Resource-List
advertisement
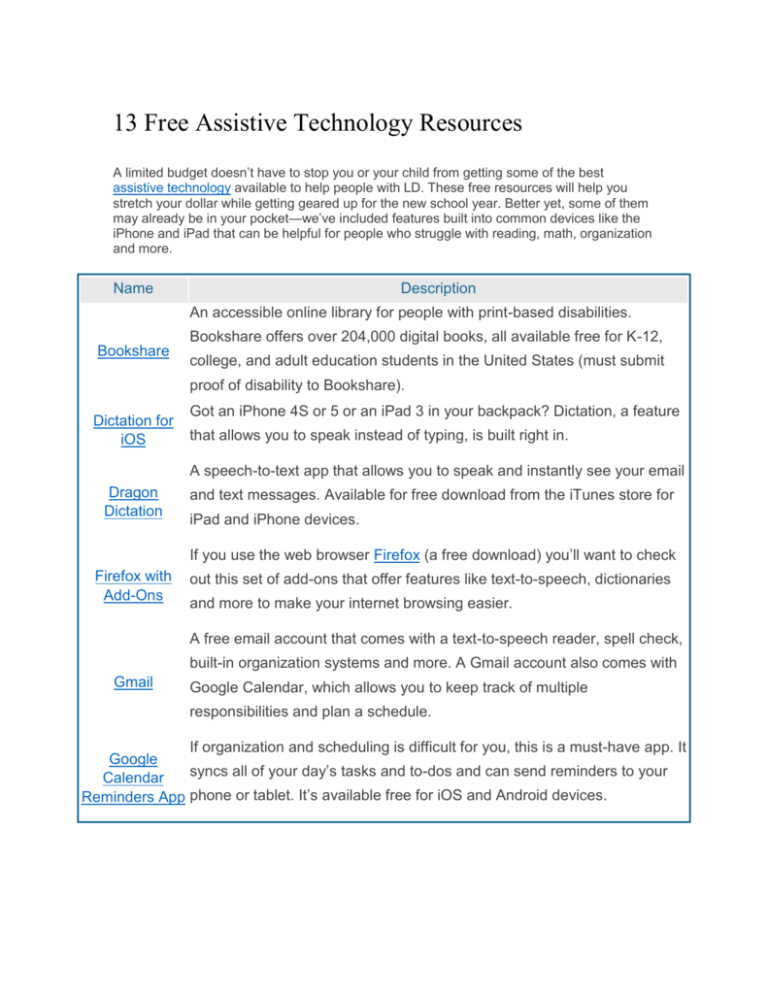
13 Free Assistive Technology Resources A limited budget doesn’t have to stop you or your child from getting some of the best assistive technology available to help people with LD. These free resources will help you stretch your dollar while getting geared up for the new school year. Better yet, some of them may already be in your pocket—we’ve included features built into common devices like the iPhone and iPad that can be helpful for people who struggle with reading, math, organization and more. Name Description An accessible online library for people with print-based disabilities. Bookshare offers over 204,000 digital books, all available free for K-12, Bookshare college, and adult education students in the United States (must submit proof of disability to Bookshare). Dictation for iOS Got an iPhone 4S or 5 or an iPad 3 in your backpack? Dictation, a feature that allows you to speak instead of typing, is built right in. A speech-to-text app that allows you to speak and instantly see your email Dragon Dictation and text messages. Available for free download from the iTunes store for iPad and iPhone devices. If you use the web browser Firefox (a free download) you’ll want to check Firefox with Add-Ons out this set of add-ons that offer features like text-to-speech, dictionaries and more to make your internet browsing easier. A free email account that comes with a text-to-speech reader, spell check, built-in organization systems and more. A Gmail account also comes with Gmail Google Calendar, which allows you to keep track of multiple responsibilities and plan a schedule. If organization and scheduling is difficult for you, this is a must-have app. It Google syncs all of your day’s tasks and to-dos and can send reminders to your Calendar Reminders App phone or tablet. It’s available free for iOS and Android devices. Need to easily share and collaborate on documents with a teacher, tutor or Google Drive classmate? Google Drive lets you create documents, spreadsheets and slideshows and share them with others...all for free. Library of Congress The Library of Congress provides a free library of audio materials for circulation to eligible borrowers with reading disabilities. LibriVox is a volunteer-run organization that provides audiobooks of works LibriVox in the public domain, including works like religious texts and classic literature. Got some Charles Dickens or Mark Twain on your reading list this year? Project Gutenberg Project Gutenberg provides free ebooks (in multiple formats) of noncopyrighted works, including many classic and historical texts. If you have an iPhone 4S or above, you have one of today’s best AT tools right in your pocket. Siri is a “personal assistant” that is more than just Siri dictation: It lets you use your voice to ask your phone questions or give commands. You can use it to make calls and set reminders. Like the sound of Siri, but use an Android, BlackBerry, or Windows Mobile device? Vlingo is a virtual assistant that uses speech-to-text technology to Vlingo help you send messages and find information, and is available free on all major smartphone and tablet platforms. A free plugin for Microsoft Word (available only for Windows users) that WordTalk will speak the text of any Word document and highlight as it goes. This article is adapted from the LD Resources Foundation, which assists college students and adults with LD and ADHD by granting assistive technology awards to meet their educational and vocational needs. http://www.ncld.org/students-disabilities/assistive-technology-education/free-assistivetechnology-resources Assistive Tech Innovations: 14 New Apps & Other Tools Here’s the roundup that came from a combined #LDchat/#ATchat hosted by The National Center for Learning Disabilities Dragon Dictation: Speech-to-text for a variety of mobile applications (think: messaging, emailing, blog writing) 1. ModMath: Designed for individuals with dyslexia and dysgraphia for whom the mechanics of writing math problems causes a barrier. ModMath takes care of the construction of, for example, the long division problem. After that, solving that problem is up to you. 2. VoiceDream: Text-to-speech to aid in reading. This app also allows for screen, font and text size customization and highlighting. It has a built-in dictionary and works with text from lots of sources (PDF, ebooks, email). If you’ve looked into text-to-speech apps, you’ll agree that the power of VoiceDream does sound dreamy in comparison. 