Slideshow Script Draft
advertisement

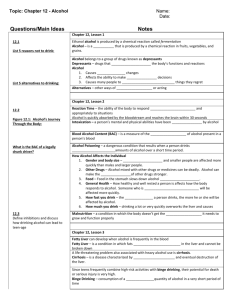
Title Slide (Image) Title Slide Text: “How Alcohol Effects the Human Body” (Image One) (Image One) In this day and age, it is not uncommon to find alcohol at social events. People enjoy drinking alcohol. Many often consume it with the full intention of becoming intoxicated because alcohol indulgence gives off a euphoric feeling that most people enjoy. Most people that drink do not, however, stop to think what alcohol is doing to their body to give off that “euphoria.” Whether you party a little (Image Two), or party a lot (Image Three),(Image Four) alcohol seriously impairs and damages the body. Image Two (Image Five) Most people are aware of the symptoms of someone who is “drunk.” People tend to have slurred speech, a lack of coordination, and a higher likelihood of making fools of themselves. But how does alcohol do this? (Image Six) According to Healthguidance.org, alcohol is mainly absorbed in the small intestine. This defends the statement that one gets drunk faster if they haven’t eaten. If there is no food in the way of the alcohol, it is going to get absorbed faster. From the small intestine, the alcohol enters the bloodstream, where it will travel directly to the organ that requires the most blood flow and oxygen: the brain. Once it hits the brain, symptoms of intoxication begin to occur. (Image Seven) Image Three The cerebral cortex is the first part to be affected. This is what makes people more talkative and outgoing. The hippocampus, which controls memory and emotion, is the next part of the brain to be affected. If one was happy before he began drinking, he is even happier now. If he was depressed to begin with, he is even worse. Memories probably will not form properly at this Image Four stage, and this explains why some parts of a night of heavy drinking are more difficult to remember. The cerebellum is the next to be affected. This is the stage where one begins to slur speech and have difficulty walking straight. If drinking occurs after this stage, eventually the alcohol will work its way back to the medulla, which attaches directly to the brainstem. At this point, higher order functions are at stake, such as breathing and staying conscious. If a person Image Five reaches this point, they will require stomach pumping, or they could face serious injury or death. (Image 8) Remember that alcohol is a depressant. Notice in this brain scan from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism the lack of color in the intoxicated brain images. This lack of color is actually a lack of functioning due to slowed metabolism. After the alcohol leaves the system, the brains will return to normal functioning. However, if one continues to binge drink on a regular basis, the entire anatomy of the brain will Image six change. (Image 9) Compared to a normal 43 year old’s brain, the 43 year old alcoholic’s brain is drastically smaller in size. According to LifeSpan.org, neurotransmitters and the blood flow to the frontal lobe of the brain are affected by long-term alcohol use. Eventually, feel-good neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine are only released during alcohol consumption, which explains why alcoholics need to drink to improve their mood. After chronic use, alcohol will no longer trigger these impulses. (Image Ten) Not only is the brain seriously affected by long term alcohol abuse. Several other parts of the body also suffer. According to the American Heart Association, there are several cardiovascular risks that arise in alcoholics such as an increase of triglycerides (or Image Seven fat) in the blood, high blood pressure, and heart failure. Several cancers may also arise from alcoholism. The biggest problem with drinking is disease of the liver, the organ that has to filter all of the alcohol consumed. Alcoholic liver disease starts out with excessive fat buildup on the liver, making it much larger and yellowish in appearance. Activeforever.com states that this is the most common disease found among problem drinkers. This is reversible if problem drinking ceases, but it can turn into alcoholic hepatitis if drinking continues. Alcoholic Hepatitis defined by Activeforever.com is where the liver becomes inflamed, scar tissue forms, and cells begin to die Image Eight off. After ten years or more of problem drinking, this will develop into Alcoholic Cirrhosis, which is where the liver is no longer able to function properly. This damage is permanent, and people often die from this if their liver shuts down completely. This is an actual image of what a human liver looks like in all stages. Notice how the healthy liver is small, and brown in appearance. The middle liver is yellow due to the fat buildup. The cirrhosis liver is twice the Image Nine size of the first two, and resembles an overcooked piece of steak more than a human organ. (Image 13) Excessive alcohol consumption is dangerous to an individual, but it is even more dangerous when the individual is carrying a child. