2014-15 MID-TERM EXAM REVIEW diagram the earth`s orbit
advertisement

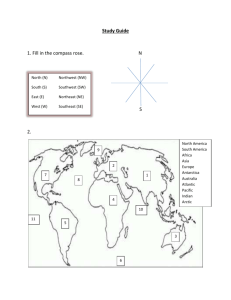
2014-15 MID-TERM EXAM REVIEW diagram the earth’s orbit including the following: tropic of cancer, tropic of capricorn, equator, sun’s most direct rays, first day of each season, solstices, equinox, hours of sunlight at the north pole, date of the start of each season, arrows showing the direction of orbit explain why each season is not the same length; include gravity and average orbital speed what is the name of the north star and explain the apparent motion of all celestial objects in respect to the north star explain what eccentricity is and how it is calculated: what is the eccentricity of a circle and what is the apparent shape of all the planets’ orbits describe the difference and give an example of real motion and apparent motion Planetary characteristics: terrestrial vs jovian etc... List 2-3 characteristics for each planet Latitude & Longitude: Be able to define latitude (parallels). What is 0° latitude ? What is the maximum degree of latitude ? Be able to define longitude (meridians). What is 0° longitude ? What is the maximum degree of longitude ? Be able to determine the latitude and longitude of a place on earth. Compare and contrast lines of latitude and longitude. Where on earth does the day start ? Does it get later or earlier as you move east ? Use a world map to answer these questions. What is the longitude and latitude of Iceland ? What is the longitude and latitude of Japan ? What country is located at 35° S 55° W ? What country is located at 42° S 170° E ? Composition of the Atmosphere What makes up approximately 99% of the atmosphere ? What is the difference between the good ozone and the bad ozone ? Structure of the Atmosphere 2014-15 MID-TERM EXAM REVIEW Be able to label the 2 different layers of the atmosphere and their characteristics? Atmospheric Pressure Give an example that shows that air has weight. What instrument measures atmospheric pressure ? How does altitude effect air pressure ? How does temperature effect air pressure ? How does altitude effect temperature ? Energy From the Sun What is the energy from the sun called ? What causes and effects of the Greenhouse Effect? How is it different from Climate Change? Why does the temperature decrease as you increase altitude in the troposphere ? What is the difference between the energy from the sun and the heat that the earth gives off ? List and give examples of the 3 types of heat transfer. Which heats up faster soil or water ? Which cools down faster soil or water ? Explain why. Does warmer air rise or sink ? Does sinking air create higher or lower pressure ? Does air go from high to low pressure or low to high pressure ? Using heating differences and pressure differences, explain and diagram a land/sea breezes and monsoons. Percent Error You calculate the density to be 12 grams/milliliter. The actual density is 16 grams/milliliter. What is the percent error ? Variables Be able to distinguish between independent and dependent variables. Example: Study examining if television violence increases aggression in children. Independent variable: _________________________ Dependent variable: _____________________________ Pressure Systems low pressure vs high pressure circulation of air vertical movement of air evaporation vs condensation weather associated with creation of wind cause air masses to move 2014-15 MID-TERM EXAM REVIEW Storms: characteristics of hurricanes & tornadoes the source of energy for both storms compare & contrast the two parts the USA effected what causes the damage in each Air Masses Be able to locate the place of origin for all 4 air masses on a map. You need to be able to describe the characteristics (humidity & temperature) of each air mass given its 2 letter symbol, ie: cT is dry and hot. Fronts You only need to know about cold and warm fronts. Know which front has a steep profile. Know the type of clouds, weather before, during, and after the passage of each front. Know the weather map symbols for each type of front. Station Models ** You can use the station models key ** Be able to abbreviate the weather info. Be able to read the weather off a station model. What will station R’s weather be like after the front passes? Oceans What percent of the earth's surface is covered by water? If the displaced water weighs more than the object, does the object sink or float? What are the general circulations of surface currents in the northern and southern hemispheres? Do warm surface currents flow toward or away from the equator? What about cold surface currents? Do warm surface currents generally affect east or west coasts of continents? Which coast do cold surface currents affect? 2014-15 MID-TERM EXAM REVIEW Explain how tides form and their locations. How many high and low tides occur daily? What factors create neap and spring tides? What moon phases create neap and spring tides? Moon Be able to diagram and name all 8 moon phases. Does the moon revolve around the earth clockwise or counterclockwise? Be able to diagram the locations of the sun, earth and moon during solar and lunar eclipses. What is an umbra and a penumbra? Why do we only see one side of the moon ? Using the Star Charts posted on the my web page, answer the following 3 questions: Is Ursa Major a seasonal or circumpolar constellation ? If you wanted to see Polaris in the Winter, what part of the sky would you look at ? Name a star in the constellation Canis. explain the three uses of angular measurements what is zenith what is the angle along the horizon for the following compass directions: 225°, 45°, 360°, 180° what is the angular separation for the following: HONORS only: Causes and effects of El Nino.