3.02 Notes FINAL - biologybostian
advertisement
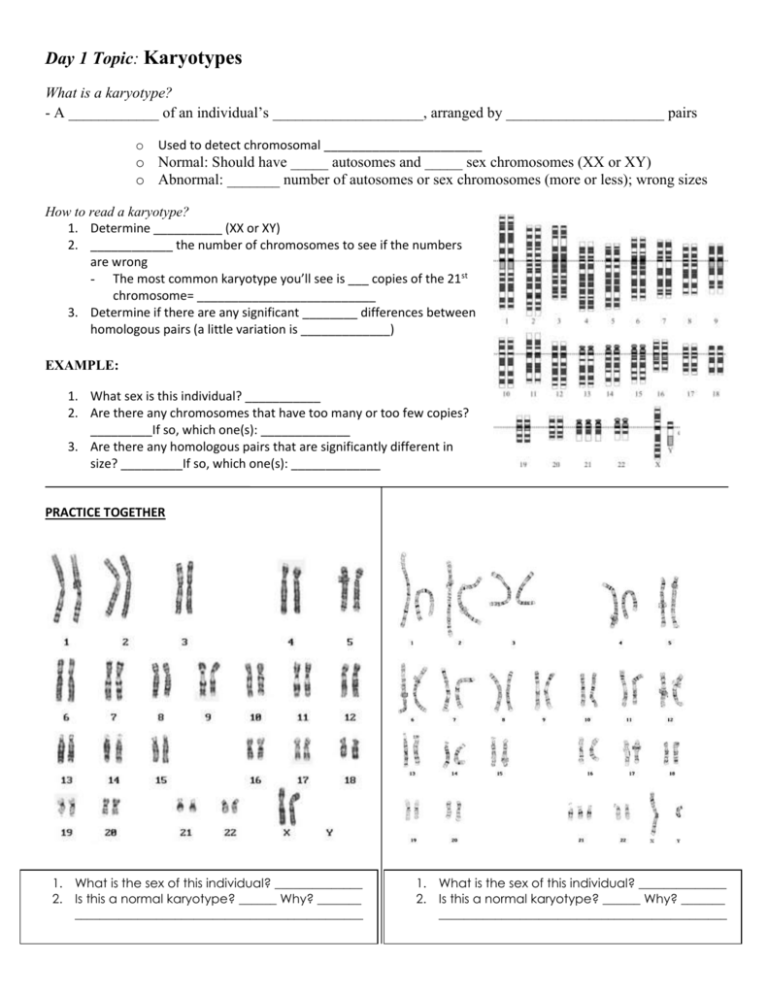
Day 1 Topic: Karyotypes What is a karyotype? - A ____________ of an individual’s ____________________, arranged by _____________________ pairs o Used to detect chromosomal _______________________ o Normal: Should have _____ autosomes and _____ sex chromosomes (XX or XY) o Abnormal: _______ number of autosomes or sex chromosomes (more or less); wrong sizes How to read a karyotype? 1. Determine __________ (XX or XY) 2. ____________ the number of chromosomes to see if the numbers are wrong - The most common karyotype you’ll see is ___ copies of the 21st chromosome= __________________________ 3. Determine if there are any significant ________ differences between homologous pairs (a little variation is _____________) EXAMPLE: 1. What sex is this individual? ___________ 2. Are there any chromosomes that have too many or too few copies? _________If so, which one(s): _____________ 3. Are there any homologous pairs that are significantly different in size? _________If so, which one(s): _____________ PRACTICE TOGETHER 1. What is the sex of this individual? ______________ 2. Is this a normal karyotype? ______ Why? _______ ______________________________________________ 1. What is the sex of this individual? ______________ 2. Is this a normal karyotype? ______ Why? _______ ______________________________________________ Day 2Topic -- Mitosis and Meiosis Quick Vocab Review! - Chromosome: A ___________ molecule that contains many ______________ Homologous chromosomes: Organisms have ______ of the same chromosome in every cell (one from each ________________) In humans… Pairs of Chromosomes Total Chromosomes - Diploid: ______________ number of chromosomes (in humans: ____) Haploid: ________ the number of chromosomes (in humans: ____) Gamete: A _________ sex cell (_____/sperm) that come together to make a __________ zygote and then ________! MITOSIS Type of Reproduction Used for? Starts with? Makes? # of times cell divides? Creates variation MEIOSIS Asexual 1 diploid cell (____) 2 _____________ diploid (2n) cells NO (genetic differences)? Cycle of LIFE: Zygote Gametes Embryo Adult Reproduction 1 diploid cell (2n) 4 haploid (n) ___________ Twice Day 3 Topic -- Sources of Variation 1. Crossing over: when homologous chromosomes ______________ genetic information to create genetic ____________________. - Happens ONLY in _________________! - THIS MEANS THAT ____________________________________________________________________! 2. Random assortment of chromosomes: it is completely random which ____________________________________________________________________________ ! 3. - Mutations: ________________________________________________ Can be good, bad, or ______________. In a ___________ cell= only affects that ____________. In a ___________ cell= could be passed on to their _______________! 4. Nondisjunction: _____________________________________________ ______________________________________. - Results in the wrong ________________of chromosomes in each cell - Famous example: _______________________ is caused by nondisjunction of the _____st chromosome 5. Fertilization: when an egg and sperm come together, they create a _____________________________________________________, that can then go on to make its own unique __________________. Day 1 Activity: Analyzing Karyotypes I. Look at the scenarios below, and determine what the outcome will be. Use the descriptions (1-4) below for help. Answer Choices : Normal male, Normal female, Down Syndrome, Turner’s Syndrome, Klinefelter’s Syndrome II. For each of the karyotypes below, determine 1) the sex of the individual 2) if there are any disorders 1. Klinefelter’s syndrome: Individuals that have XXY sex chromosomes. Individual appears male, but has smaller testes, are infertile, and may have some female sex characteristics 2. Turner’s Syndrome: These girls are often described as “XO” instead of “XX” because they are missing the 2nd X chromosome. 3. Down Syndrome: These individuals have three copies of chromosome #21. Also called trisomy 21. 