blood answer sheet
advertisement

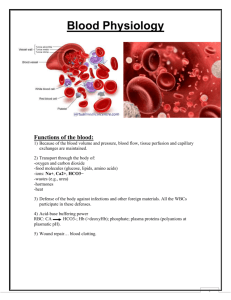
Science Department April 2015 Grade 7 Name _________________________________ The Blood (Revision sheet) Read the paragraphs below then answer the questions that follow All humans can be typed for the ABO blood group. There are four principal types: A, B, AB, and O. There are two antigens (A and B) and two antibodies (anti-A and anti-B) that are mostly responsible for the ABO types. An antigen is found on a red blood cell, it is what determines the type of blood group a person is. An antibody is a protein that fight antigens that are different than the body’s antigens (antigens coming from outside the body). The specific combination of these antigens and antibodies determines an individual's blood type. An example is if a person is blood type A then his red blood cells have antigen A but has the opposite antibody which is anti-B. Complete the boxes below: Blood type A Blood type B Antigen ____A_____ Antigen ____B_______ Antibody ____anti-B_____ Antibody ____anti- A______ Some people do not have antigens on their red blood cells (neither antigen A nor antigen B) these are known as blood group O. These people have both antibodies anti-A and anti-B. Others may have both antigens A and B and no antibodies not anti-A nor anti-B these are known as blood group AB. Complete the boxes below: Blood type O Blood type AB Antigen ____None______ Antigen ___A and B____ Antibody ___AntiA and AntiB____ Antibody ___None__ Why is it important to know your blood group? Sometimes people need blood transfusion. If anyone is transfused with incompatible blood (doesn’t match his blood type) it may lead to his death. This is a Red blood cell with antigens on it. This is what an Anti-A antibody looks like When an antigen combines with its antibody , for example Antigen A with antibody A they combine together and the red blood cells are destroyed. These cells will be destroyed Therefore it is important when transfusing blood to know the blood type and which types are compatible to prevent the destruction of blood cells causing death. Erythrocyte = Red Blood Cells Remember: Antigens tell us the blood type Antibodies fight antigens so they are always the opposite of our blood group. Looking at the table above we realize that: 1. 2. 3. 4. Anti B cannot attack antigen A on RBCs of blood group A. Anti B can attack antigen B which are on RBCs of blood group B. Anti A cannot attack antigen B on RBCs of blood group B. Anti A can attack antigen A which are on RBCs of blood group A. 5. Blood group AB has no antibodies and therefore do not attack any blood cells entering. 6. Blood group O on the other hand has both antibodies A and B and therefore they attack any blood group with antigens (A or B). Using the table and the information above complete the boxes below (the first one has been done for you) Blood type A Blood type B Antigen ___A_______ Antigen ____B______ Antibody ___anti B_______ Antibody ___AntiA______ Can donate to blood group(s) __A, AB__ Can donate to blood group(s) __B,AB___ Can receive blood from ___A, O_____ Can receive blood from ___B,O____ Blood type AB Blood type O Antigen ___A and B____ Antigen ____None_____ Antibody _____None___ Antibody _antiA and antiB____ Can donate to blood group(s) __AB____ Can donate to blood group(s) A, B, AB and O Can receive blood from _A, B, AB and O Can receive blood from __O_____ Blood group AB are known to be universal recipients because they can receive blood from anyone but only donate to themselves (AB). Blood group O are known to be universal donors because they can donate blood to anyone but only receive from themselves (O). When an antigen attaches to its antibody they form clusters called antigen antibody complex, which settles down and may block capillaries. When the antigen antibody complex form clusters this process is called agglutination. In the lab when we test for blood typing we add the antibody to the blood sample from the person tested to check for the antigen. Anti-A Anti-B In the sample above we added anti-A antibody to the blood which combined with the antigen A causing agglutination which shows in the first circle. The blood did not agglutinate in the second circle with the anti-B which means the blood does not have antigen B. This means that this blood is blood group A. For the blood samples below circle the correct answer Anti-A Anti-B 1. When we added Anti-A the blood (Agglutinates -- Does not agglutinate) this means that this blood (has –does not have) antigen A. 2. When we added Anti-B the blood (Agglutinates -- Does not agglutinate) this means that this blood (has –does not have) antigen B. 3. This is blood group ____B_____ Anti-A Anti-B 4. When we added Anti-A the blood (Agglutinates -- Does not agglutinate) this means that this blood (has –does not have) antigen A. 5. When we added Anti-B the blood (Agglutinates -- Does not agglutinate) this means that this blood (has –does not have) antigen B. 6. This is blood group __AB______ Anti-A Anti-B 7. When we added Anti-A the blood (Agglutinates -- Does not agglutinate) this means that this blood (has –does not have) antigen A. 8. When we added Anti-B the blood (Agglutinates -- Does not agglutinate) this means that this blood (has –does not have) antigen B. 9. This is blood group _____O_ Question one 1. How many blood types do we have in the ABO system? ___________4__________________________________________ 2. What part of the red blood cell determines your blood type? ________The antigen_______________________________________ 3. Why is it important to know your blood type? Because if you need a blood transfusion you must receive a compatible blood type (i.e a blood type that matches your blood) because when an antigen combines with its antibody , for example Antigen A with antibody A they combine together and the red blood cells are destroyed. So if you receive a blood with an antibody that matches your antigen your blood with agglutinate blocking the blood vessels. 4. Complete the table below Blood group A Antigens A Antibodies antiB B B antiA AB A and B None O none Both antiA and antiB 5. Complete the sentences below a. An antigen is found on the surface of ____RBC____________. b. An antibody is a __Protein___ that fights the __pathogens___. c. The ___antigen_______ determines the blood group. d. When the antigen combines with its antibody to form an __antigen antibody____ complex in a process called _agglutination____. e. Blood group __O__ is known as a universal donor while blood group _AB___ is known as a universal recipient. 6. Look at the example then complete in the same pattern: a. Antigen A + ___Anti-A___ causes agglutination. Antigen A + ___Anti-B___ does not cause agglutination. b. Antigen B + __AntiB_____ causes agglutination. Antigen B + ___AntiA____does not cause agglutination. 7. Complete the table below Blood group A Receives blood from (can take from) A and O Donates blood to (can give to) A, AB B B and O B, AB AB A, B, AB and O AB O O A, B, AB and O 8. In the lab the lab technician received 4 blood samples to test for blood grouping. Look at the diagrams below and determine the blood group of each sample. This means no agglutination This means agglutination is seen The letter on the test tubes indicate the Antibody used so In this test tube anti A has been added to the blood sample In this test tube anti B has been added to the blood sample Now look at the samples and determine the blood types: a. Anti A shows ___no agglutination__ Anti B shows __ agglutinates____ Then this is blood group _B___ b. Anti A shows __ agglutinates ____ Anti B shows __ agglutinates __ Then this is blood group __AB__ c. Anti A shows __ no agglutination ___ Anti B shows ___ no agglutination __ Then this is blood group __O__ d. d Anti A shows __agglutinates_____ Anti B shows __ no agglutination _____ Then this is blood group _A_