Mars 1 - Odysseus Contest
advertisement

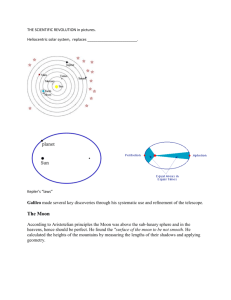
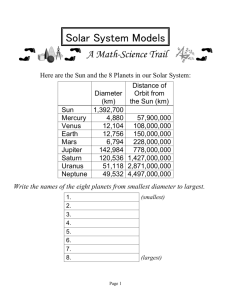
Translation of the presentation slides Entry of Team Pindűr Panúrok Sun 1 Basic Details o o o o o o Diameter: 1392000 km Surface temperature: 5800°C Core temperature: 15 million °C Mass: 33000 times that of Earth Rotational period at the equator: 26,9 days Rotational period at the poles: 32 days Sun 2 Embedded video about the sizes of planets and stars Mercury 1 Basic Details o o o o o o Distance from the sun: 57 909 176 km Diameter: 4879 lm Maximum temperature on the surface: 430°C Minimum temperature on the surface: -170°C One year on Mercury: 88 days on Earth One day on Mercury: 58 days on Earth Mercury 2 Atmosphere o Traces of Helium o Most of the atmosphere escapes, because Mercury has low gravitaty, and the solar wind is strong, because Mercury is too close to the Sun Mercury 3 Surface and the core o The core contains iron and nickel o On the crust there are lots of craters, they are from the early ages of the Solar system when meteors crashed into the planet. Mercury 4 Mariner-10 o It started its trip at the of November in 1973. Its destinations were Mercury and Venus. o At 29th of March in 1974, it got close to Mercury for the first time o It stayed until 1975, and it got close three time to the planet o During this time, it mapped the planet 45% 3rd Mercury 5 At March in 1973 scientists determinded the Mercury-Earth distance with great precision. “Élet és Tudomány” (an old Hungarian science magazine) reported about this. Mercury 6 MESSENGER o o o o o o Mercury’s first satellite. It started its trip at 3rd of March in 2004 At 14th of January in 2008 it arrived to Mercury It mapped the 80% of the planet At 18th of March in 2011 it stood ecliptic way At 17th of March in 2012 NASA extended its mission for one year. Mercury 7 Recommendatory o This is an really great book, written by Isaac Asimov. It takes place Mercury. Read it! Venus 1 Basic informations Average distance from the Sun: 108210000km Diameter: 12 104 km Surface temperature: 500 ° C Rotation period: 243,2 days One day on Venus: 118 (Earth) days Venus 2 Name It was named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love It is the only planet in the Solar System, which was named after a woman It helped people in orientation, so it was popular People enjoyed giving different names to Venus: In the morning -> Morning Star, In the evening-> Evening Star This indent is about a phrase that exists only in the Hungarian language, thus impossible to translate Signal (in the left with a small picture) Venus 3 Atmosphere Its surface is covered by a 25 km thick cloud layer which consist of dense sulfuric acid Sunlight does not penetrate it Atmosphere contains: o 96% of CO o 3,2% of nitrogen o 0,8% of other substances Air pressure is 92 times higher than that of the Earth Venus 4 Surface There are volcanic lowlands on the surface. Because of the massive eruptions deep hollows have been formed -> they look like they would have been carved by rivers This is the hottest planet, the surface temperature is 480 °C, which hardly changes due to the thick meteoric cloud layer Greenhouse effect has been developed on the planet due to the cloud layer situated higher Its surface is calm, there aren’t any clouds at low height, therefore the mountains which average height is 10 km can be seen very well Venus 5 Magnetic field Weaker and smaller than than those of the Earth Too weak to protect the atmosphere from the cosmic rays and the solar wind-related damage It doesn’t have an inner magnetic field, altough it is the same size as Earth Venus 6 Observations First spacecraft to Venus: Ferbuary 12, 1961. -> Venera-1., the Soviet Venera program’s first spacecraft. On the seventh day of the flight the connection has been lost. Venera-9: October 20, 1975. The lander operated for 53 minutes and took the first images of the surface of Venus. Venera-13: March 1, 1982. The lander radiated measurements of the surface of Venus for 127 minutes and sent the first color photos. Venus Express: April 11, 2006. It studied the atmosphere and clouds in detail and mapped the properties of the surface of the planet Venus 7 The