Below are ten sample prompts that you may be asked to address on
advertisement

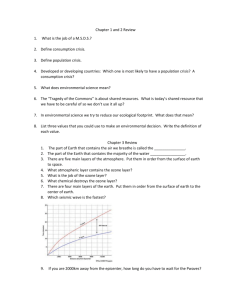
Below are ten sample prompts that you may be asked to address on the final exam. 5 of the short answer questions and 1 of the essays will be on the test. Describe the trophic levels in a typical ecosystem. Discuss the flow of energy through the ecosystem, the relationship between the different trophic levels, and the factors that limit the number of trophic levels. If global warming increases average temperatures on Earth by 4 degrees Celsius in this century, predict which biome is most likely to replace tundra in some locations as a result. Explain your answer. Explain why a constant rate of increase for a population produces an exponential growth curve. Also, explain why this growth could not continue indefinitely and must be replaced by a logistic growth curve. Describe or Draw the shapes of these graphs Living organisms play an important role in the recycling of many elements within an ecosystem. Discuss how various types of organisms and their biochemical reactions contribute to the recycling of either carbon or nitrogen in an ecosystem. Include in your answer one way in which human activity has an impact in the nutrient cycle you have chosen. Describe two hypotheses that explain why food chains are usually short, and state a key prediction of each hypothesis. Summarize key differences between allopatric and sympatric speciation. Which type of speciation is more common, and why? Describe the process of speciation. Include in your discussion the factors that may contribute to the maintenance of genetic isolation. Explain how the following statement is inaccurate: “Antibiotics have created drug resistance in MRSA” Write an essay responding to the following: Charles Darwin proposed that evolution by natural selection was the basis for the difference that he saw in similar organisms as he traveled and collected specimens in South America and on the Galapagos Islands. a. Explain the theory of evolution by natural selection as presented by Darwin. b. Each of the following relates to an aspect of evolution by natural selection. Explain three of the following. i. Convergent evolution and the similarities among species (ecological equivalents) in a particular biome ( for example, tundra, taiga, etc) ii. Natural selection and the formation of insecticide resistant insects or antibiotic resistant bacteria. iii. speciation and isolation Write an essay responding to the following: Compared with other terrestrial biomes, deserts have extremely low productivity. (a) Discuss how temperature, soil composition, and annual precipitation limit productivity in deserts. (b) Describe a four-organism food chain that might characterize a desert community, and identify the trophic level of each organism. 52. Explain why a constant rate of increase for a population produces an exponential growth curve. Also, explain why this growth could not continue indefinitely and must be replaced by a logistic growth curve. Describe or Draw the shapes of these graphs. 53. Describe two hypotheses that explain why food chains are usually short, and state a key prediction of each hypothesis. 54. Summarize key differences between allopatric and sympatric speciation. Which type of speciation is more common, and why? 55. Explain how the following statement is inaccurate: “Antibiotics have created drug resistance in MRSA” 56. Write an essay responding to the following: Charles Darwin proposed that evolution by natural selection was the basis for the difference that he saw in similar organisms as he traveled and collected specimens in South America and on the Galapagos Islands. a. Explain the theory of evolution by natural selection as presented by Darwin. b. Each of the following relates to an aspect of evolution by natural selection. Explain three of the following. i. Convergent evolution and the similarities among species (ecological equivalents) in a particular biome ( for example, tundra, taiga, etc) ii. Natural selection and the formation of insecticide resistant insects or antibiotic resistant bacteria. iii. speciation and isolation