Unit 6 South and East Asia - Alief Independent School District
advertisement
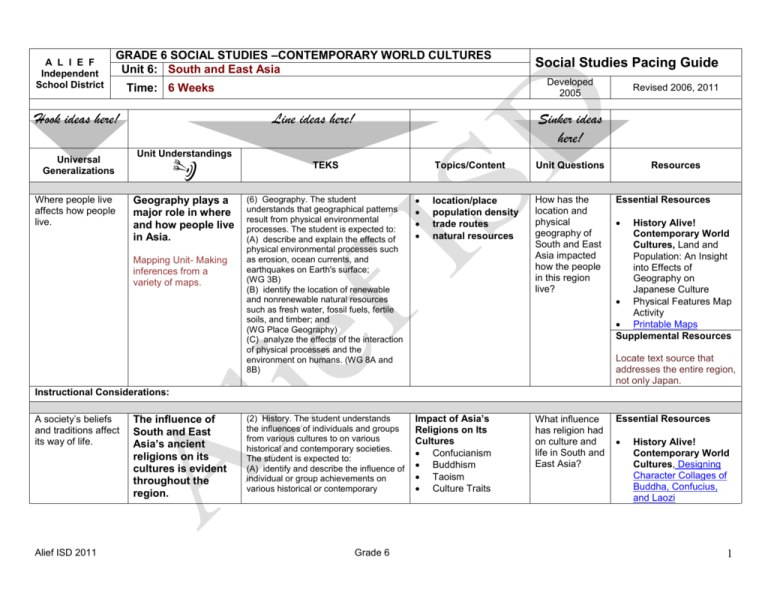
A L I E F Independent School District GRADE 6 SOCIAL STUDIES –CONTEMPORARY WORLD CULTURES Unit 6: South and East Asia Universal Generalizations Where people live affects how people live. Developed 2005 Time: 6 Weeks Hook ideas here! Social Studies Pacing Guide Line ideas here! Revised 2006, 2011 Sinker ideas here! Unit Understandings TEKS Geography plays a major role in where and how people live in Asia. Mapping Unit- Making inferences from a variety of maps. Topics/Content Unit Questions location/place population density trade routes natural resources How has the location and physical geography of South and East Asia impacted how the people in this region live? (6) Geography. The student understands that geographical patterns result from physical environmental processes. The student is expected to: (A) describe and explain the effects of physical environmental processes such as erosion, ocean currents, and earthquakes on Earth's surface; (WG 3B) (B) identify the location of renewable and nonrenewable natural resources such as fresh water, fossil fuels, fertile soils, and timber; and (WG Place Geography) (C) analyze the effects of the interaction of physical processes and the environment on humans. (WG 8A and 8B) (2) History. The student understands the influences of individuals and groups from various cultures to on various historical and contemporary societies. The student is expected to: (A) identify and describe the influence of individual or group achievements on various historical or contemporary Impact of Asia’s Religions on Its Cultures Confucianism Buddhism Taoism Culture Traits Resources Essential Resources History Alive! Contemporary World Cultures, Land and Population: An Insight into Effects of Geography on Japanese Culture Physical Features Map Activity Printable Maps Supplemental Resources Locate text source that addresses the entire region, not only Japan. Instructional Considerations: A society’s beliefs and traditions affect its way of life. Alief ISD 2011 The influence of South and East Asia’s ancient religions on its cultures is evident throughout the region. Grade 6 What influence has religion had on culture and life in South and East Asia? Essential Resources History Alive! Contemporary World Cultures, Designing Character Collages of Buddha, Confucius, and Laozi 1 Concepts : religion, culture, tradition, cultural transmission societies such as the classical Greeks on government and the American Revolution on the French Revolution; and (B) evaluate the social, political, economic, and cultural contributions of individuals and groups from various societies, past and present. Supplemental Resources Affected by Religion vocabulary: ceremonies, rituals, institution, ancestor, tradition Character Collage Samples (18) Culture. The student understands the relationship that exists between the arts and the societies in which they are produced. The student is expected to: (B) relate ways in which contemporary expressions of culture have been influenced by the past; (C) describe ways in which contemporary issues influence creative expressions; (19) Culture. The student understands the relationships among religion, philosophy, and culture. The student is expected to: (A) explain the relationship among religious ideas, philosophical ideas, and cultures; and (WG 17A) Instructional Considerations: Groups of people develop customs and traditions, whether on their own or by borrowing from others. South and East Asia’s diverse cultures have developed both on their own and through cultural borrowing. Concepts : cultural diffusion, religion (15) Culture. The student understands the similarities and differences within and among cultures in various world societies. The student is expected to: (A) define culture and the common traits that unify a culture region; (WG 16B and 17A) (B) identify and describe common traits that define cultures; (WG 16A, 16B and 17A) (C) define a multicultural society and consider both the positive and negative qualities of multiculturalism; (D) analyze the experiences and evaluate the contributions of diverse groups to multicultural societies; (WG 17D) What cultures are found in South and East Asia and how did they arise? Essential Resources History Alive! Contemporary World Cultures, Encountering Ancient Traditions in Modern Chinese Family Life HA! Understanding Japan’s “Adaptive Creativity” Text, Ch. 26, Sec. 1-3 Supplemental Resources (17) Culture. The student understands relationships that exist among world Alief ISD 2011 Grade 6 2 cultures. The student is expected to: (A) identify and describe how culture traits such as trade, travel, and war spread; (WG 1B and 18D) (B) identify and describe factors that influence cultural change such as improved communication, transportation, and economic development; (C) evaluate the impact of improved communication technology among cultures; (WG 20A) (D) identify and define the impact of cultural diffusion on individuals and world societies; and (WG 1B) (E) identify examples of positive and negative effects of cultural diffusion. (WG 1B and 18D) Instructional Considerations: Conflict often produces lasting change. Asia’s economic and government systems are partly a result of the conflict between communism and capitalism. Concepts : economic system, factors of production (8) Economics. The student understands the factors of production in a society's economy. The student is expected to: (A) describe ways in which the factors of production (natural resources, labor, capital, and entrepreneurs) influence the economies of various contemporary societies; and (WG 12A) (B) identify problems and issues that may arise when one or more of the factors of production is in relatively short supply. (C) explain the impact of relative scarcity of resources on international trade and economic interdependence among and within societies. (WG 12A and 12B) (9) Economics. The student understands the various ways in which people organize economic systems. The student is expected to: (A) compare ways in which various societies organize the production and distribution of goods and services; (WG 10A) (B) compare and contrast free enterprise, socialist, and communist economies in various contemporary Alief ISD 2011 Grade 6 Asia’s Economic Systems Types of Economic Systems Impact of Tradition Impact of Colonialism (Capitalism, Market) Impact of Communism (Command) What accounts for the wide differences between government and economic systems in Asia? Essential Resources History Alive! Contemporary World Cultures, Writing Journals about Life in a Chinese Village, Text, Ch. 3.4 Text, Ch. 25.1-25.3 Text, Ch. 27.4 Supplemental Resources vocabulary: economy, producer, goods, services, market, market economy, free enterprise, command economy tradition economy, means of production 3 societies, including the benefits of the U.S. free enterprise system; (WG 10A and 10B) (12) Government. The student understands various ways in which people organize governments. The student is expected to: (A) identify and give examples of governments with rule by one, few, or many; (WG 14B) (B) compare ways in which various societies such as China, Germany, India, and Russia organize government and how they function; and (WG 14B) Instructional Considerations: To reach full comprehension of the unit understanding, it is essential that the teacher teach utilizing the textbook lessons. Alief ISD 2011 Grade 6 4