the: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. WHMIS Symbols Symbol Class A _______________________ Examples: fire extinguishers, propane, chlorine, welding gases. Hazards and Safe Handling Measures - Is kept under pressure - Heat may cause to explode - Dropping may cause to explode - Keep container closed tightly and ensure valves are effective. Symbol Class B Hazards and Safe Handling Measures Includes any solid, liquid or gas that will burn. _______________________ - May burn at relatively low temperatures _______________________ - May burst into flame spontaneously when in contact with air Examples: propane, gasoline - May release flammable gas when in contact with water - Keep away from heat or sources of ignition - Keep container tightly closed Class C _______________________ Examples: Oxygen gas, hydrogen peroxide, bleach Oxidizers cause other substances to burn or continue to burn because they release oxygen. Oxidizers will not usually catch fire by themselves. - May cause a fire if it contacts combustibles such as wood. - Keep away from heat - Keep away from flammable and combustible materials Class D – ______________________________________________ Class D1 These materials are highly poisonous and immediately dangerous to life. _______________________ _______________________ Examples: carbon monoxide, cyanide - May be fatal or cause permanent damage if it enters the body through the skin, is inhaled or ingested. - Do not breath gas or vapours - Avoid skin contact - Wear suitable personal protective equipment Symbol Class D2 _______________________ Hazards and Safe Handling Measures Materials in this class are toxic, but their effects are not immediate but likely to harm you in some way. _______________________ - May cause death if repeatedly exposed Examples: asbestos, saccharin, mercury - May irritate eyes and skin and cause chemical allergies - May cause cancer, birth defects and sterility - Do not breath gas or vapours - Wear suitable personal protective equipment - Wash hands thoroughly after using these materials Class D3 _______________________ These materials are organisms (and the toxins of organisms) that cause disease in persons and animals. They are germs – bacteria, viruses, fungi, etc. _______________________ - May cause serious illness and death Examples: HIV, Hepatitis B, salmonella - Keep containers tightly closed - Wear suitable protective equipment - Seek medical attention if you feel ill Class E These materials effects are permanent. Acids and bases are corrosive. _______________________ Examples: ammonia gas, chlorine - Causes severe eye and skin irritation upon contact - Tissue damage with extended exposure - May be harmful if inhaled/avoid skin contact - Use recommended respiratory protective equipment and other personal protective equipment Symbol Class F Hazards and Safe Handling Measures This includes a wide variety of chemicals that are potentially self-reactive. _______________________ - It is very unstable _______________________ Examples: benzoyl peroxide, epoxy resins. - May react with water to release toxic or flammable gas - May explode if subjected to shock, friction or heat - Keep away from heat and water - Wear suitable protective clothing International Symbol Hazards • Not all products are controlled by the WHMIS legislation. You’ll see other symbols on products you commonly find around the house and garden, including cosmetics (like hairsprays), pesticides, and some household products (like oven cleaners). These products use the International Hazard Symbols you see below. Note: The border that surrounds each symbol signifies the danger level of the hazard • An _______________ (same shape as a stop sign) indicates “DANGER” and represents the most dangerous hazard. • A ____________ indicates “WARNING” and represents a moderate or medium hazard level. A warning diamond does not pose as extreme a risk as the danger octagon. • The _________________________ indicates “CAUTION” and represents the slightest or least hazard of the three borders. This does not make it hazardless! Use these products with caution. WHMIS Worksheet 1. What does WHMIS stand for? 2. What is the purpose of WHMIS? 3. What information would you find on a WHMIS label? 4. Do all products have WHMIS labels? Explain. 5. Identify the following symbols, write down at least one hazard the symbol represents and one example of a material that might have this symbol A B C Identify Symbol A B C D E F G H D E One Hazard F G Example H 6. What is an MSDS and what kind of information can be found on it? 7. Identify the following International Safety Symbols A ________________________ B ________________________ C ________________________ D ________________________ E ________________________ F ________________________ G ________________________ H ________________________ I ________________________ J ________________________ K ________________________ L ________________________