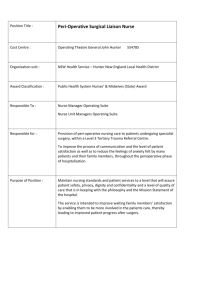
Elsevier Test Taking Module Quiz Key
advertisement

QUIZ on Elsevier’s Test-Taking Tutorials Critical Thinking and Testing 1. Nurses use an understanding of nursing knowledge to set priorities, make decisions, and take actions to ensure that individualized client care is safe and effective. True or False 2. When you study for critical thinking, you should ask yourself how will the nurse _________ the information in a clinical setting? 3. At which level are critical thinking questions written? (Select all that apply) a. Application b. Comprehension c. Analysis d. Knowledge e. Evaluation 4. Identify seven study tips for Knowledge level. 5. HESI HINT for Knowledge level!! Create study index cards. Carry your study cards with you. Study them when you find yourself with 5 minutes downtime. 6. Dr. B.’s STUDY HINT for Knowledge level: Challenge yourself to write 5 index study cards a day. That means every day. Just think you will have 35 cards at the end of the week. Always have a stack of index cards handy in your backpack and write study notes when you find yourself with downtime. Reward yourself for having accomplished your challenge each day. 7. To study for Comprehension you should ask yourself ________, ___________ and What is an example of this principle or concept. 8. When studying for comprehension use the ____________ and ______________ approach. 9. The forward approach includes looking at the heading, repeating and memorizing the _________ under the heading. 10. To study backward for comprehension look at the list and using that information, identify the _____________. 11. DR. B. HINT: Write the medical diagnosis on the front of the index study card. Flip it over and write the symptoms on the back. Study using the forward approach with the diagnoses facing you. Study using the backward approach with the symptoms facing you. Looking at the list of presenting symptoms, ask yourself what might this patient’s diagnosis be AND what is my first nursing action. (You can do this same technique with nursing diagnoses, Maslow prioritization, concepts etc.) 12. Another great tip: Ask yourself: How does this problem cause these ______________. What other problem looks like this? How might the nurse distinguish between the two ________________? 13. HESI HINT for comprehension level: Rearrange your notes into ______________, tables and ________________. 14. Dr. B. HINT for comprehension level: When creating tables, visual cognitive science has determined that using 2x2 block tables to display related information aids the memory process. (There is a natural 2x2 block in our brains across the hemispheres and the central sulcus making it easier for our brains to segment the information.) (Will Beischel, personal correspondence) 15. Teach someone else or at least explain the why’s and how’s ______ _________. 16. Form visuals of the nurse using the information that you are studying to make decisions. Do you see the nurse deciding what to do? What to teach the client? Monitoring the patient’s symptoms? 17. Change up the scenario by changing the age of the client or changing the context or give the client different symptoms. a. This is especially useful when studying in _______________. But it’s also great when studying alone. 18. HESI HINT to study for Application level: a. Using the information you are studying, create _______________, _________ _____________, and care plans b. Draw pictures with lots of color c. Be sure to use all parts of the _______________ ______________ and picture using the information in a clinical setting 19. DR. B. HINT to study for Application level: Imagine the nurse charting the evaluation of an intervention that you are studying (medication administration, delegation, blood transfusion). Let’s say the nurse performed the intervention 30 minutes ago. What indicators (vitals, skin color and temperature, client statements, etc.) did the nurse evaluate to determine if the intervention was effective? What did the nurse expect to happen? If the intervention was not effective, how did the nurse know? What was the nurse’s next response? 20. Study Tips for Analysis Level a. Create client __________ based on the material you are studying. b. ____________________ and __________________ the different situations. i. Which situation needs immediate attention? Why? ii. Which situation can wait? Why? 21. HESI HINT for Analysis level: a. Create concept maps that are easy for you to understand. b. Ask yourself “how is this related to what I already know?” c. Write your own ____________ questions on index cards using information from multiple index study cards. d. Create four ______________ _________________ from each lecture. Arrange them in order of ________________ actions for the nurse. 22. DR. B. HINT for Analysis level: Create scenarios of patients who have the same diagnosis who present with varying symptoms. Arrange these patients in order of priority. Basic Principles of Nursing Practice to Guide Your Critical Thinking When the question says “First, Initial, Best, Priority, Most important…” 1. Remember Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: a. ____________________ needs (ABC’s) must be met before psycho-social needs. b. Measures promoting _________________ must be met as well. c. Choosing between 2 good answers? Look for the answer that addresses the client’s physiological needs first. If they both address the client’s physiological needs, look for an option that promotes __________________. 