Rectifier Lab
advertisement

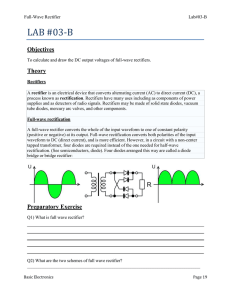
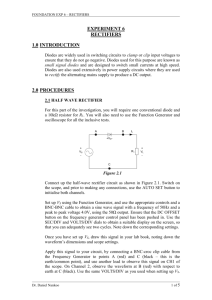
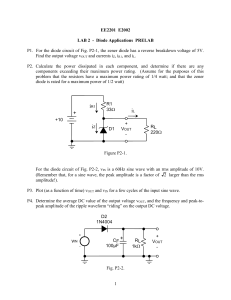
Diodes & Power Supplies Hazard Identification: AIMS 1. To construct and observe a half wave rectifier 2. To construct and observe a full wave bridge rectifier 3. To observe the effect of a simple capacitor output filter 4. To construct and observe a simple zener regulator 5. To use oscilloscope DC and AC input coupling as appropriate APPARATUS Rectifier module: diodes 470 resistor 5W 470 F capacitor Diode board: 8.2 V zener diode 4x resistors Also: Variac transformer RMS volt meter Oscilloscope Jumper leads EXPERIMENTAL Set the output of the Variac to 20Vpk. What value RMS voltage is this? __________Vrms PART A: Half-wave rectifier 1. Using one rectifier diode, construct a half-wave rectifier as shown. 0V 470R Vout Page 1 2. Use an oscilloscope to observe the output waveform. Ensure that the scope input coupling is set to DC. Note. If the peak value is greater than 20V, recheck the wiring. Do not proceed until the circuit is wired correctly. Sketch the output waveform, (and record peak values and the frequency). Channel 1 sensitivity: ......... V/div Time base: ................. ms/div PART B: Half-wave rectifier + reservoir capacitor 1. 2. Add a 470 F capacitor in parallel with the load resistor. Don't forget about polarity!! + 0V 470R 470 F Vout Observe the output waveform with an oscilloscope. Superimposed on the sketch in Part A/2, sketch the observed waveform. Page 2 3. "Zoom up" the ripple by changing the input coupling to AC and increasing the sensitivity. Carefully sketch the ripple waveform, and record the peak to peak amplitude. Channel 1 sensitivity: ......... V/div Time base: ................. ms/div PART C: Full-wave bridge rectifier 1. Construct the full-wave bridge rectifier circuit shown below: + 470R Vout 0V _ 2. Ensure the scope coupling is set back to DC!! Sketch the output waveform, recording peak values and the frequency. Channel 1 sensitivity: ......... V/div Time base: ................. ms/div Page 3 PART D: Full-wave rectifier + reservoir capacitor + Add a 470 F capacitor in parallel with the load resistor. 1. + 470 Vout 0V _ 2. Observe the output waveform with an oscilloscope. On the same sketch in Part C/2, sketch the observed waveform. 3. As in part B, use AC coupling to "zoom in" to observe the ripple. Examine the ripple waveform, and record the peak to peak amplitude. Vripple(p-p) = .............. PART E: Using a Zener Diode as a Simple Regulator 1. 2. Turn off the power to your circuit. Change the input AC voltage to 10 Vrms. Remove the 470 load resistor and construct the zener shunt regulator as shown below. Use the 8.2 V zener. DON'T FORGET TO INCLUDE THE 150 VOLTAGE DROPPING RESISTOR 3. To the output of this supply, connect a load resistor (combination of resistors; minimum 400) 4. 150R R load Full Wave Bridge Rectifier Complete the following table. (Use the scope to read Vout.) Table 1. Zener regulated supply: load regulation R load V out (pk-pk) Page 4 5. Present these results as a graph of Vout versus RL (load regulation). Page 5 PROBLEMS 1. Use measured values of the frequency (PARTS A2 and C2) to verify the relationship between fripple for a half-wave rectifier and a full-wave rectifier. 2. For the full-wave rectifier, how did the measured ripple compare with the theoretical value as calculated in PART C? 3. a) Explain why the zener regulation fails if the load resistance becomes too small. b) For what load resistance is the zener dissipating the most power? EXTRA A. Complete the following statements for the power supply shown in Figure 1. Transform er 230:10+10 + Figure 1. Centre tapped DC supply: Mains 230V(rms) 470 F Vout 10V(rms) 10V(rms) (a) This power supply uses ............. wave rectification. aluminium electrolytic. (b) The capacitor type is most likely to be ceramic. mylar. regulated (c) This is a power supply. non-regulated Page 6 B. (a) For Figure 1, the output wave shape with no load (as shown) is approximately: Vp (i) Vp (ii) 0V Vp (iii) 0V Vp (iv) 0V 0V (b) The value of Vp is approximately ................. volts. C. If a 470 load resistor is connected to the output of the power supply in Figure 1, calculate an approximate magnitude for the ripple voltage. Ripple voltage (peak to peak) ....................... D. Sketch a simple shunt regulated DC supply comprising of: a transformer with turns ratio 230:10 a bridge rectifier a 470 F reservoir capacitor a 470 resistor a zener diode Page 7