ba_hons_applied_sign_language_studies
advertisement
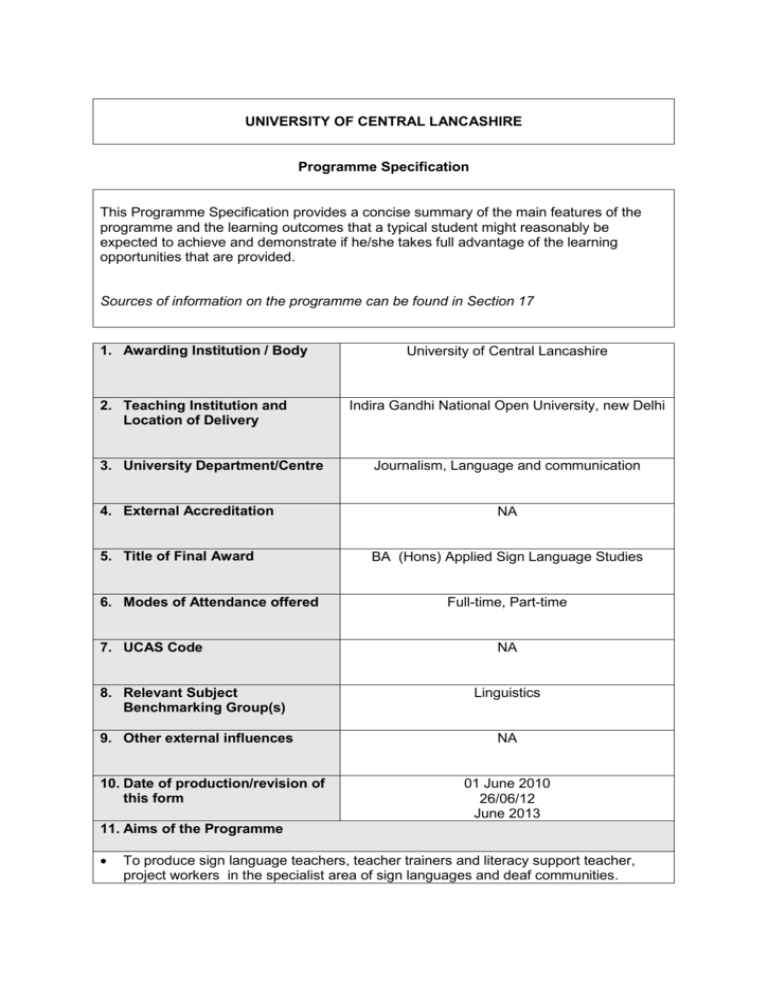
UNIVERSITY OF CENTRAL LANCASHIRE Programme Specification This Programme Specification provides a concise summary of the main features of the programme and the learning outcomes that a typical student might reasonably be expected to achieve and demonstrate if he/she takes full advantage of the learning opportunities that are provided. Sources of information on the programme can be found in Section 17 1. Awarding Institution / Body 2. Teaching Institution and Location of Delivery 3. University Department/Centre 4. External Accreditation 5. Title of Final Award 6. Modes of Attendance offered 7. UCAS Code University of Central Lancashire Indira Gandhi National Open University, new Delhi Journalism, Language and communication NA BA (Hons) Applied Sign Language Studies Full-time, Part-time NA 8. Relevant Subject Benchmarking Group(s) Linguistics 9. Other external influences NA 10. Date of production/revision of this form 01 June 2010 26/06/12 June 2013 11. Aims of the Programme To produce sign language teachers, teacher trainers and literacy support teacher, project workers in the specialist area of sign languages and deaf communities. To produce graduates with an excellent understanding of the different approaches and methodologies used in language acquisition, language teaching and learning. To create practitioners with a thorough understanding of relevant sub fields of sign language linguistics with special reference to applied dimensions of sign language studies. To develop in the graduates a high level of literacy and other academic skills. To create learning opportunities in the field of applied sign language studies, widen the scope of professional practice in this field, and promote further relevant research. 12. Learning Outcomes, Teaching, Learning and Assessment Methods A. Knowledge and Understanding By the end of the course, students will have understanding of e.g. A1. sign language linguistics and applied sign linguistics with related sub-fields of applied sign language studies, e.g Language acquisition, language teaching and learning and bilingualism. A2. issues in applied linguistics in the context of sign languages and deaf communities, and related research methods. A3. deaf communities, deaf culture, the sociolinguistics of sign languages, policy and practice related to sign languages A4. pedagogical practice and related professional requirements in a classroom where sign language is used. Teaching and Learning Methods A number of teaching and learning strategies including lectures, seminars, group discussion; self guided reading, IT training on research tools, external placements; and resource based learning. Assessment methods Core assessment methods are: Essay, in class assessment, oral test, and participation in discussion forum, portfolio of activities, working with a set of data, critical commentary and web search reports. B. Subject-specific skills by the end of the course, students will be able to: e.g. B1. meet and resolve the challenges involved in teaching a first or second language in a classroom where sign language is used. B2. demonstrate basic research skill in analysing language data and language learning contexts B3. reflect upon their own experience in teaching and learning as well as relate the learned theories to appropriate professional practice. B4. demonstrate knowledge of academic needs and opportunities in higher level of study in the relevant area. Teaching and Learning Methods The core teaching methods applied to achieve the subject specific skills are lectures, seminars, individual and group work, individual or group presentation, mock teaching; lab training on use of data, resources, archives etc. Assessment methods Portfolio of activities, essay, presentation (individual or group), web search report, mock teaching with peer observation; design of short curriculum and teaching materials C. Thinking Skills by the end of the course, students will be able to: e.g. C1. apply critical reflection and cognitive skills in order to identify, analyse and solve problematic issues C2. find and use a range of complex relevant information and derive appropriate conclusions C3. construct lines of argumentation, defend a point of view, and develop sound judgment. C4. establish logical links between different subject areas and to extend current knowledge to new issues. Teaching and Learning Methods Lectures, seminars, group discussion, guided reading, lab based workshop on using IT for research purpose, will form the core part of the teaching and learning methods. Assessment methods Essay, critical research review, presentation, analyse a set of data, portfolio of activities, web search report, critical