4. Hermaphroditism: A true hermaphrodite has XXXY chromosomes- two from the mother, two from the father. Male or Female? _________________________ Name of Syndrome: _______________________ Total Number of Chromosomes: _____________ Male or Female? _________________________ Name of Syndrome: _______________________ Total Number of Chromosomes: _____________ Male or Female? _________________________ Name of Syndrome: _______________________ Total Number of Chromosomes: _____________ Male or Female? _________________________ Name of Syndrome: _______________________ Total Number of Chromosomes: _____________ Day 2 Activity Part 1: Reproduction (sex or not??) reading questions Instructions: Use Page 17 in your textbook to answer the following questions. 1. What process do organisms use to make more of themselves (new organisms)? 2. What are the two types of reproduction? 3. Use your book to write the definition of SEXUAL REPRODUCTION in your notes (page 17). 4. How many parents are required during sexual reproduction? 5. Use your book to write the definition of ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION in your notes (page 17). 6. How many parents are required during asexual reproduction? Pre-reading Questions: Brainstorm!! 1. What do you know about gonorrhea or syphilis? 2. How does DNA replication occur (you learned this in Unit 4!)? Reading: Ever wonder why a bacterial infection can be so dangerous for your body? Like when you get Strep throat or if someone contracts gonorrhea or syphilis from unprotected sex. Once invaders enter your body they try their best to take over and make themselves at home, like a rude house guest. Worse yet, bacteria make more of themselves by a process called asexual reproduction. Basically, they are very poor house guests trying to crash your party. More specifically, they grow larger, replicate their DNA and divide into two new identical daughter cells once inside your body. Then all of these new, identical daughter cells grow, replicate their DNA, and divide into more identical daughter cells. It is a vicious cycle that allows one single bacteria cell to become several million identical cells over only a few hours. That one dangerous bacterial cell that entered your body on its own made identical copies of itself called daughter cells. These identically dangerous bacterial cells attack your body by taking over together. Post-reading Questions: What did you learn? 1. What is the process called where a cell splits into two identical daughter cells? 2. Why does the article describe the bacteria as poor house guests (use asexual reproduction in your answer)? 3. Describe the two cells produced during asexual reproduction in one sentence. 4. How many parents participate in asexual reproduction? Who are we even talking about?! What organisms even participate in this asexual reproduction that only requires ONE parent? Do humans or other complex or simple animals make babies this way? No! We all know that it “takes two to tango” for animals like humans and lions and dogs and birds. So which types of organisms can make babies that are identical to themselves without the help of a mate? There are a few types of organisms that usually do ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION, make identical copies of themselves: bacteria and fungi. But wait! Plants can too! So each of these three types of organisms: bacteria, fungi and plants can make identical copies (clones) of themselves. 1. What three types of organisms can undergo asexual reproduction? 2. So how many parent cells are involved in asexual reproduction that does NOT require a mate? 3. Describe the organism (baby) produced during asexual reproduction compares to the parent in one sentence. Part 2: Reproduction stations Directions: Visit the reproduction stations and view the pictures and read the text. Write your answers to the questions posed at each station in the space below. STATION 1 STATION 2 STATION 3 STATION 4 STATION 5 STATION 6 Part 3: ASEXUAL reproduction micro-viewers Using the clues below, predict if each example under the micro-viewer is an example of budding, binary fission, sporulation, vegetative propagation, or regeneration. See examples of each type below! Budding Sporulation Regeneration Vegetative Propagation Binary Fission Slide # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Type of Asexual Reproduction Question: What do all of these reproduction methods have in common that make them asexual? 