Name: : :___ DNA Questions ANSWER KEY Use the following
advertisement
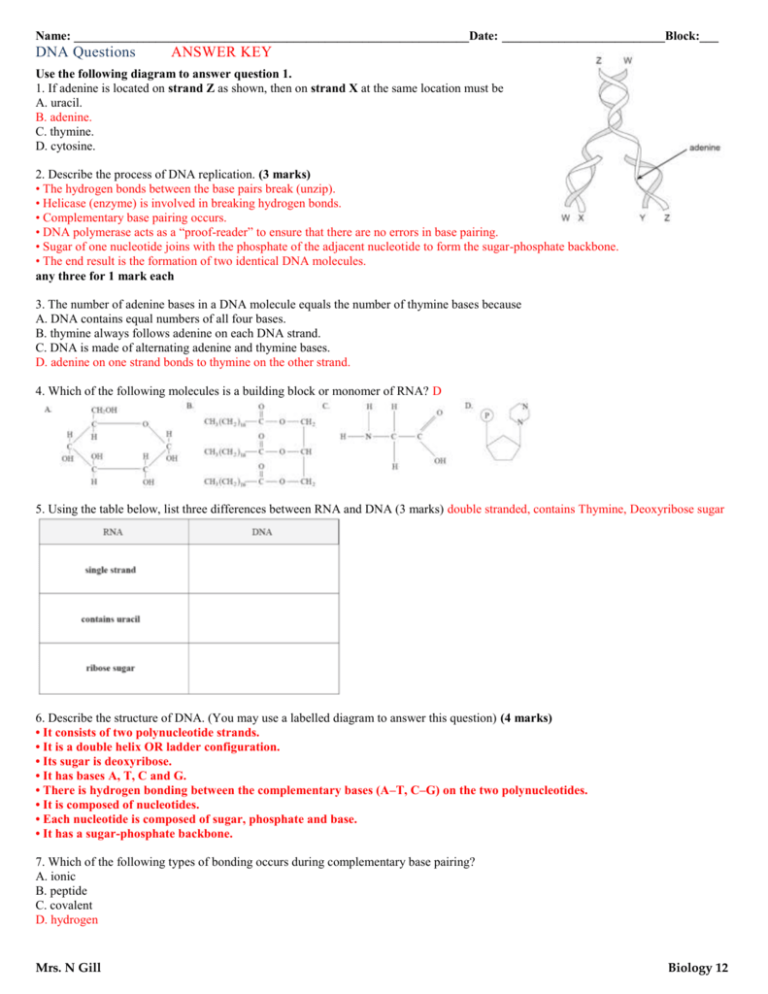
Name: _______________________________________________________________Date: __________________________Block:___ DNA Questions ANSWER KEY Use the following diagram to answer question 1. 1. If adenine is located on strand Z as shown, then on strand X at the same location must be A. uracil. B. adenine. C. thymine. D. cytosine. 2. Describe the process of DNA replication. (3 marks) • The hydrogen bonds between the base pairs break (unzip). • Helicase (enzyme) is involved in breaking hydrogen bonds. • Complementary base pairing occurs. • DNA polymerase acts as a “proof-reader” to ensure that there are no errors in base pairing. • Sugar of one nucleotide joins with the phosphate of the adjacent nucleotide to form the sugar-phosphate backbone. • The end result is the formation of two identical DNA molecules. any three for 1 mark each 3. The number of adenine bases in a DNA molecule equals the number of thymine bases because A. DNA contains equal numbers of all four bases. B. thymine always follows adenine on each DNA strand. C. DNA is made of alternating adenine and thymine bases. D. adenine on one strand bonds to thymine on the other strand. 4. Which of the following molecules is a building block or monomer of RNA? D 5. Using the table below, list three differences between RNA and DNA (3 marks) double stranded, contains Thymine, Deoxyribose sugar 6. Describe the structure of DNA. (You may use a labelled diagram to answer this question) (4 marks) • It consists of two polynucleotide strands. • It is a double helix OR ladder configuration. • Its sugar is deoxyribose. • It has bases A, T, C and G. • There is hydrogen bonding between the complementary bases (A–T, C–G) on the two polynucleotides. • It is composed of nucleotides. • Each nucleotide is composed of sugar, phosphate and base. • It has a sugar-phosphate backbone. 7. Which of the following types of bonding occurs during complementary base pairing? A. ionic B. peptide C. covalent D. hydrogen Mrs. N Gill Biology 12 Name: _______________________________________________________________Date: __________________________Block:___ Use the following diagram to answer questions 8 and 9. 8. Which of the following correctly identifies the parts labelled W, X, Y and Z? C 9. The parts labelled X, Y and Z in the diagram above make up A. a fatty acid. B. a nucleotide. C. an amino acid. D. a monosaccharide. 10. One DNA strand is attached to another DNA strand by A. hydrogen bonds between the bases. B. hydrogen bonds between the sugars. C. covalent bonds between the sugars and bases. D. covalent bonds between the sugars and the phosphates. 11. Using the chart below, contrast DNA and mRNA. (3 marks: 1 mark for each contrasting pair) 12. The symbols shown below represent parts of a DNA molecule. Construct the DNA molecule by redrawing the parts to make a complete section. (4 marks) two strands (1 mark) correct base pairing (1 mark) sugar-phosphate backbone (1 mark) correct location of hydrogen bonding (1 mark) (Number of H bonds not critical to receiving mark.) 13. In a solution of nucleotides made from a ground-up segment of DNA, adenine makes up 33% of the solution. What percentage of the solution would be guanine? A. 17% B. 33% C. 34% D. 67% Mrs. N Gill Biology 12 Name: _______________________________________________________________Date: __________________________Block:___ Use the following diagram to answer question 14. 