2. Remember the Hippocratic Oath, “Above all, do no _________________.” a. Attempt to resolve an issue with the least invasive ____________________ first. 3. Remember that ____________________ problems are much better than allowing the problem to occur and then treating it. 4. Use the Nursing Process: a. Assess then take _________________. b. Do you have the assessment data you need to make a decision? Great! Make a decision and take action! c. If the test situation indicates that one step of the _________________ ______________ is completed, look for an answer that uses the very next ____________. d. For instance, if the nurse has implemented a nursing action look for an answer where the nurse must ______________ the action. 5. Ask yourself, “Is this within the nurse’s ______________ of ___________________?” 6. Determine the top _________________ interventions that can be carried out by the registered nurse, the licensed practical nurse, or unlicensed assistive personnel. 7. This is a nursing exam – be sure to have all the necessary information and take all possible relevant _______________ ________________ before you call the physician. But know when it’s time to call the physician. 8. When the questions asks which client should be assessed first or which client can wait to be cared for last, look for clients who are at greatest risk, who are most _____________________ __________________ and give them attention first. 9. DR. B. HINT: A patient with a non-typical symptom of the disease process is a high priority out of a list of patients with typical symptoms of the disease process. 10. Remember: The client is the center of all care. 11. Create plans and intervene to _________________ clients. Do not reinforce dependency on the healthcare team. Test Taking Skills Steps to answering critical thinking questions: 1. Cover the ___________ 2. READ the _____________ question. 3. Ask yourself “Does the question have a positive or _______________ focus?” 4. Ask yourself “What are the _____________ words in the question?” 5. Ask yourself, “What is really being asked in this question?” or “What concept are they making sure I know?” 6. __________________ the question 7. _______________ the options. 8. READ each option entirely. 9. Look for one that matches your own answer. 10. Rule out options 11. Consider the options that are left using __________________ principles and knowledge of the subject. 12. ______________ your answer. Avoid using _________________ work experience. Do NOT play the “What ____ game” Do not insert words that are not in the question or the options!! Remember in test taking scenarios: unless instructed otherwise in the question, this is the Garden of Eden. You have an unlimited amount of ________________, ______________, medications, and _______________. References: Test Taking Modules retrieved January 25, 2015 from https://evolve.elsevier.com Kelly Beischel at http://drbpresents.com 01/2015 kpb KEY QUIZ on Elsevier’s Test-Talking Tutorials Critical Thinking and Testing 1. Nurses use an understanding of nursing knowledge to set priorities, make decisions, and take actions to ensure that individualized client care is safe and effective. True or False 2. When you study for critical thinking, you should ask yourself how will the nurse _use___ the information in a clinical setting? 3. At which level are critical thinking questions written? (Select all that apply) a. Application b. Comprehension c. Analysis d. Knowledge e. Evaluation 4. Name seven study tips for Knowledge level. a. Read the material b. Highlight the key points c. Make note cards d. Use memorization aids e. Grouping similarity f. Acronyms g. Rhymes 5. HESI HINT!! Carry your study cards with you. Study them when you find yourself with 5 minutes downtime. 6. Dr. B.’s STUDY HINT: Challenge yourself to write 5 index study cards a day. That means every day. Just think you will have 35 cards at the end of the week. Always have a stack of index cards handy in your backpack and write study notes when you find yourself with downtime. Reward yourself for having accomplished your challenge each day. 7. To study for Comprehension you should ask yourself __Why______, ____How_______ and What is an example of this principle or concept. 8. When studying for comprehension use the forward and backward approach. 9. The forward approach includes looking at the heading, repeating and memorizing the ___list______ under the heading. 10. To study backward for comprehension look at the list and using that information, identify the ___heading__________. 11. DR. B. HINT: Write the medical diagnosis on the front of the index study card. Flip it over and write the symptoms on the back. Study using the forward approach with the diagnoses facing you. Study using the backward approach with the symptoms facing you. Looking at the list of presenting symptoms, ask yourself what might this patient’s diagnosis be AND what is my first nursing action. (You can do this same technique with nursing diagnoses, Maslow prioritization, concepts etc.) 12. Another great tip: Ask yourself: How does this problem cause these __symptoms____________. What other problem looks like this? How might the nurse distinguish between the two ____problems_________? 13. HESI HINT for comprehension level: Rearrange your notes into graphs, tables and charts. 