8 Part 4: Put the steps of mitosis in the correct order WITHOUT GLUING THEM DOWN. Once you are sure the order is correct, glue them. Finally, explain in your own words what is happening at each stage. Part 5: Use the following chart to compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis: MITOSIS Chromosome number stays the same Chromosome number divides in half DNA must first replicate Takes place in somatic (body) cells Takes place in sex cells Divides once Divides twice Makes 2 cells Makes 4 cells Used for sexual reproduction Used for asexual reproduction Cells made are different from their parent cells Cells made are identical to their parent cells Used for growth Used only for reproduction If you start with 40 chromosomes, you end with 20 chromosomes If you start with 40 chromosomes, you end with 40 chromosomes Makes gametes Makes daughter cells Makes haploid cells Makes diploid cells MEIOSIS Part 6: Fill in the blanks. Mitosis happens in __________ (sex/body cells). In mitosis, one cell divides to form _____ cells. In mitosis, each new cell has ____________________ (the same/a different) number and type of chromosomes as the original cell. Meiosis happens in ___________________ (sex/body cells). In meiosis, one cell divides to form ______ cells. In meiosis, each new cell has _________________ (twice/half/the same) the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Part 7: A human has 46 chromosomes in its skin cells. If one skin cell makes a copy of itself What type of reproduction is this? _________________ How many daughter cells are created? ________________ How many chromosomes are in each daughter cell? _____ If the human needs to create sex cells What type of reproduction would occur? ______________ How many daughter cells are created? ________________ How many chromosomes are in each gamete? ________ Part 8: Answer the following questions in complete sentences! 1. Healthy cells know when to stop dividing. What happens when cells do not stop dividing and what might have caused this to happen in the DNA of the cell? 2. A colony of bacteria reproduces for 16 generations. All of the offspring are genetically identical. This bacteria reproduced by which method? EXPLAIN how you know! Part 9: EOC STYLE QUESTIONS 3. During normal meiotic (meiosis) division of a diploid cell, the change in chromosome number that occurs is represented as: A. 4n n C. 2n 4n B. 2n n D. n ½ n 4. What process is represented in the diagram below? A. Asexual reproduction B. Sexual reproduction C. Meiosis D. DNA Replication 5. Which is a true statement about normal diploid cells? A. They contain only one chromosome of each homologous pair B. They contain only half the number of chromosomes as a gamete C. They contain homologous pairs of chromosomes D. They contain chromosomes that are all of equal length 6. Which process is represented by the series of diagrams below? A. Gametogenesis B. Fertilization C. Meiotic cell division D. Mitotic cell division 7. A cell with a diploid chromosome number of 12 divided two times, producing 4 cells with 6 chromosomes in each. The process that produced these four cells was most likely: A. Internal fertilization B. Asexual reproduction C. Mitotic cell division D. Meiotic cell division 8. Which process is represented by the diagram to the left? A. Fertilization B. Meiosis C. Binary fission D. Vegetative propagation 9. Warts result when certain viruses cause skin cells to reproduce at a high rate. This rapid reproduction of skin cells is due to: A. Cellular digestion B. Mitotic cell division C. Synthesis processes D. Meiotic cell division Day 3 Activity: A Closer Look at Mitosis!!! Use the micro-viewer and the insert to help you complete these notes. 1) Early Prophase: “pre-division stage” a. What is the plant cell doing right now? b. What are the chromosomes doing? 