my chapter 13 Cornell notes example
advertisement
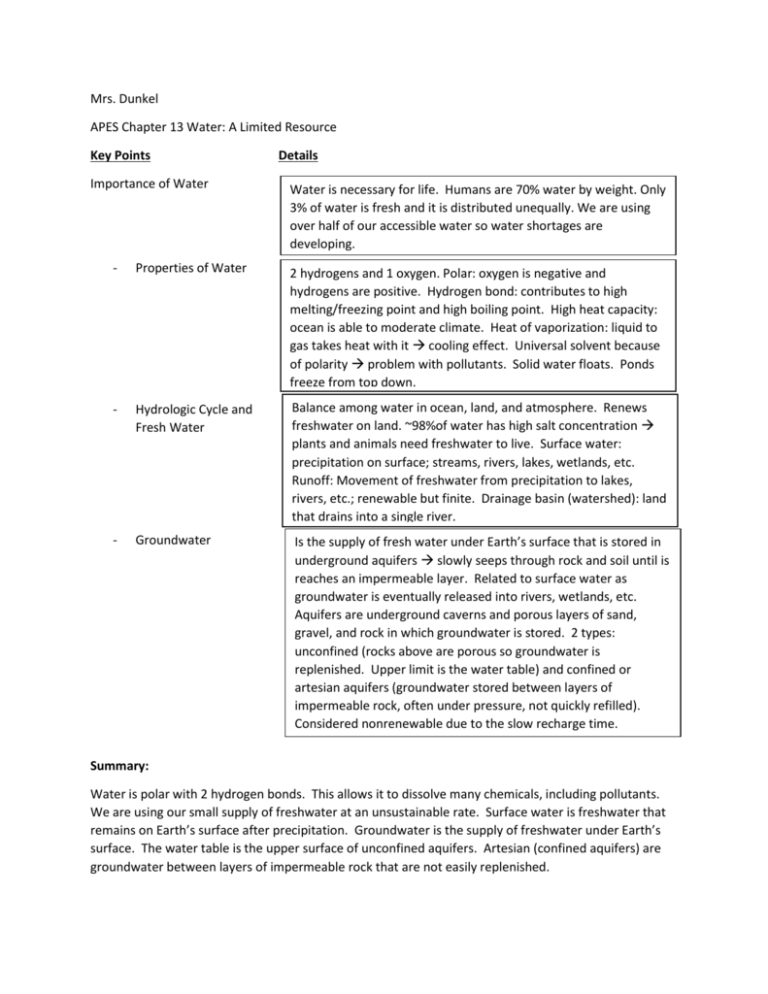
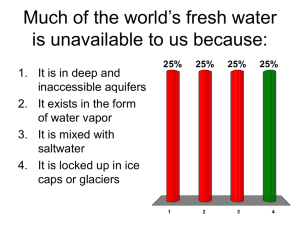
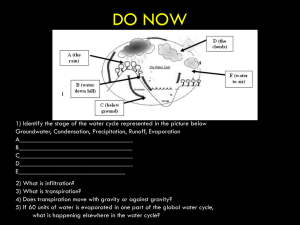
Mrs. Dunkel APES Chapter 13 Water: A Limited Resource Key Points Importance of Water Details Water is necessary for life. Humans are 70% water by weight. Only 3% of water is fresh and it is distributed unequally. We are using over half of our accessible water so water shortages are developing. - Properties of Water 2 hydrogens and 1 oxygen. Polar: oxygen is negative and hydrogens are positive. Hydrogen bond: contributes to high melting/freezing point and high boiling point. High heat capacity: ocean is able to moderate climate. Heat of vaporization: liquid to gas takes heat with it cooling effect. Universal solvent because of polarity problem with pollutants. Solid water floats. Ponds freeze from top down. - Hydrologic Cycle and Fresh Water Balance among water in ocean, land, and atmosphere. Renews freshwater on land. ~98%of water has high salt concentration plants and animals need freshwater to live. Surface water: precipitation on surface; streams, rivers, lakes, wetlands, etc. Runoff: Movement of freshwater from precipitation to lakes, rivers, etc.; renewable but finite. Drainage basin (watershed): land that drains into a single river. - Groundwater Is the supply of fresh water under Earth’s surface that is stored in underground aquifers slowly seeps through rock and soil until is reaches an impermeable layer. Related to surface water as groundwater is eventually released into rivers, wetlands, etc. Aquifers are underground caverns and porous layers of sand, gravel, and rock in which groundwater is stored. 2 types: unconfined (rocks above are porous so groundwater is replenished. Upper limit is the water table) and confined or artesian aquifers (groundwater stored between layers of impermeable rock, often under pressure, not quickly refilled). Considered nonrenewable due to the slow recharge time. Summary: Water is polar with 2 hydrogen bonds. This allows it to dissolve many chemicals, including pollutants. We are using our small supply of freshwater at an unsustainable rate. Surface water is freshwater that remains on Earth’s surface after precipitation. Groundwater is the supply of freshwater under Earth’s surface. The water table is the upper surface of unconfined aquifers. Artesian (confined aquifers) are groundwater between layers of impermeable rock that are not easily replenished. Key Points Water Use and Resource Problems Details There is a huge disparity is daily water use among countries. A few liters per day to several hundreds of liters per day. Agriculture requires a lot of water. Total water use: irrigation (71%), industry (20%), domestic and municipal use (9%). - Too much water - Floods of 2008 For 100s of years, Midwestern wetlands have been drained for farmland, restricting