Terms wk1 - WordPress.com
advertisement

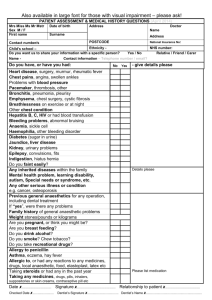
Christina Leanos Sherry Ann General Medical Terms Terms Week 1 Asthma- Is a condition disorder of respiration, characterized by bronchospasm, wheezing, and difficulty in expiration, often accompanied by coughing and a feeling of constriction in the chest. S&S- range from person to person.Shortness of breath, chest tightness or pain, trouble sleeping caused by shortness of breath, coughing or wheezing, and bouts of coughing or wheezing that are worsened by a respiratory virus such as a cold or the flu Treatment options Treatment- Exercise-induced asthma occurs during exercise. For many people, exercise-induced asthma is worse when the air is cold and dry. Have medication on you at all times and keep watch for any difficulty breathing. Medication- Inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, long-acting beta agonists, theophylline, combination inhalers that contain both a corticosteroid and a LABA. *This affects an athlete 1/10 but is easily monitored. Bronchitis- acute or chronic inflammation of the membrane lining of the bronchial tubes, caused by respiratory infection or exposure to bronchial irritants, as cigarette smoke. S&S- Cough Production of mucus (sputum), which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray or green in color Fatigue Slight fever and chills Chest discomfort Treatment- Getting more rest Taking over-the-counter pain medications Drinking fluids Breathing in warm, moist air Medication- Antibiotics, cough medicine, possibly inhaler Pneumothorax- Presence of air or gas in the pleural cavity S&S- You may feel chest pains and be short of breath.Your chest may feel constricted, and you could feel the urge to cough.Your cough would be dry, not full of phlegm.Your heart may feel like it is beating quickly.The symptoms of pneumothorax may feel similar to a heart attack or other conditions. Only a doctor can determine whether or not you are having a pneumothorax. That is why it is important to get expert medical help If you experience these symptoms, you should go to the Emergency Room in a hospital. A doctor will usually order a chest X-ray to see if you are having a pneumothorax. Treatment- Relieve the pressure on your lung, allowing it to re-expand, and to prevent recurrences. the best method for achieving this depends on the severity of the lung collapse and sometimes on your overall health. Medication- Surgery/ put a needle in to let out the excessive air. *Athlete needs to not participate and taken to the emergency room. Hemothorax- Blood in the pleural cavity. S&S- Shortness of breath, pain, anxiety, restlessness, fast heartbeat, and possibley respiratory failure. Treatment- The goal of treatment is to get the patient stable, stop the bleeding, and remove the blood and air in the pleural space. A chest tube is inserted through the chest wall to drain the blood and air. It is left in place for several days to re-expand the lung. Medication- puncture a tube in the lung and or surgery. *Athlete needs to not participate and taken to the emergency room. Pleurisy- Inflammation of the pleura, with or without a liquid effusion in the pleural cavity, characterized by a dry cough and pain in the affected side. S&S- Chest pain, cough, shortness of breath, and you may also get a fever. Treatment- identify the root cause of the problem, There are also helpful herbal remedies for pleurisy treatment available in the market. Wild cherries are known to be a tonic fruit that is used to treat pleurisy since the early times. Common herbs such as coltsfoot, buckthorn, thyme and comfrey also have some traces in records that is said to alleviate the pain felt by affected individuals. It is also noted that tilgner has expectorant and antispasmodic properties that is indicative for pleurisy treatment. However, this should not be given to pregnant patients as this may cause untoward reactions to the pregnancy. Another herbal medicine for pleurisy treatment is the use of camphor. It has properties of muscle relaxant and acts as a counter irritant promoting blood flow and distribution. Medication- Pleurisy treatment may involve the use of antibiotics once the infection is confirmed from laboratory results. It is necessary to have confirmation from the laboratory of pleuritis to identify if it is bacterial in nature. If the causative agent is viral in nature, antibiotic therapy would be regarded as null and ineffective. It is also necessary to undergo chest tube draining once there is an increased pressure due to pleural fluid accumulation. It is done by inserting local anesthesia to the site and placing the chest tubes for suction. Influenza- an acute, commonly epidemic disease, occurring in several forms, caused by numerous rapidly mutating viral strains and characterized by respiratory symptoms and general prostration S&S- Fever over 100 F (38 C), aching muscles, especially in your back, arms and legs, chills and sweats. My also have, headache, dry cough fatigue and weakness, nasal congestion. Treatment- rest Medications- antibiotics *Stay home to prevent other athletes from getting sick. Upper respiratory infection- inflamamation of your sinuses located around your nose. S&S- runny nose, sore throat, and coughing Treatment- rest and stay in bed Medication- antibiotics *Stay home to prevent other athletes from getting sick. If it does not go away with in a week seed a doctor. Tuberculosis- an infectious disease that may affect almost any tissue of the body, especially the lungs, caused by the organism. S&S- cough, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, fever, night sweats, chills, loss of appetite. Treatment- take medications for about 6 months. Medication- TB drug, resistant strain, will require several drugs at once. Common cold- a mild viral infection of the upper respiratory tract, characterized by sneezing, coughing, watery eyes, nasal congestion, sore throat, etc. S&S- runny nose, itchy or sore throat, cough, congestion, slight body aches, sneezing, watery eyes, low fever, mild fatigue. Treatment- drink lots of fluids, get some rest, use saline nasal drops. Medication- zinc, vitamin c, Echinacea *Stay home rest and to avoid from getting others sick. Tetanus- an infectious, often fatal disease caused by a specific bacterium that enters the body through wounds and characterized by respiratory paralysis and tonic spasms and rigidity of the voluntary muscles, especially those of the neck and lower jaw. Compare lockjaw. S&S- spasms, stiffness in jaw MM, stiffness of neck, difficulty swallowing p! all over body with spasms lasting for min. Treatment- no cure for tetanus Medication- Antitoxin, antibiotics, vaccine sedatives, and other drugs. *Cleaning the wound essential to prevent growth of tetanus. Keep from touchy sports. Hyperventilation- a condition characterized by abnormally prolonged and rapid breathing, resulting in decreased carbon dioxide levels and increased oxygen levels that produce faintness, tingling of the fingers and toes, and, if continued, alkalosis and loss of consciousness. S&S- Bloating, burping, passing excessive gass, fainting, dizziness, weakness, confusion, agitation, seeing images.. Treatment- goal is to try to raise carbon dioxide levels in blood Medication- Benzodiazepines are effective in reducing stress that may provoke hyperventilation syndrome (HVS) and are thought to reset the CNS response to a variety of "panicogens." *Athletes need to be careful with how much activity they are doing.. Hay fever- type of allergic rhinitis affecting the mucous membranes of the eyes and respiratory tract, affecting susceptible persons usually during the summer, caused by pollen of ragweed and certain other plants. S&S- Runny nose, nasal congestion, watery or itchy eyes, itchy nose, sinus pressure Treatment- rest Medication- Antibiotics *Athlete needs to rest and pulled out of some fast activities.