transit of Venus The last transit of Venus was on June 06, 2012. and the next one will be 105 years later Venus crossed above the Sun, it took 6 and a half hours We saw more than 2 hours of the transit in Hungary Earth 1 Basic informations Average distance from the Sun: 152 million km Diameter: 12756 km Minimum surface temperature: -70 °C Maximum surface temperature: +55 °C Rotational period: 23 hours and 56 minutes An Earth year: 365,25 days The length of one day: 24 hours Earth 2 Life on Earth Ca. 3,5 billion years ago a process called life has started on Earth. To our knowledge this is exceptional throughout the universe it occurs exclusively on Earth. Earth is home to millions of species, including human beings. There is a search for extraterrestrial life but so far no clear evidence has been found for it Earth 3 Shape Determined by two physical effects: 1. Gravitation, 2. Centrifugal force It’s very close to a rotational ellipsoid shape The theoretical shape of the Earth is geoid, so we use this It is often simplified and called globe Earth 4 Atmosphere and compositions The gas shell surrounding the surface of the planet is held in place by gravity The border of space is called Kármán-line, which is an imaginary line situated at a height of 100 km The atmosphere is always on the move, which is called wind The atmosphere contains: 78,08% nitrogen 20,95% oxygen 0,93% argon 0,038% carbon dioxide It may contain traces of hydrogen, helium and rare gases Earth 5 Surface It’s also called the „Blue planet” 71% of it is water and 29% of it is land The three oceans are called: Atlantic, Pacific and Indian ocean Land: consists of continents and islands Continents: Europe, Asia, Africa, America, Australia, Antarctica The highest point is Mount Everest, it’s 8848 m high The surface of Earth is constantly changing because of the volcanic activity, plate tectonics and erosion Earth 6 Internal structure The internal part of Earth has a belt structure The outmost layer is the crust, this is a rock layer. It contains solid, magmatic, metamorphic or sedimentary rock. It has an average thick of 30-40km. It has two parts: Oceanic -> It has thinner material, it’s composed of basalt Continental -> 15-20 km long, it’s composed of basalt and granite Earth 7 Internal structure II The second layer is the mantle. It’s 2900 km wide and it is sometimes solid. It combines the core and the Earth's crustal. It's parts are: Lower mantle: 660-2900 km. We haven’t got much informations about it. Buffer mantle: Also known as mesosphere, and spreads until 60 km. It sharply separates the upper and the lower mantle. Upper mantle: The top layer is solid, the lowermost is plastic. The innermost layer is the Earth’s core which is globular. It has 2 parts, the external and the internal core. The inner core streches roughly up to 1220 km of Earth radius and the outer goes up to 2300 km. The external core is liquid, the internal is solid. They contain iron and nickel. Earth 8 This is a video of Earth's natural beauty. Moon 1 Basic data Average distance from Earth: 384402 km Diameter: 3476 km (about a quarter of the diameter of the Earth) Weight: 7347673*10^22 kg Min. surface temperature: 40 k Max. surface temperature: 396 K Rotational period: 29,53 days Moon 2 Announcements It is the fifth biggest moon of the Solar System The gravitational acceleration is 1/6 than on Earth. It is proportional to our weight, that’s why it is easy to jump on the Moon despite of the heavy astronaut suit It doesn’t have an atmosphere, so the sky is dark all day Only one side of it is visible from Earth Long ago the moon was considered a divinity The first spacecraft reached the surface in 1959. (it crashed) Moon 3 Exploraions January, 1959., Luna-1-> Passed the Moon September, 1959., Luna-2 -> Crashed into it July,1964., Ranger-7 -> Before the crash it took high-resolution images February, 1966., Luna-9 -> Landed on the Moon April, 1966. , Luna 10 -> Luna became the first artificial moon of the Moon Moon 4 Moon landing Apollo program 20., July, 1969. -> Apollo-11 landed Neil Armstrong was the first human landing on the Moon His famous phrase: „That's one small step for a man, a giant leap for mankind” Neil Armstrong died on August 25, 2012. Mars 