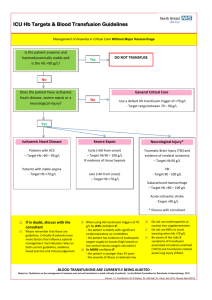
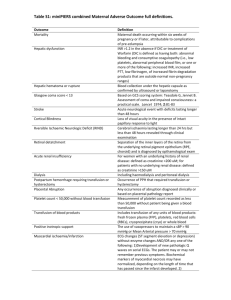
Blood Transfusion
advertisement

Fabrice Schweizer Science Mrs. Sonja D Block Class 8A Blood Transfusion 1. A blood transfusion is the process in which you receive blood through an intravenous (IV see picture) line inserted into one of your blood vessels. Blood transfusion can be life-saving in some situations or can be used to replace blood lost during surgery. During a blood transfusion, a small needle is used to insert an IV line into one of your blood vessels. You then receive healthy blood through this IV line. This process usually takes around 1-4 hours depending on how much blood you need. 2. Blood is most commonly donated as whole blood by inserting a catheter into a vein and collecting it in a plastic bag. Then the blood bank collects all the blood and screens it. But what is a blood bank? Blood banks Blood banks collect, test, and store blood. They carefully screen all donated blood for infectious agents (such as viruses) or other factors that could make you sick. They also screen all the donated blood to find out whether it's type A, B, AB, or O and whether it's Rh-positive or Rhnegative. You can get very sick if you receive a blood type that doesn't work with your own blood type. Some blood banks also remove the white blood although rare, some people are allergic to white blood cells in donated blood. Removing these cells makes allergic reactions less likely. 3. 1628 British physician William Harvey discovers the circulation of blood. The first known blood transfusion is attempted soon afterward. 1658 Microscopist Jan Swammerdam observes and describes red blood cells. 1665 The first recorded successful blood transfusion occurs in England: Physician Richard Lower keeps dog alive by transfusing blood from other dogs. 1667 Jean-Baptiste Denis in France and Richard Lower and Edmund King in England separately report successful transfusions from sheep to humans. 1818 British obstetrician James Blundell performs the first successful transfusion of human blood to a patient for the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage. 1873-1880 U.S. physicians attempt transfusing milk from cows, goats and humans. 1901 Karl Landsteiner, an Austrian physician, discovers the first three human blood groups. So the first blood transfusion was done in England in 1665 from a dog to a dog. The first human blood transfusion was done in 1818 of human blood to a patient for the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage. 4. Science makes it even possible to do blood transfusions every day. You use science to find out what blood type the donor has and what blood the receiver needs. You also need science to find out if the blood is healthy and if the red blood cells are good. This is like the labs that we do just at a higher level. To get the blood is easy but all these tests that you have to do afterwards like check if the blood is healthy, remove the white blood cells etc. is impossible to do without science. 5. Of course blood transfusion saves lives and is helpful especially fore the ones who need blood often but there are also side effects and risks that you take with a blood transfusion. The benefits are: Most people who receive blood feel better, have more energy, and are able to participate in more activities. Children who receive blood transfusion therapy may grow better than they did while on other therapy. Blood transfusion can safe lives Side effects: The allergic reaction is the most common type of reaction. This reaction happens during the process of a blood transfusion and the problem is that the body reacts to plasma proteins in the donated blood. The symptoms are hives and itching. The febrile reaction means that that the person gets a sudden fever during or within 24 hours of the transfusion. Headache, nausea, chills, or a general feeling of discomfort may come with the fever. 6. The blood transfusion makes it possible for people to survive who might have died 100 years ago. Less people dying means less pain in the world. For example if my mom would have blood cancer 100 years ago she most likely would of died. Now 100 years later the doctors could save her thanks to blood transfusion. The economical impacts is that if 100`000 of people die because they don’t get blood, there are people missing who might be important for the government of for a certain company. It also helps the economy because today, these blood banks trade and send the blood all over the planet. In some countries it is common for organisations to pay for blood. Even in the United States, many plasma donors are still paid for their bodily fluids. So that makes money for the government etc. So overall blood transfusion has a huge economical and social impact on our society. 7. Medical treatment and procedures changed because today a lot of people need blood immediately and through the blood transfusion its possible for them to survive. The doctors today are way more developed then 50 years ago so that also helps to minimize the side effects after or during a blood transfusion. Overall the blood transfusion makes life easier for the hospitals because it only takes around 4 hours to give blood to someone. Bibliography: "What Is a Blood Transfusion?" - NHLBI, NIH. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Sept. 2013. "History of Blood Transfusion." American Red Cross. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Sept. 2013. "What Is a Blood Transfusion?" What Is a Blood Transfusion? N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Sept. 2013. "Possible Risks of Blood Transfusions." Possible Risks of Blood Transfusions. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Sept. 2013. "Blood Transfusion Therapy." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 03 Jan. 2011. Web. 29 Sept. 2013. "Blood for Money? We Need More of an Incentive to Donate." Blogsindependentcouk. N.p., n.d. Web. 30 Sept. 2013. .