commentary, reflective log, problem solving task. D. Other skills relevant to employability and personal development by the end of the course, students will be able to: e.g. D1. demonstrate English language and literacy skills necessary to function in teaching and learning contexts. D2. develop appropriate awareness of professional ethics and be able to function confidently in a teaching, learning or management role either alone or together with others as a team. D3. demonstrate IT skills in the areas of multimedia, materials development and communication technologies. D4. analyse one’s own knowledge and skills in order to devise strategies for personal development planning. Teaching and Learning Methods Lectures and seminars, group discussion, team work, workshops on relevant area of study. Assessment methods Essay, presentation, discussion forum participation, development of teaching materials, IT lab project 13. Programme Structures* Level Module Code IK 3003 IK 3991 IK 3990 Current issues in Applied Sign linguistics Sign language Policy and planning: An international perspective Dissertation: double (year long) Dissertation: single (year long) IK 3005 IK 3006 IK3007 Structure of foreign sign languages Student initiated module Work placement Level 5 Level 6 IK 3004 Level 4 Module Title 14. Awards and Credits* Credit rating 20 20 40 20 20 20 20 IK3008 Peer mentoring 20 Students will take one of the following two compulsory modules: IK2001 Bilingualism and Literacy in Deaf 20 education IK2011 Bilingualism and Literacy in Deaf 40 education with Project Work And: IK2002 Second Language Acquisition 20 IK2007 First Language Acquisition 20 IK2003 Models of Teaching and Learning 20 in Language and Literacy IK2004 Sociolinguistics of deaf 20 communities IK2005 Advanced sign linguistics 20 IK2006 Applied Linguistics Research and 20 Development IK2008 Sign language interpreting: theory 20 and practice IK2009 Work placement 20 IK2010 Student Initiated Module 20 IK1001 Introduction to Language & Sign 20 Language IK1002 Foundations of teaching and 20 training Theory and application IK1003 Deaf community & Culture 20 IK1004 Student Experiential Module 20 IK1005 Meta-linguistic prerequisites for sign language teaching Foundations in the practice of sign language teaching Introduction to Applied Sign Linguistics Student Initiated Module 20 IK1009 IK1010 IK1008 20 20 20 Bachelor Honors Degree Requires 360 credits including a minimum of 220 at Level 5 or above and 100 at Level 6 to include either IK3990 or IK3991 Bachelor Degree Requires 320 credits including a minimum of 180 at Level 5 or above and 60 at Level 6 HE Diploma Requires 240 credits including a minimum of 100 at Level 5 or above. HE Certificate Requires 120 credits at Level 4 or above = Compulsory modules 15. Personal Development Planning Personal Development Planning (PDP) is managed through a number of inter-linked measures to support the development of academic, personal and professional skills in students: 1. The department student tutoring system is designed to monitor the students’ PDP; students’ personal tutors are contacted by students at regular intervals for individual meetings on PDP. 2. A peer mentoring system matches up senior with junior students; senior students assist in PDP planning in coordination with department tutors. 3. PDP tools are made available to students, which include self-assessment forms, supervision logs, and written records of PDP planning and progress. 4. Joint activities are arranged for students and alumni for the purpose of networking and PDP advice to students. 16. Admissions criteria Programme Specifications include minimum entry requirements, including academic qualifications, together with appropriate experience and skills required for entry to study. These criteria may be expressed as a range rather than a specific grade. Amendments to entry requirements may have been made after these documents were published and you should consult the University’s website for the most up to date information. Students will be informed of their personal minimum entry criteria in their offer letter. For admission to the programme, students must: Either have successfully completed the Certificate of Achievement in Applied Sign Language Studies (Foundation Entry) Or fulfil the following requirements: 1. Academic qualifications: Students will be able to attend without prior experience of Higher Education, and with UCLan undergraduate entry requirements as per applicant’s home country, except English language requirements. Equivalence of non-standard qualifications and experience will be considered during a mandatory interview. 