1 Basic Details Diameter: 6794 km Distance from the sun: 227900000km Circulation time: 684 days on the Earth Maximum temperature on the surface: -120°C Minimum temperature on the surface: 25°C One day on Mars: 24,66 days on the Earth Mars 2 Origin of its name In ancient Rome Mars was the god of war and manhood. The planet got this name for its red colour, because red was the symbol of war and militancy. The symbol for males and Mars is the same. It’s not a coincidence. In an old legend, Mars was always on the sky, when the people fought great wars. It was the same in the famous battle in Thermopylae. This was fought by the Persians and the Greeks in B. C. 448. They thought Mars watched the huge massacres. Mars 3 The surface The planet’s surface is very varied, so this is an interesting place for the planetary scientist. Usually we divide it into two parts. The southern highlands are covered by craters. The other part is the northern lowlands Mars isn’t red accidentally. In the sand and the dust are lots of iron-oxide, which means lots of rust. Mars 4 Olympus Mons This is the biggest mountain in the Solar System It is 25km high from the Mars’s surface It is 540 meter wide at its feet The mount is in a 2 km deep cove The last eruption was 10-20 million years ago Mars 5 Mariner-valley system The biggest canyon system in the Solar System It’s a system of independent canyons Greatest depth is 7km Approximately 3800 km long The scientist think that erupting magma ripped the crust Mars 6 2.) Humanity sent the most satellites to Mars. We will go through the most important missions. (The dates mean date of arrival) Mars 7 Mariner-4 It took the first photo of Mars in 1965. They were the first photos of another planet made by a probe It’s just a flyby Mars 8 Mariner-9 It arrived in 1971 It was the Mars’s first satellite It made the first global picture Mars 9 Viking program NASA launched two missions during the Viking-program Both of contained a rover and an orbiter The rover searched for traces of life. They did three biology researches. Two were negative, and one wasn’t unequivocal Mars 10 Mars Pathfinder 1996 The first rolling vehicle on Mars was the Sojourner It worked for 83 days It landed with the help of a tetrahedron balloon Mars 11 Mars Global Surveyor 1997 It worked from 1997 to 2006, which is interesting because the NASA planned the mission for two years In its picture scientist discovered water traces. Mars 12 Phoenix 2008 It took samples from the ground It found water ice in the ground The water ice is evidence of water on Mars today Mars 13 Spirit It was sent as part of the Mars Exploration rover program It arrived in 2004 Originally the NASA planned the mission to be 90 days long, but the Spirit stopped in 2010 It searched for water It landed in the Gusev Crater, and it went to the Columbia Mountains. Mars 14 Opportunity Twin sibling of Spirit 2004 It is still working today It landed in the Eagle Crater, and it went to the Endurance Crater Mars 15 Mars Science Laboratory 2012 Name of the rover is Curiosity It searches for traces of life It does geological searches It has an robotic arm, which helps in the laboratory work It has 17 cameras Jupiter 1 Basic informations Average distance from the Sun: 778,3 million km Diameter: 142800 km Surface temperature: -140° C Rotational period: 9,8 hrs Jupiterian day lenght: 9,92 hrs Orbital period: 11,86 earth years Jupiter 1 Origin of name Jupiter was known by astronomers in the ancient era, it was given mythological and religional substance in many cultures It is named after Iuppiter, the supreme god of Roman religion The sign of the planet indicates the lighning in his hand Jupiter 3 Structure This is the fastest rotating planet in the Solar System. A day on Jupiter is just 9,92 hours on Earth Because of this, the planet apparently is very splay The deeper mantle contanis a great amont of electricity, this feeds the magnetic field of this planet, which is the strongest in the Solar System In the center of the planet, temperature is 20000°C Jupiter 4 Atmosphere Moving upwards, the atmosphere thickens The outer atmosphere is stormy, it is built up by 3 layers of clouds, these are made of o ammonia ice o ammonia-hydrosulphide ice o