Bronchiolitis Resident Education

Bronchiolitis Resident Education
January 2014
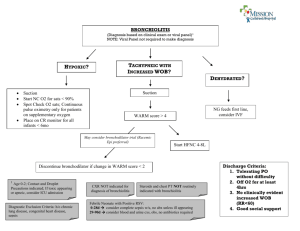
Recommendations:
1.
American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Bronchiolitis
Recommendation 1a: Clinicians should diagnose bronchiolitis and assess disease severity on the basis of history and
physical examination. Clinicians should not routinely order
laboratory and radiologic studies for diagnosis.
2.
AAP Bronchiolitis Guideline Recommendation 2a:
Bronchodilators should not be used routinely in the
management of bronchiolitis. A carefully monitored trial of alpha-adrenergic or beta-adrenergic medication is an option.
Inhaled bronchodilators should be continued only if there is
a documented positive clinical response. a.
If ordering albuterol or racemic epi, one of the following options on the order set must also be chosen: i.
This is the patient's first trial of albuterol for this infection. ii.
Patient has a clinical response to albuterol. iii.
Patient has been given albuterol previously for this infection, but the response is unknown or unclear.
3.
AAP Bronchiolitis Guideline Recommendation 6a: Consider placing infant NPO on IVF if respiratory rate is greater than
60-70 breaths per minute.
4.
AAP Bronchiolitis Guideline Recommendation 7a:
Supplemental oxygen is indicated if SPO2 falls persistently
below 90% in previously healthy infants. The clinician should be aware that oxygen might be used for increased work of breathing and not hypoxia during the acute phase of the
illness.
5.
Continuous Cardio/Respiratory Monitoring for patients during the first 12 hrs and then as needed for increased work of breathing, abnormal vital signs or corrected gestational age less than 3 months.
6.
Society of Hospital Medicine: Pediatric Hospital Medicine
Choosing Wisely Campaign. Continuous Pulse Oximetry should not be routinely used in children with acute
respiratory illness unless they are on supplemental oxygen.
Use of continuous pulse oximetry has been associated with increased admission rates and increased length of stay.
7.
2013 Cochrane Review concludes that 3% hypertonic saline
use can decrease LOS and improve respiratory scores in the inpatient - similar results not seen in the emergency room.
Name of order set is
“Bronchiolitis Admission”
Key Nursing Education Topics:
Bronchodilator Effectiveness o Studies show only a small percentage of patients respond to bronchodilators. o Single trial use only if indicated. o Continue use only if clinical improvement is observed.
Hypoxia o Persistently <90% pulse ox
Continuous Monitoring o Inpatient
Cardio/Respiratory monitoring: First 12 hours then
PRN.
Pulse Oximetry: Continuous monitoring for patients on concurrent oxygen, spot checks for all other patients. o ED
Continuous pulse oximetry.
Suction and Documentation o Technique
Recommendation: Suctioning no further than the nasopharynx.
Avoid deep suction. Suctioning past the nose
(deep suctioning) can lead to airway trauma. o Documentation
Inpatient - H2T
ED – Interventions
Key fields: “Depth” and “Response”
Depth Options:
Nose
Oral
Nasopharynx
Deep
Other
(Comment)
Response Options:
No Significant change
Increased/Decreased
Breath Sounds
Cleared
Increased/Decreased
Aeration
Increased/Decreased SaO2
*Refer to Epic for the complete list of response options
Respiratory Treatments Documentation o Respiratory Therapy documents under doc flowsheets in the “Respiratory Therapy” tab. o Documentation for suction and aerosol tx will interface so both RN and RT documentation can be viewed under H2T and Respiratory Therapy.
Parent Education Tools o Bronchiolitis and suctioning education documents are available for parents.
Viral Testing o Not routinely indicated for the care of a bronchiolitic patient.