Study Guide for Cell Transport Quiz
advertisement
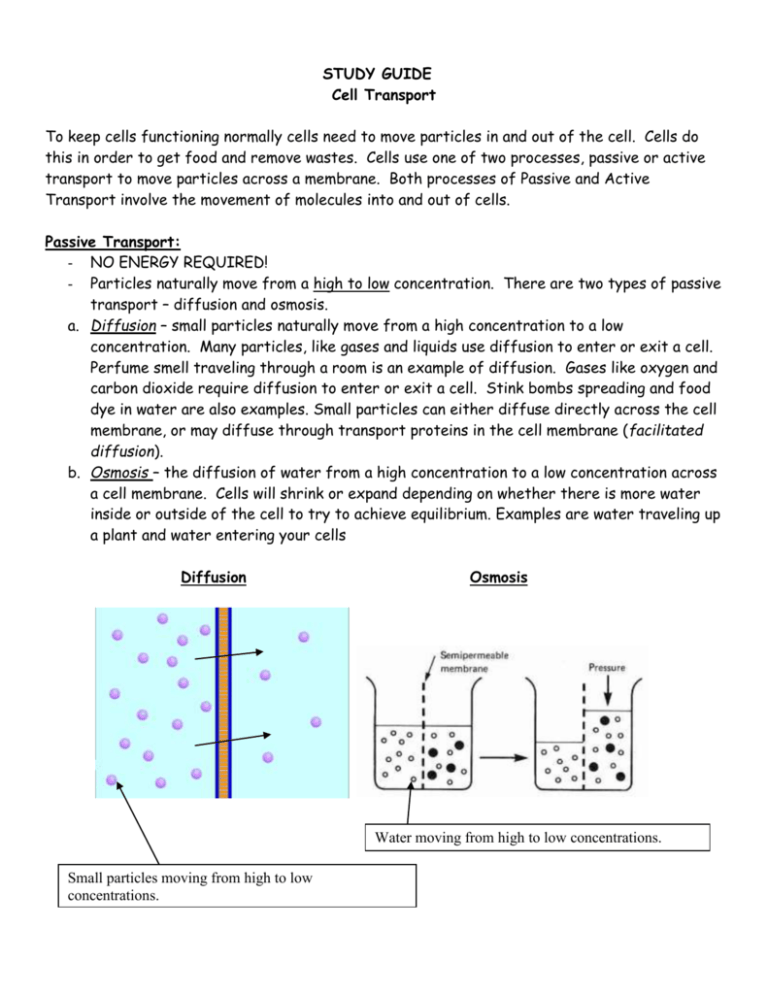
STUDY GUIDE Cell Transport To keep cells functioning normally cells need to move particles in and out of the cell. Cells do this in order to get food and remove wastes. Cells use one of two processes, passive or active transport to move particles across a membrane. Both processes of Passive and Active Transport involve the movement of molecules into and out of cells. Passive Transport: - NO ENERGY REQUIRED! - Particles naturally move from a high to low concentration. There are two types of passive transport – diffusion and osmosis. a. Diffusion – small particles naturally move from a high concentration to a low concentration. Many particles, like gases and liquids use diffusion to enter or exit a cell. Perfume smell traveling through a room is an example of diffusion. Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide require diffusion to enter or exit a cell. Stink bombs spreading and food dye in water are also examples. Small particles can either diffuse directly across the cell membrane, or may diffuse through transport proteins in the cell membrane (facilitated diffusion). b. Osmosis – the diffusion of water from a high concentration to a low concentration across a cell membrane. Cells will shrink or expand depending on whether there is more water inside or outside of the cell to try to achieve equilibrium. Examples are water traveling up a plant and water entering your cells Diffusion Osmosis Water moving from high to low concentrations. Small particles moving from high to low concentrations. Equilibrium – Particles naturally move from a high to a low concentration toward equilibrium, a state in which particles are evenly distributed: Active Transport: - USES ENERGY! - Active Transport- small particles need to also move from low concentrations to high concentrations at times, in this case it is called active transport. When small particles move against the normal direction, it is just called active transport. Small particles moving from a low concentration to a high concentration There are two special types of active transport that deal with moving large particles in and out of the cell. These processes are called endocytosis and exocytosis. a. Endocytosis: the process in which a cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses it and brings it into the cell through the semi-permeable membrane. Glucose is an example of something that would enter a cell through the process of endocytosis. Or, when our white blood cells ‘eat’ bacteria to kill it. b. Exocytosis: the process used to remove a large particle from a cell. Waste from a cell would exit the cell through the semi-permeable membrane through the process of exocytosis.