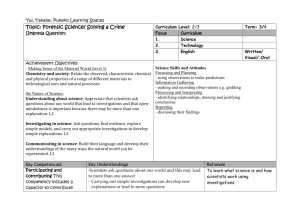
Forensic Science Review Outline Topic Objective Key Terms/Vocab
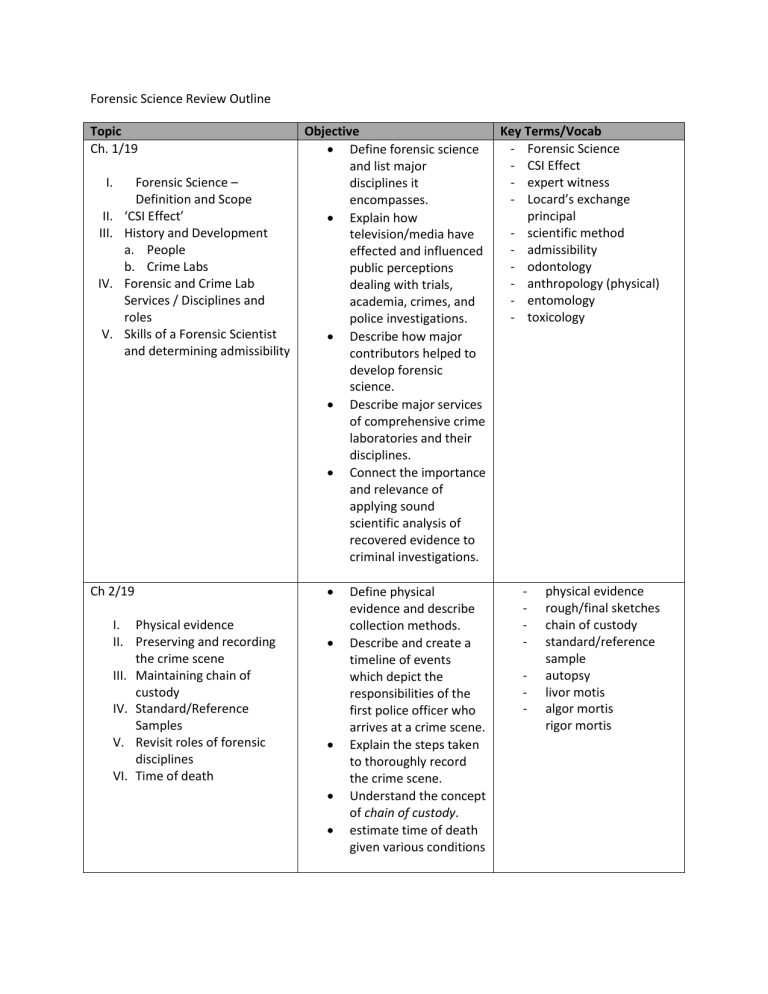
Forensic Science Review Outline
Topic
Ch. 1/19
I.
Forensic Science –
Definition and Scope
II.
‘CSI Effect’
III.
History and Development a.
People b.
Crime Labs
IV.
Forensic and Crime Lab
Services / Disciplines and roles
V.
Skills of a Forensic Scientist and determining admissibility
Ch 2/19
I.
II.
Physical evidence
Preserving and recording the crime scene
III.
Maintaining chain of custody
IV.
Standard/Reference
Samples
V.
Revisit roles of forensic disciplines
VI.
Time of death
Objective
Define forensic science and list major disciplines it encompasses.
Explain how television/media have effected and influenced public perceptions dealing with trials, academia, crimes, and police investigations.
Describe how major contributors helped to develop forensic science.
Describe major services of comprehensive crime laboratories and their disciplines.
Connect the importance and relevance of applying sound scientific analysis of recovered evidence to criminal investigations.
Define physical evidence and describe collection methods.
Describe and create a timeline of events which depict the responsibilities of the first police officer who arrives at a crime scene.
Explain the steps taken to thoroughly record the crime scene.
Understand the concept of chain of custody.
estimate time of death given various conditions
Key Terms/Vocab
Forensic Science
CSI Effect
expert witness
Locard’s exchange principal
scientific method
admissibility
odontology
anthropology (physical)
entomology
toxicology
-
-
-
physical evidence rough/final sketches chain of custody standard/reference sample
autopsy
livor motis
algor mortis rigor mortis
Topic
Ch 3
I.
Common types of physical evidence
II.
Identification vs.
Comparison
III.
Individual characteristics vs. class characteristics
IV.
Significance and value of physical evidence
V.
Forensic Databases
Ch 4
I.
Properties of Matter
II.
III.
IV.
a.
temp b.
c.
d.
a.
states of matter weight/mass density
Theory of Light refractive index
Metric system
Anthropometry
Objective
Identify and describe three categories of physical evidence along with common types within each category.
Explain the difference between the identification and comparison of physical
evidence define; compare and contrast individual and class characteristics of physical evidence o explain the significance of assessing value of physical evidence
Define and distinguish the physical and chemical properties of matter
Compare and contrast between solids, liquids, and gases.
Define and distinguish between atoms and molecules; elements and compounds.
Understand how to use the basic units of the metric system
Describe the electromagnetic spectrum and basic behaviors of light.
analyze anthropometric measurements; evaluate the validity of this identification method.
Key Terms/Vocab
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
(DNA)
Impressions
Identification
Comparison
Individual characteristics
class characteristics
-
-
-
-
-
chemical property
physical property
matter
Anthropometry wavelength frequency density physical state sublimation
Topic
Ch 4
I.
Ch 15
I.
Ch. 11
I.
Glass Analysis a.
b.
c.
composition comparing fragments fractures
Fingerprint analysis a.
history b.
principles c.
classification d.
detecting and developing
Examination of hair a.
b.
c.
morphology identification and comparison examination
Objective
Define and understand the properties of density and refractive index and its connection to glass analysis.
Evaluate glass fractures to determine the direction of impact.
Explain the three principles of fingerprints.
Identify the common fingerprint patterns and characteristics.
Identify and describe the three layers of the of hair
compare and contract differences between human and animal hair
describe hair features used in microscopic hair analysis
Key Terms/Vocab
tempered glass
laminated glass
radial fractures
concentric fractures
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
minutiae (ridge characteristics) ridge patterns arch loop whorl iodine fuming cuticle cortex medulla o medullary index scale pattern medulla patterns