Exploring Data Distributions: Shapes, Centers, and Spreads
advertisement

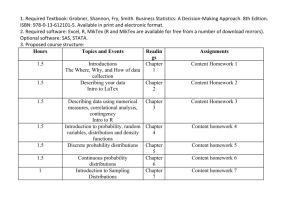
Unit 2 Patterns of Data Lesson 1 Exploring Distributions Investigation 1 Shapes of Distributions Name:__________________________________________________ 1) As part of an effort to study the wild black bear population in Minnesota, Department of Natural Resources staff anesthetized and then measured the lengths of 143 black bears. (The length of a bear is measured from the tip of its nose to the tip of its tail.) The following dot plot (or number line plots) show the distributions of the lengths of the male and the female bears. a. Compare the shapes of the two distributions. When asked to compare, you should discuss the similarities and differences between the two distributions, not just each one separately. i. Are the shapes of the two distributions fundamentally alike or different? ii. How would you describe the shapes? b. Are there any lengths that fall outside the overall pattern of either distribution? c. Compare the centers of the two distributions. d. Compare the spreads of the two distributions. 2) When describing a distribution, it is important to include information about its shape, its center, and its spread. a. Describing shape. Some distributions are approximately normal or mound-shaped, where the distribution has one peak and tapers off on both sides. Normal distributions are symmetric – the two halves look like mirror images of each other. Some distributions have a tail stretching towards the larger values. These distributions are called skewed to the right or skewed to the larger values. Distributions that have a tail stretching towards the smaller values. These are called skewed to the left or skewed to the smaller values. A description of shape should include whether there are two or more clusters separated by gaps and whether there are outliers. Outliers are unusually large or small values. How would you use the idea of skewness and outliers to describe the shape of the distribution of lengths of female black bears in Problem #1. b. Describing center. The measure of center that you are most familiar with is the mean (or average). How could you estimate the mean length of the female black bears? c. Describing spread. You may already know one measure of spread, the range, which is the difference the maximum and minimum value: range = maximum value – minimum value What is the range of lengths of the female black bears? d. Use these ideas of shape, center, and spread to describe the distribution of lengths of the male black bears. 3) In the late 1940s, scientists discovered how to create rain in times of drought. The technique, dropping chemicals into clouds, is called “cloud seeding.” The chemical cause ice particles to form, which become heavy enough to fall out of the clouds as rain. To test how well silver nitrate works in causing rain, 25 out of 50 clouds were selected at random to be seeded with silver nitrate. The remaining 25 clouds were not seeded. The amount of rainfall from each cloud was measured and recorded in acre-feet (the amount of water to cover an acre 1 foot deep). The results are given in the following dot plots. a. Describe the shapes of these two distributions. b. Which distribution has a larger mean? c. Which distribution has a larger spread in the values? d. Does it appear that the silver nitrate was effective in causing more rain? Explain.