14. Dr. B. HINT for comprehension level: When creating tables, visual cognitive science has determined that using 2x2 block tables to display related information aids the memory process. (There is a natural 2x2 block in our brains across the hemispheres and the central sulcus making it easier for our brains to segment the information (Will Beischel, personal correspondence)). 15. Teach someone else or at least explain the why’s and how’s out loud. 16. Form visuals of the nurse using the information that you are studying to make decisions. Do you see the nurse deciding what to do? What to teach the client? Monitoring the patient’s symptoms? 17. Change up the scenario by changing the age of the client or changing the context or give the client different symptoms. a. This is especially useful when studying in groups. But it’s is also great when studying alone. 18. HESI HINT to study for Application level: a. Using the information you are studying, create diagrams, flow charts, and care plans b. Draw pictures with lots of color c. Be sure to use all parts of the nursing process and picture using the information in a clinical setting 19. DR. B. HINT to study for Application level: Imagine the nurse charting the evaluation of an intervention that you are studying (medication administration, delegation, blood transfusion). Let’s say the nurse performed the intervention 30 minutes ago. What indicators (vitals, skin color and temperature, client statements, etc.) did the nurse evaluate to determine if the intervention was effective? What did the nurse expect to happen? If the intervention was not effective, how did the nurse know? What was the nurse’s next response? 20. Study Tips for Analysis Level a. Create client situations based on the material you are studying. b. Compare and contrast the different situations. i. Which situation needs immediate attention? Why? ii. Which situation can wait? Why? 21. HESI HINT for Analysis level: a. Create concept maps that are easy for you to understand. b. Ask yourself “how is this related to what I already know?” c. Write your own test questions on index cards using information from multiple index study cards. d. Create four clinical scenarios from each lecture. Arrange them in order of priority actions for the nurse. 22. DR. B. HINT for Analysis level: Create scenarios of patients who have the same diagnosis who present with varying symptoms. Arrange these patients in order of priority. Basic Principles of Nursing Practice to Guide Your Critical Thinking When the question says “First, Initial, Best, Priority, Most important…” 12. Remember Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: a. Physiologic needs (ABC’s) must be met before psycho-social needs. b. Measures promoting safety must be met as well. c. Choosing between 2 good answers? Look for the answer that addresses the client’s physiological needs first. If they both address the client’s physiological needs, look for an option that promotes safety. 13. Remember the Hippocratic Oath, “Above all, do no harm.” a. Attempt to resolve an issue with the least invasive intervention first. 14. Remember that preventing problems are much better than allowing the problem to occur and then treating it. 15. Use the Nursing Process: a. Assess then take action. b. Do you have the assessment data you need to make a decision? Great! Make a decision and take action! c. If the test situation indicates that one step of the nursing process is completed, look for an answer that uses the very next step. d. For instance, if the nurse has implemented a nursing action look for an answer where the nurse must evaluate the action. 16. Ask yourself, “Is this within the nurse’s scope of practice?” 17. Determine the top priority interventions that can be carried out by the registered nurse, the licensed practical nurse, or unlicensed assistive personnel. 18. This is a nursing exam – be sure to have all the necessary information and take all possible relevant nursing actions before you call the physician. But know when it’s time to call the physician. 19. When the questions asks which client should be assessed first or which client can wait to be cared for last, look for clients who are at greatest risk, who are most physiologically unstable and give them attention first. 20. DR. B. HINT: A patient with a non-typical symptom of the disease process is a high priority out of a list of patients with typical symptoms of the disease process. 21. The client is the center of all care. 22. Create plans and intervene to empower clients. Do not reinforce dependency on the healthcare team. Test Taking Skills Steps to answering critical thinking questions: 13. Cover the options 14. READ the WHOLE question. 15. Ask yourself “Does the question have a positive or negative focus?” 16. Ask yourself “What are the key words in the question?” 17. Ask yourself, “What is really being asked in this question?” or “What concept are they making sure I know?” 18. Rephrase the question 19. Uncover the options 20. READ each option entirely. 21. Look for one that matches your own answer. 22. Rule out options 23. Consider the options that are left using nursing principles and knowledge of the subject. 24. Choose your answer. Other Tips 1. Avoid using personal work experience. 2. Do NOT play the “What IF game” 3. Do not insert words into the question or the answer!! Remember in test taking scenarios: unless instructed otherwise in the question, this is the Garden of Eden. You have an unlimited amount of time, staff, medications, and equipment. Reference: https://evolve.elsevier.com 01/2015 kpb