Immuno Revision Notes
advertisement
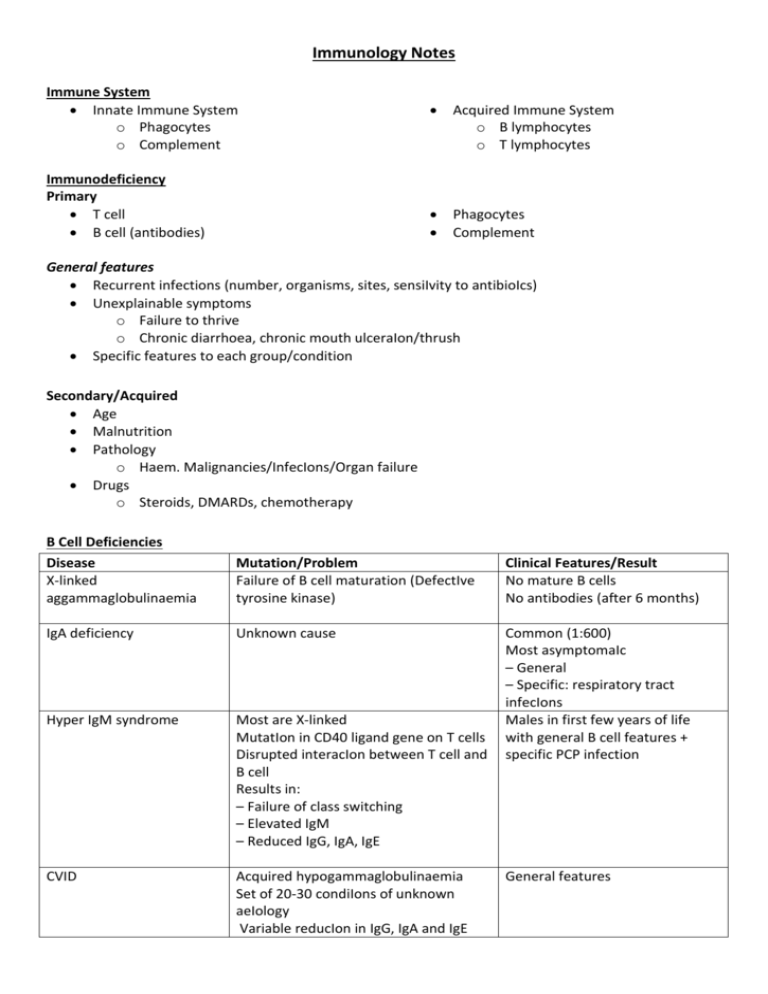
Immunology Notes Immune System Innate Immune System o Phagocytes o Complement Immunodeficiency Primary T cell B cell (antibodies) Acquired Immune System o B lymphocytes o T lymphocytes Phagocytes Complement General features Recurrent infections (number, organisms, sites, sensiIvity to antibioIcs) Unexplainable symptoms o Failure to thrive o Chronic diarrhoea, chronic mouth ulceraIon/thrush Specific features to each group/condition Secondary/Acquired Age Malnutrition Pathology o Haem. Malignancies/InfecIons/Organ failure Drugs o Steroids, DMARDs, chemotherapy B Cell Deficiencies Disease X-linked aggammaglobulinaemia Mutation/Problem Failure of B cell maturation (DefectIve tyrosine kinase) Clinical Features/Result No mature B cells No antibodies (after 6 months) IgA deficiency Unknown cause Hyper IgM syndrome Most are X‐linked MutatIon in CD40 ligand gene on T cells Disrupted interacIon between T cell and B cell Results in: – Failure of class switching – Elevated IgM – Reduced IgG, IgA, IgE Common (1:600) Most asymptomaIc – General – Specific: respiratory tract infecIons Males in first few years of life with general B cell features + specific PCP infection CVID Acquired hypogammaglobulinaemia Set of 20‐30 condiIons of unknown aeIology Variable reducIon in IgG, IgA and IgE General features Investigations Lymphocyte counts + serum immunoglobulins Flow cytometry Measure antibody response to known pathogens (tetanus, H.influenza, Strep. Pneumoniae) Management Ig replacement – i.v. every 3‐4 weeks Immunisation is not effective (except IgA) T cell deficiencies General PresentaIon Infections o Viral, fungal, mycobacterial Disease DiGeorgeʼs Syndrome Bare L syndrome Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome Malignancy Autoimmunity Mutation/Problem Chromosomal deleIon – 22q11 Pathology – Failure of thymic development – Immunodeficiency • Reduced T cells • Normal/increased B cells • Reduced anIbody response • Immunodeficiency can improve with age Deficiency of CD4 cells – Lack of expression of MHC Class II – Normal B cells, reduced IgG/IgA MutaIon in WASP gene X‐linked Ataxic telangiectasia MutaIon in ATM gene Autosomal recessive SCID T cell +/‐ B cell problem 2 important types: X‐linked • Mutation of IL‐2 receptor (gamma chain) • Reduced T cells/Normal B cells Autosomal recessive • Adenosine deaminase deficiency • Reduced T and B cells Phagocyte Deficiencies General Presentation Recurrent deep bacterial + fungal infecIons o Staph. Aureus o Candida albicans o Aspergillus fumigatus Clinical Features/Result Cardiac anomalies (Fallot’s) Abnormal facies (low set ears/ fish mouth/high forehead) Thymic hypoplasia (T cell lymphopaenia) Cleft Palate Hypoparathyroidism (hypocalcaemia) General features in infancy AssociaIon with primary sclerosing cholangitis Immunodeficiency + Thrombocytopenia & Eczema Lymphoma at a young age Immunodeficiency + Ataxia, Nystagmus & Telangiectasia Lymphomaa/leukaemia at a young age Infants present by 3 months - Persistent infections - Failure to thrive Graft vs. host disease – Funny rashes – Colonisation of bone marrow with maternal lymphocytes Poor response to antibiotics Disease Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency (LAD) Mutation/Problem Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD) Granuloma formation Kostmannʼs syndrome (KS) Severe congenital neutropenia Cyclic neutropenia Episodic neutropenia Investigations Neutrophil count Presence of leukocyte adhesion markers Treatment