2. Sign language skills Students must have a high degree of fluency in any sign language and must be able to cope with an international signing environment sufficiently. An indicative minimum level would be sign language level 4 in the UK, but certified level 4 signers are not guaranteed to meet the required standards because an ability to cope with a certain degree of international signing is expected, and courses teaching a national sign language do not usually include international signing even at the highest level. Conversely, it is not necessary to provide proof of certified learning, and Deaf users of sign languages, in particular those for whom a sign language is the first and/or preferred language, can have their signing skills assessed during the interview. This is appropriate because the certified learning of sign language is virtually always directed at hearing learners acquiring the sign language as a second language (e.g. with the aim of becoming sign language interpreters). Certified learning for Deaf native sign language users is very rare, as no systems exist in sign language teaching for this target group. Therefore, it is quite rare for even the most fluent Deaf signers to have a certified level of sign language skills. 3. English literacy skills Students must have sufficient English literacy to be able to cope with the course content. As all assignments can be produced in sign language, it is not necessary to demonstrate writing skills. However, students need to have reading comprehension skills at an intermediate level (roughly equivalent to IELTS 4.5). This is an indicative level, and it is not necessary to provide evidence of IELTS test scores because these tests are unsuitable for deaf students. The acquisition of English literacy by deaf students is very different from the literacy of hearing students, and therefore, literacy should be assessed by course tutors, who are familiar with these issues. Moreover, the ability to cope with the specific course content in terms of the necessary reading comprehension skills cannot be simply equated with IELTS scores, as reading comprehension is a complex interplay of skills that are not limited to the level of English language only. In the case of deaf students, sign language skills substitute some of the English skills that are usually required of students, in particular with respect to text production during assessment. 4. Successful personal interview All students will be individually assessed by the course tutors in a mandatory interview for the above criteria. The above rationale justifies compulsory interview for all students by course tutors. The criteria constitute reasonable adjustment to the needs of deaf students as endorsed by specialists in the subject area and policy advice from concerned bodies. 17. Key sources of information about the programme Departmental website www.uclan.ac.uk/islands Fact sheets (also available online) Student handbook (also available online) iSLanDS centre flyer 18. Curriculum Skills Map Please tick in the relevant boxes where individual Programme Learning Outcomes are being assessed Programme Learning Outcomes Core (C), Compulsor y (COMP) Module or Option Knowledge and Thinking Level Code Module Title (O) understanding Subject-specific Skills Skills IK3003 LEVEL 6 IK3004 IK3991 IK3990 IK3005 IK3006 LEVEL 5 IK3007 IK3008 IK2001 IK2002 IK2003 IK2004 IK2005 Current issues in applied sign linguistics (COMP) Sign language policy and planning: An international perspective (COMP) Dissertation: double (year long) (O) Dissertation: single (year long) (COMP) Structure of foreign sign languages (O) Student initiated module (O) Work placement (O) Peer mentoring (O) Bilingualism and Literacy in Deaf education (COMP) Second language acquisition (COMP) Models of teaching and learning in language and literacy (O) Sociolinguistics of Deaf communities (O) Advanced sign linguistics (O) A1 A2 A3 A4 B1 B2 B3 Other skills relevant to employability and personal development B4 C1 C2 C3 C4 D1 D2 D3 D4 IK2006 IK2007 IK2008 IK2009 IK2010 IK2011 LEVEL 4 IK1001 IK1002 IK1003 IK1004 IK1005 IK1009 IK1010 IK1008 Applied linguistics research and development (O) First language acquisition (COMP) Sign language interpreting: theory and practice (O) Work placement (O) Student Initiated module (O) Bilingualism and Literacy in Deaf education with Project Work (COMP) Introduction to language & sign language (COMP) Foundations of teaching and training: theory and application (O) Deaf community & culture (COMP) Student experiential module (O) Meta-linguistic prerequisites for sign language teaching (O) Foundations in the practice of sign language teaching (O) Introduction to applied sign linguistics (COMP) Student lnitiated module (O) Note: Mapping to other external frameworks, e.g. professional/statutory bodies, will be included within Student Course Handbooks