Topic 2.1 quiz Answer Key (2)
advertisement

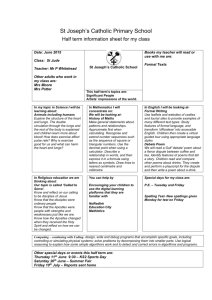
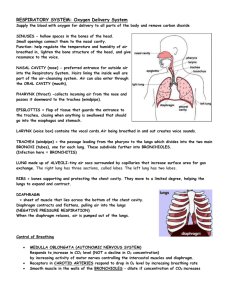
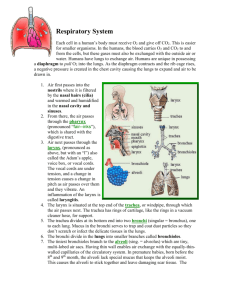
IB SEHS SL Topic 2.1 – The Ventilatory System Name ___________________________________________ Date _______ 1. List the principal structures of the ventilatory system. [4.5 marks] Nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, lungs and alveoli. [1/2 mark each] 2. Define the following terms. [2.5 marks] Pulmonary ventilation: inflow and outflow of air between the atmosphere and the lungs. Also called breathing. [1/2 mark] Total lung capacity: volume of air in the lungs after maximum inhalation. [1/2 mark] Vital capacity: maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inhalation. [1/2 mark] Tidal volume: volume of air breathed in and out in any one breath. [1/2 mark] Residual volume: volume of air still contained in the lungs after a maximal exhalation. [1/2 mark] 3. Explain the mechanics of ventilation in the human lungs. [4 marks] The diaphragm is the primary muscle involved in breathing/ventilation. [1 mark]During inhalation/inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and lowers, the ribs rise and chest cavity opens, allowing air to enter the lungs. [1 mark] During exhalation/expiration, the diaphragm relaxes and moves up, the ribs lower, forcing air out of the lungs. [1 mark] The intercostal muscles located along the ribs aid in ventilation by contracting and relaxing. [1 mark] 4. Explain the process of gaseous exchange at the alveoli. [4 marks] Gas exchange occurs when O2 reaches the alveoli in the lungs. [1mark] When air is breathed in, there is more O2 and less CO2 in the lungs, and more CO2 and less O2 in the blood being pumped back into the lungs. [1 mark] The higher concentration (higher partial pressure) of O2 in the lungs diffuses into the blood to supply blood to the body’s tissues, and the higher concentration of CO2 in the blood diffuses to the lungs [1mark]. During exhalation, CO2 in the lungs is released in the atmosphere and the process repeats. [1 mark] 1