water ice The atmosphere consists mostly of o 90% Hidrogen o 10% Helium Jupiter 5 Surface It’s a colorful planet, there are very distictive stripes on it these are formed due to the fast rotation on the surface, swirling stroms rage above the clouds a system of ring exsist (though hardly visible) does not have a solid surface the gases can warm up due to the huge pressure, and they make lighter stripes called „zones” Jupiter 6 Great Red Spot This mysterious spot is a huge anticyclone it has been raging on the surface for 300 years it’s diameter is bigger than Earth itself stable, steady can be observed by telescopes from Earth Jupiter 7 Moons Currently it has 64 known moons, but the discovery of more can be expected Most of the moons are little hunks of rock, some of them doesn’t have a name yet Theye are a few kilometers large asteroids the 4 biggest and most famous moons are the Galilei moons They were discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610 Jupiter 8 The Galilei moons, Io Year of discovery: 1610 Diameter 3643 km Prometheus is a distinctive volcano on it There are several volcanoes, lava rivers, melt sulphur and a few craters Jupiter 9 The Galilei moons, Europa Year of discovery: 1610 Diameter 3121,6km The surface is covered in water ice A moon made of rocks, with a few craters, below the surface there is probably liquid water Jupiter 10 The Galilei moons, Ganymede Year of discovery: 1610 Diameter 5262 km The bigges moon in the Solar System The surface is covered in craters It has it’s own magnetic field Jupiter 11 The Galilei moons, Callisto Year of discovery: 1610 Diameter 4820,6 km Lots of impact craters and ice on the surface 2 great impact craters: Valhalla, Asgard Saturn 1 Basic information Average distance from the Sun: 14270 million km Diameter: 120600 km Surface temperature: -180° C Rotational period: 9,8 hrs Jupiterian day lenght: 10,2hrs Orbital period: 29,46 earth years Saturn 2 Atmosphere Contains o o o o o o 93% Hidrogen 5% Helium 0,2% Methane 0,1% water 0,01% Ammonia 0,0005% Ethane Saturn 3 Origin of name Roman god Father of Jupiter Youngest of the Titans The symbol of the planet is the sickle of the god Saturn Saturn 4 History of the rings First to discover was Galilei, but he coudn’t interpret what he saw Huygens was the first with the idea of Saturn having rings Cassin was the one to discover that the rings are not a whole, there are space between them Maxwell suggested that the rings may not be solid objects, instead they are made of tiny particles Saturn 5 The rings As we know now, the rings have spaces between them o All rings are indicated with a letter, these were given to them in the order of their discovery They are made of rubble and pieces of ice o That is why they look so bright, the ice reflects the sunrays Saturn 6 Cassini-Huygens Cassini is the probe, Huygens is the lander Joint project of NASA, ESA and ASI It arrived to Saturn in June, 2004 Objectives of Cassini o 3D mapping of the rings o Examination of the moons o Observing the rotation of Saturn Objectives of Huygens o Mapping of Titan Saturn 7 Titan 3rd largest moon of the Solar System Discovered in 1655 (very early) The only moon having an atmosphere There is possibility of life It was announced in 2008, that lakes of Ethane and Methane are on the surface (even very big ones) The only moon where we sent a probe apart from our Moon: the Huygens Saturn 8 Mimas 7th moon of Saturn Its curiosity is the Herchel crater, which formed upon an impact , and is one third of the moon is diameter o Because of this, it eeriely resembles the Death Star Uranus 1 Basic data Distance form Sun: 2873 millon km Diameter: 52450 km Surface temperature: -210C Orbital period: 84 earth yrs Rotational period: 17,2 hrs Uranus 2 Origin of name leader of the eldest generation of gods in Roman mythology husband of Gaia (mother earth) acconding to this, Jupiter is son of Saturn, Uranus is father of Saturn,and grandfather of Jupiter Uranus 3 Interesting facts I It’s argument of periapsis is huge, so it looks like it’s rotated on a horizontal string (opposing to the other planets, that are rotated on a nearly vertical string) Uranus 4 Interesting facts II It’s diameter is about 4 times that of Earth, and