2) Prophase – “the division begins” a. Draw the nucleus shown in the center cell in the box b. Where have all the condensed chromosomes moved to? 3) Metaphase: “Let’s meet in the middle” a. Draw the nucleus and chromosomes in the box b. The chromosomes have all moved to the ____________________ of the cell. 4) Early Anaphase: a. Observe the chromosomes starting to separate. As they move apart they begin to form to Vs facing each other. 5) Anaphase and Late Anaphase: Apart a. Draw the chromosomes at anaphase in cell F in frame 6 in the box b. All chromosomes have completely _____________________________________ and are moving to ___________________________ sides/poles of the cell. 6) Telophase: Two Cells! a. Draw the chromosomes in cell G in their 2 newly forming nuclei b. Can you see individual chromosomes anymore? ________ c. Can you see a faint line beginning to form between the cells? _____ On either side of this line the plant cells will begin to form new cell _______________ made of cellulose. d. Observe frame 8. What do you see at G? e. How do the cells at letter A compare to those cells? REPRODUCTION (UNIT 5) STUDY GUIDE Basic Vocabulary: In 5 words or less, define the essential vocabulary below DO NOT JUST COPY YOUR NOTES, CREATE A NEW DEFINITION! VOCAB Mitosis 5 WORDS OR LESS DEFINITION Meiosis Fertilization Diploid Haploid Zygote Somatic Gamete Asexual Sexual Draw & label the phases of MITOSIS in the correct order. Below are two sources of variation that leads to different gametes during Meiosis. 1) Identify what type of variation it is and then describe what is happening. Type: ________________________________ Type: _____________________ _________________ What is happening: What is happening? _______________________________________ ________________________________________________ COMPARE & CONTRAST CHART CHARACTERISTICS TYPE OF REPRODUCTION (a/sexual) MITOSIS MEIOSIS Chromosome Number of human parent cell (# and hap/diploid) Number of cell division cycles Number of DAUGHTER CELLS formed CHROMOSOME # of each daughter cell Genetically identical or variation Purpose? Plant Parent Cell: (hint: a pair of hearts represents a pair of chromosomes) DRAW a possible daughter cell after MITOSIS DRAW a possible daughter cell after MEIOSIS EXPLAIN THE FINAL PRODUCTS OF MITOSIS VS. MEIOSIS (in other words, how are the daughter cells of each process different?): Complete the sentences: 1. Meiosis is considered (asexual/sexual) _______________ because the daughter cells are (genetically identical/genetically different) _____________________________________. 2. The chromosomal number of all somatic cells is (Diploid/haploid) ___________________, which in humans is (23 or 46) _________ 3. The chromosomal number of all gametes is (diploid/haploid) ______________________, which in humans is (23 or 46) ________ 4. During Meiosis, a single (somatic or gamete) _______________ cell undergoes cell division to form 4 daughter (somatic or gamete) _________________ cells that are each (haploid or diploid) __________________. 5. During fertilization, a (haploid or diploid) sperm & egg fuse together to restore the (haploid or diploid) ______________ chromosomal number. 6. The zygote will then undergo (meiosis or mitosis) ____________________________ to grow and develop. Answer the following practice test questions. A zebra has 48 chromosomes in it somatic cells. What most likely will be the chromosomal number in each daughter somatic cell? a) 48 b) 96 c) 12 d) 24 12. What most likely will be true about the daughter cells formed during meiosis in the zebras ovaries or testicles? a) All daughter cells will be identical c) Meiosis will restore the diploid number b) All daughter cells will have genetic variation d) More sperm will be formed once the sperm undergo meiosis 10. The daughter cells formed during meiosis will always be haploid. How is it possible that all our somatic cells are diploid(have TWO copies of each chromosome) if the cells that formed us are haploid (only one copy)? (Hint: it takes a male and a female to make a child) ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________