the ability of wetlands to moderate the flooding. Problems occur around Mississippi river in Missouri, Illinois, and Iowa. Levees are built to protect many cities, but they are not fail proof. Possible solutions including restoring some floodplains to their natural condition and moving towns to higher ground. - Too little water Arid lands (deserts): fragile ecosystems where plant growth is restricted by lack of precipitation. Semiarid lands: receive more precipitation than deserts, but subject to frequent, long droughts. Irrigation is necessary to grow food in these regions. Lands are also overgrazed so plants die and ground is not able to absorb the water as well, leading to less ground water. - Aquifer depletion Many locations are removing surface water with disastrous consequences. Wetlands are drying up and estuaries become saltier reducing local biodiversity and ecosystem health. Aquifer depletion: removal of groundwater more rapidly than it can be recharged by precipitation of melting snow. This can empty an aquifer. Aquifer depletion can lead to subsidence (ground above it sinks, 33ft in 50 yrs in San Joaquin Valley in CA). Floodplains are areas bordering river channels that have the potential to flood. Problems arise with people live in floodplains. Natural vegetation helps absorb excess water during floods clear cutting contributes to flooding and erosion. Buildings and pavement don’t absorb water increased risk of flooding. Local governments are restricting human development in flood plains. Limestone bedrock can erode as water moves through it, causing sinkholes (collapse of underground cave roof). When groundwater is removed faster than it can recharge around coasts, saltwater intrusion (movement of sea water into freshwater aquifers) can occur. Summary: Agriculture uses most of the available freshwater worldwide. Wetland removal and humans developing floodplains has caused increased flooding damage. Aquifer depletion can lead to wetlands drying up, saltier estuaries, subsidence, sinkholes, and saltwater intrusion. Key Points Details Water Problems in US and Canada - Surface Water - Mono Lake - Colorado River Basin - Delaware: A state without water? - Drought in Southeast - Groundwater - Ogallala Aquifer Summary: Key Points Details Global Water Problems - Water and Climate Change - Drinking-Water Problems - Population Growth and Water Problems - Sharing Water: Rhine River Basin - Sharing Water: The Aral Sea - Sharing Water: Volatile International Situations Summary: Key Points Water Management - Providing a Sustainable Water Supply - The Columbia River - The Missouri River - Water Division Project - Desalinization Summary: Details Key Points Water Conservation - Reducing Agricultural Water Waste - Reducing Industrial Water Waste - Reducing Municipal Water Waste - Impacts on Water Resources You Can Make a Difference Summary: Details