Conservative o Manage infections aggressively o Vaccination + septrin/itraconazole o Surgical drainage of abscess Clinical Features/Result Delayed separation of the umbilical cord No adhesion of phagocytes High neutrophils Treat with IFN‐gamma No oxidative killing Normal or high neutrophil count No granulocyte precursors No neutrophils, abnormal NBT Nitric‐blue test of oxidaIve killing (NBT test) FormaIon of pus Definitive o BMT o IFN therapy in chronic granulmatous disease Complement deficiencies Allergy Type Type I Type II Type III Type IV Mechanisms IgE-mediated hypersensitivity IgG/IgM reactive with self antigen Immune complexmediated damage T-cell mediated damage/delayed hypersensitivity Examples Allergies, Asthma Grave’s disease, Goodpastures Syndrome, Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia Lupus, Polyarteritis Nodosa Rheumatoid, IDDM, MS, Transplant rejection Clinical Features Primary o Skin changes o Smooth muscle contraction (lungs/gut) o Mucus secretion (lungs) o Vascular permeability (shock) Delayed o Onset 2‐24 hours after exposure, o Lasts many days o Inflammatory cell infiltration (associated tissue damage) Investigations RAST o Quantity of IgE to proposed antigen o Less sensitive and specific cf. skin prick o Useful for dermatographism; Hx of anaphylaxis; cannot stop antihistamine Mast Cell Tryptase o During an acute episode (1‐6 hours after) Skin Prick Testing o Gold standard test o Rapid; cheap; sensitive; specific o Safe (relatively) o Anti‐histamines stopper prior to testing o Ineffective in food allergies Management Avoidance of allergen Supportive (bronchodilators/adrenaline/fluids) Drugs o Block MC activation – sodium chromoglycate o H1‐receptor antagonists – antihistamines o Anti‐inflammatory – corticosteroids o Leukotriene receptor antagonist ‐montelukast Allergen specific immunotherapy Autoimmunity Hypersensitivity Inappropriate immune reaction that produces Issue damage on exposure to an antigen Autoimmune Disease Immune reaction produces Issue damage due to a reaction against self‐protein Breakdown in self‐tolerance Central tolerance – failure to delete autoreactive T cells in thymus/ B cells in bone marrow Peripheral tolerance – reactivation of weakly autoreactive T/B cells, Inflammation, infection, tissue damage Autoimmune Disease Organ Specific Non-Organ Specific Hashimoto’s Graves’ Pernicious anaemia Addison’s disease Lupus Scleroderma Rheumatoid ANA’s ANA dsDNA SLE Autoimmune Disease’s Disease SLE ENA Ro, La SLE, Sjogrens (Cross placenta) Sm SLE (v. Specific) RNP MCTD, SLE Jo-1 Myositis Anti-centromere CREST Anti-SCL70 Diffuse Scleroderma Anti-CCP Rh. Arthritis Auto-antibodies Anti-sm Anti Ro Anti-LA Anti-dsDNA Drug-induced lupus Anti-Histone Sjogrenʼs Syndrome Ant-LA Anti-Ro Anti-CCP Anti-SCL 70 RA Diffuse Scleroderma Limited Scleroderma/CREST Anti-centromere Dermatomyositis/ polymyositis Wegnerʼs granulomatosis Pernicious anaemia Anti-Jo-1 Features F:M = 9:1 Serositis, Oral ulcers, Arthritis, Photosensitivity, Blood changes, Renal involvement, ANA, Immunological changes, Neuro stuff, Malar rash, Discoid rash – Procainamide – Hydralazine – Isoniazid – Clindamycin CREST + Pulmonary fibrosis, Renal disease, Polyarthritis, Myopathy/muscle atrophy Calcinosis, Raynauds Phenomenon, Osephageal dismotility, Sclerodactyly, Telangectasia C-ANCA 90% anti‐parietal cell antibodies Autoimmune attack on parietal cells - atrophic gastritis & lack of intrinsic factor 50% anti‐IF antibodies Graveʼs disease Hashimotoʼs thyroiditis Anti‐TSH receptor antibodies Anti‐thyroid eroxidase/ anti‐thyroglobulin AB Anti‐microsomal Anti‐thyroglobulin Anti‐peroxidase Mixed Connective tissue Anti-RNP disease Anti-phospholipid Anti-Cardiolipin syndrome Autoimmune Haemolytic Anaemia Addisons Disease ↓serum vit. B12 Associations: other autoimmune disease, gastric adenocarcinoma Low TSH Elevated free T4 (if T4 normal – consider T3) Autoimmunne destruction of thyroid Diffuse lymphocyte infiltraIon High TSH Firm goitre → atrophy Autoantibodies →RBC haemolysis Features of haemolysis Raised unconjugated bilirubin ↓ haptoglobin ↑LDH ↑ urinary urobilinogen Reticulocytes Positive DAT test ↑Potassium ↓Sodium Vasculitides Inflammation of blood vessels, cause is largely unknown Disease Temporal arteritis (Giant cell arteritis) Vessels Affected Large Takayasu’s Large Polyarteritis nodosum Medium Kawasaki’s Medium Wegener’s Small Features Affects carotids and temporal arteries 2:1 (F:M), > 50yrs Headache and tender over scalp “combing” Risk of blindness Affects aorta and vessels coming off it Asian women 20s – 30s Difference in blood pressure between arms Affects many organ system Symptoms are often nonspecific Classically affects renal vessels and coronary arteries Affects Children ? secondary to infection - Fever for more than 5 days -Erythema/desquamation of palms and soles - Cervical lymphadenopathy - Conjunctivitis - Changes to lips/oral cavity = dry, swollen, strawberry tongue - Erythematous rash Midline structures cANCA +ve Churg‐Strauss Small Microscopic polyangitis Small Epistaxis, Pulmonary pain, saddle nose nodules, haemoptysis, Glomerulonephritis Late onset asthma, eosinophilia Primarily the lung Gut, kidney or nerve involvement cANCA or pANCA +ve Huge number of systems affected pANCA +ve Mononeuritis Multiplex, Haemoptysis, Renal failure, Skin rash Transplantation Hyperacute rejection Acute cellular rejection Acute vascular rejection Chronic allograft rejection Timeframe Minutes to hours Pathophysiology Pre‐existing anti‐donor antibodies Massive inflammatory vasculitis→ graft thrombosis Days to 1 month Recognition of CD4 cells → activation of CD4 cells → type IV hypersensitivity response Unwell, reduction in graft function, pain/tenderness 1‐2 weeks Mediated by antibodies post‐transplant Results in vasculitis + thrombosis > 30 days Major cause of graft loss post‐transplant affects all types of solid organ transplant Risk factors: - Repeated acute rejection episodes - Pro‐atherogenic factors - Drug toxicity - Non‐compliance with medication Therapeutics in Immunology Class Examples Steroids Prednisolone Hydrocortisone Dexamethasone Antiproliferative agents Inhibitors of cell signalling Azathioprine Cyclophosphamide Mycophenylate mofetil Ciclosporin Tacrolimus Treatment None once it occurs Blood groups and HLA to detect pre‐existing antibodies Partially treated with immunosuppressive therapy Immunosuppresion Manage atherogenic risk Drugs with low toxicity Effects Side effects ↓ Phagocyte recruitment ↑WCC (neutrophils) Lmyphocyte SequestraIon, cytotoxicity, reduced cytokine gene expression Block Purine synthesis (T>B) Blocks DNA replication (B>T) Cushingoid sx Danger of marrow suppression Haemorrhagic cystitis NephriIs Diabetes Gingival hypertrophy Antibodies to cell surface antigens OKT3 (anti-CD3 antibody) Anti-IL2 antibody (CD25) Anti-cytokine agents Infliximab Etanercept Adalimumab OKT3 - prevention and treatment of solid organ transplant rejection CD25 - rejecIon prophylaxis in transplantaIon Infliximab - murine anti‐TNF antibody Etanercept - human soluble TNF receptor Adalimumab - human anti‐TNF antibody