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome is the most damaging effect to a single individual in the shortest amount of time. Development of a fetus in the womb is critical in every stage, and chemical imbalances can easily damage the development of the unborn child, and most damage is irreversible. (Image 14) The Centers for Disease Control state that the symptoms of fetal alcohol syndrome are poor coordination, learning disabilities, speech and language difficulties, overall poor body development and abnormal facial features (Image 15). Fetal alcohol syndrome is 100% preventable if the mother Image ten abstains from alcohol throughout the entire pregnancy. The saddest part of FAS is that these children will never have a chance at a normal life. Most will need constant care for their entire duration of their life. They will face ridicule and poor self-esteem all because their mother chose to drink while she was pregnant. (image 16) I have now discussed how alcohol consumption affects your short-term and longterm health. While it is okay to drink occasionally in moderation, it is never okay to excessively binge. It is not safe for your health or the health of others. (For More Information Slide) For more information on how drinking affects your health, visit www.medicinenet.com and search alcohol. (THANK YOU slide) Thank you. Image eleven Image Twelve Image 13 Image 14 Image 15 Image 16 (For More Information Slide) (Thank you slide) Picture Bibliography kemc817 (Blog Author). (March 4, 2010). [Untitled photograph of a party in a bathroom], Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://kemc817.wordpress.com/page/2/). (November 30, 2009). [Untitled photo of people drinking champagne], Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://www.newdawnbeauty.com/wordpress/) . Josh (Photo Submitter). [Untitled photo of people playing 78-cup Beer Pong], Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://onlinebeerpong.com/random-beerpong/78-cup-beer-pong/). (July 23, 2010). [Untitled photo of person outlined by beer bottles], Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://fortwaynerealestate.wordpress.com/). Lattin, Pace (Blog Author). (April 15, 2010). [Untitled illustration of Homer Simpson and Barney in Moe’s Tavern], Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://industrypace.com/frontpage/2010/04/1 5/are-relationships-dead.html). (n.d.) [Picture of alcohol & a person’s brain]. Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://www.lifespan.org/adam/graphics/imag es/en/17020.jpg) (n.d.) [Untitled picture of the effects alcohol has on your brain]. Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://www.toosmarttostart.samhsa.gov/tea chin/teachingguide/worksheet1.aspx) (n.d.) [Untitled Picture of an alcoholic brain compared to a normal brain]. Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://www.smart- kit.com/s545/your-brain-on-alcohol/) December 2008. [Untitled picture of an intoxicated brain]. Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/Resources/Graph icsGallery/Neuroscience/Pages/brain_activit y.aspx) (n.d.) [Untitled picture of how alcohol affects the body]. Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://www.herdaily.com/health/4134/alcoh ol-and-its-harmful-effects-when-had.html) March 8, 2000 [Picture of how alcohol affects the liver]. Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://www.bettycjung.net/Wellindex2.htm) 2003. [Normal Liver, Fatty Liver, Cirrhosis]. Wadsworth. Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://fitafter40vancouver.blogspot.com/20 11_01_01_archive.html) (n.d.) [Untitled picture of mom and baby drinking]. Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://www.wyco- rpc.net/training.htm) (n.d.) [Untitled picture of young children with FAS]. Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://www.alcoholtaxincrease.org/braindra in.htm) (n.d.) [Prenatal alcohol exposure causes brain damage]. Retrieved April 6, 2011 from: URL (http://www.alcoholtaxincrease.org/braindra in.htm)