it’s mass is more than 15 times that of Earth It’s inner, solid core is approxtimately Earth size Uranus 5 Interesting facts III Uranus is the 3rd biggest planet in the solar system but only the 4th most massive his rings were only discovered in 1977, because it is very dark, in fact it contains the darkest material ever discovered in the Solar System Uranus 6 Discovery Because Saturn is the last planet that is visible to the naked eye, it was only discovered in 1781 William Herschel, english astronomer was the discoverer He originally wanted to name the planed „George”, a tribute for George III., the king of Britain at the time Uranus 7 Moons Uranus has 27 moons Their naming is unique, rather than mythological figures, their names are all from works of William Shakespeare and Alexander Pope The largest moon is called Titania, the second largest is Oberon The two were discovered by William Herschel in 1787 Neptune 1 Basic data Distance form Sun: 4496 millon km Diameter: 492000 km Surface temperature: -220C Orbital period:164,8 earth yrs Rotational period: 16,2 hrs Neptune 2 Origin of name Because of the blue color, it is named after Neptune, the Roman god of seas It’s symbol shows the trident of the god Neptune 3 Structure it’s type is a gas giant there are dark patches on the surface of the clouds, which are storms It’s the most dense gas planet it’s blue color is caused by the 1% of methane in the atmosphere, which absorbs red light It’s Great Spot is similar to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Neptune 4 Atmosphere blue color ->The 1% of methane absorbs the red light Composition of atmosphere: 80% hydrogen 19% helium 1% methane There are powerful winds blowing, up to 2160 km/h in speed, in several directions Neptune 5 Rings Surprisingly there are 4 of them, very pale Voyager-2 discovered them 3 of them are named after scientists working on their discovery (Galle , Adams, Leverrier) The widest is only 50km The two moons, Galate and Desponia herds these rings togeher Neptune 6 Moons 13 moons are discovered so far Tirton – 1846 Nereida -1949 Larissa -1981 Naiad, Thalassa, Despina, Galatea, Proteus -1989 Halimede, Sao, Laomedeia, Neso -2002 Psamathe -2003 The best known one is Triton Neptune 7 Moons II The two moons, Galate and Desponia herds the rings togeher In the ring system, two more moons are orbiting, Naiad and Thalassa After the rings come Larissa and Protheus The biggest moon is Triton 4 of the moons are orbiting in a retrograde motion (a motion that is going in the opposite direction than most objects in the Solar System) these are Neso, Halimede, Psamethe and Triton Neptune 8 Triton The 7th, biggest and most famous moon of Neptune Discovered by William Lassel in 1847 Orbits in retrograde order Neptune 9 Basic facts about Triton Distance from Neptune: 354760 km Diameter: 2706 km Mass: 2,14x10^22 kg Surface temperature: -240C There is nitrogen (in frozen state) and a bit of methane in its atmosphere Ceres Discovery: January 1,1930 Distance form Sun: 414,7 millon km Diameter:960 km Average temperature: -87C Moons: none Ceres is the only dwarf planet that is not in the Kiuper belt, buti n the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter Pluto Discovery: february 18th of 1930 Distance form Sun: 5906,4 millon km Diameter: 52450 km Average temperature: -223C Rotational period: 6 earth days Moons: Charon, Nix, Hydra, P4, P5 the smallest planet until 2004 There aren’t many pictures about it, in 2015 the probe New Horizons will examine it more closely Haumea Discovery: december 28th of 2004 Distance form Sun: 6500 millon km Diameter: 1500 km Moons: Hi’aka and Namaka It is named after the godess of fertility ont he Easter Islands Makemake Discovery: march 31th of 2005 Distance form Sun: 6784 millon km Diameter: 1790 km Average temperature: -210C Moons: doesn’t have any It’s nickname was Easter Bunny, because it was discovered on the day of Easter It is named after a godess of the Easter Islands Eris Discovery: january 5th of 2005 Distance form Sun: 10190 millon km Diameter: 2400 km Average temperature: -225C Moons: Dysomnia When Eris was discovered, the expression of „dwarf planet” had to be implemented. Soon after that, Pluto became a dwarf planet