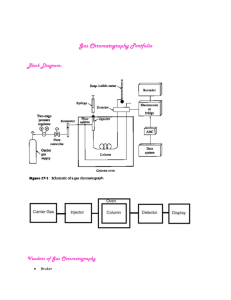
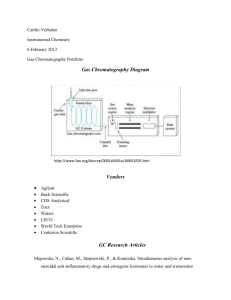
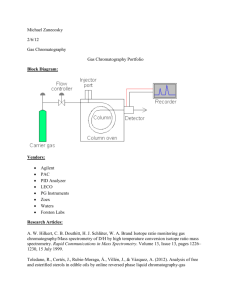
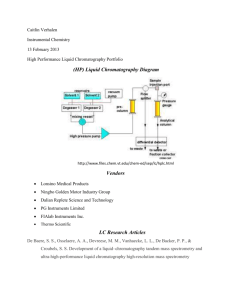
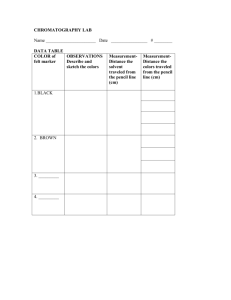
Chromatography Assignment AP Chemistry Please go to the
advertisement

Chromatography Assignment AP Chemistry Please go to the website listed below and then answer the following questions: http://www.chemguide.co.uk/analysis/chromatogrmenu.html#top. Please type your answers. Start with the section called “Introducing Chromatography: Thin Layer Chromatography”. 1) 2) 3) 4) What is the purpose of chromatography? Describe the two phases of chromatography. Describe the phases used in thin layer chromatography (TLC). What is the point of the pencil line and why must pencil be used instead of ink? 5) Why is the beaker covered? 6) What is the solvent front? 7) What is an Rf value? Skip the section on colorless substances. Continue reading “Using TLC to identify compounds”. 8) Describe the use of TLC to identify the amino acids in a mixture. 9) Sketch the structure of silica gel and describe the types of IMFs it could have with other substances. 10) What determines how fast the components of a mixture get carried up a plate? 11) Explain why a compound that can form hydrogen bonds moves up a plate at a different rate from a compound that has only LDFs (which they are calling van der Waals forces). Go back to the Chromatography menu and choose Paper Chromatography. 12) What is used for each of the two phases in paper chromatography? 13) Describe how you can use paper chromatography to determine which of 3 pens was used to write a message. Scroll down to “How does paper chromatography work”. 14) What type of molecules bind to the cellulose molecules on the surface of the paper? 15) Describe how non-polar molecules in a mixture will travel when hexane is used as a solvent. 16) Describe how polar molecules in a mixture will travel when hexane is used as a solvent. Now go back to the Chromatography menu and select Column Chromatography. 17) How is column chromatography similar to TLC? 18) Describe how column chromatography is used to separate a mixture. Include an explanation of why the yellow component exited the column before the blue component. 19) What is elution? What is an eluent? 20) Explain how you can collect the blue solvent as well. BONUS: What type of chromatography did you do in AP Bio and what was it used to separate?