14. Describe replication of this molecule. (3 marks) • Unzipping, the breaking of hydrogen bonds between the bases that run down the centre of the DNA molecule, splits the two strands apart. • Complementary base pairing occurs to bond new nucleotides into place along each strand. • DNA polymerase acts as a proofreader. • The adjacent nucleotides join together to form new sugar-phosphate backbones. • The result is two identical copies of DNA. • Two semiconservative copies are made. 15. Which of the following correctly contrasts RNA and DNA? B Use the following information to answer question 16. 16. Which of the following is the correct sequence to describe DNA replication? A. 12 34 B. 2341 C. 312 4 D. 4 321 17. Complete the table below by giving the differences between DNA and RNA. 18. Which of the following is an example of complementary base pairing? A. guanine—uracil B. adenine—cytosine C. cytosine—thymine D. cytosine—guanine Mrs. N Gill Biology 12 Name: _______________________________________________________________Date: __________________________Block:___ 19. Which of the following is a characteristic of replication? A. Sugar joins to phosphate groups, producing new DNA. B. Anticodons bond to codons by complementary base pairing, producing proteins. C. Adenine bonds with thymine and cytosine bonds with guanine, producing mRNA. D. Adenine bonds with uracil and cytosine bonds with guanine, producing new DNA. 20. What is meant by the term “unzipping” as it occurs during replication? A. denaturing of the DNA molecule B. formation of temporary bonds between mRNA and tRNA C. breaking the bonds between the bases of DNA nucleotides D. breaking the bonds between the sugar and phosphate molecules Use the following diagram to answer question 21. 21. Which of the following correctly identifies the parts labelled W, X, Y and Z? D 22. What is found in RNA but not in DNA? A. uracil B. thymine C. deoxyribose D. sugar-phosphate backbone Use the following diagram to answer question 23. 23. Where in the cell does this process take place? A. in the nucleus B. in the ribosome C. in the Golgi body D. in the rough endoplasmic reticulum 24. Which of the following are characteristics of DNA but not of RNA? B 25. Which of the following represents the structure of a nucleotide? A. Salt – lipid – base. B. Glucose – glucose – glucose. C. Phosphate – sugar – nitrogenous base. D. Amino acid – amino acid – amino acid. 26. a) Where in the cell does DNA replication occur? (1 mark) • In the nucleus. • In the mitochondria. any one for 1 mark b) What is the purpose of DNA replication? (1 mark) • To pass on identical genetic information to “daughter cells”. (1 mark) c) Which base is found in DNA but not in RNA? (1 mark) • Thymine. (1 mark) 12. At which of the following cell structures would adenine bond with thymine but not uracil? A. nucleus B. ribosomes C. Golgi bodies D. endoplasmic reticulum Mrs. N Gill Biology 12