3. Notability: Takes “handwritten” notes on documents to allow for adding sketches to PDF or graphics or editing student work (!!). Notability also has an audio recording feature for auditory learners, photo capability and it coordinates with sharing platforms like Google Drive and Dropbox. This will be my next download. 4. StoryVisualizer: Creates storybooks for students using their words and images. From Lego Education. 5. UsTyme: Allows two people to remotely read a story together by coupling FaceTime-like software with reading. Would be great for traveling parents or faraway relatives. I’m thinking about using this as a formative assessment to check-in with students who are using iPads for reading either in the classroom or for homework. 6. DyslexiaQuest: A series of games designed to “assess working memory, phonological awareness, processing speed, visual memory, auditory memory and sequencing skills.” Gamers are encouraged to keep practicing to master skills. 7. Read2Go (iOS) or Go Read (Android): Makes books accessible to people with print disabilities. Developed by Bookshare. 8. Co:Writer: Word prediction software aids writing in real-time or later when editing. Textto-speech feature reads letters, words, sentences, documents, which is great because not many have this thorough level of read-aloud. Produced by Don Johnston and features the grammar-smart word prediction that his company is famous for. Opt for the SOLO Suite and get Co:Writer; Read:Outloud; Write:Outloud and Draft:Builder. General productivity apps: 1. Corkulous: For everything you’d tack on a corkboard or jot on a sticky note (phone numbers, reminders, dates, etc.). Sounds like a more practical Pinterest. 2. Voxer: Voice messaging somewhere between walkie-talkie and phone conversation. Allows users to skip the ringing and the voice mail message and cut straight to leaving a message/“vox”. Quick & practical. 3. The Little Memory: If Twitter had a journal feature, it’d be The Little Memory. Write short memories or accounts of your day. I’m thinking this could digitize the exit ticket to save trees & time. 4. Haiku Deck: Prettier, more powerful slide presentations. At a glance, it seems like a Prezi contender. (Prezi is awesome!) 5. Finally, Graphite is a site for educators to find and review tech to use in class, including apps, sites and games. Go there for more. What are your favorite educational apps? Annie Krut is a special education teacher with more than 10 years’ experience working with children and their families. http://ncld.org/students-disabilities/assistive-technology-education/apps-assistivetechnology Assistive Technology: Checklist of Questions to Ask Colleges Are you a college-bound teen who relies on assistive technology (AT) to compensate for your LD or AD/HD? As you prepare for college, it’s important to know your rights and responsibilities regarding AT accommodations as a college student. Once on campus, it’ll be up to you to advocate for your needs and take the initiative to get the AT accommodations you need to succeed. Sound overwhelming? Don’t worry! We’ve created a checklist of questions to ask campus disability services counselors about their school’s AT policies in general, as well as specific questions about your individual needs. This “AT interview process” may help you choose the right college and prepare you to hit the ground running once you’re there. http://ncld.org/learning-disability-resources/checklists-worksheets/assistive-technologychecklist-questions-ask-colleges Accessibility from a distance in higher education Today’s digital learning platforms come with varying degrees of accessibility for students with disabilities By: Matt Zalaznick University Business, November 2013 http://www.universitybusiness.com/accessibilitydistance