Atomic
advertisement

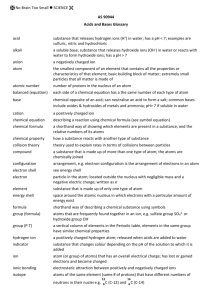
Grade 8 Study Guide – Science- Exam date: Wednesday, June 6 th Scientist John Dalton - He believed that matter was made of atoms that were too small to be seen by the human eyes His model became known as the atomic theory of matter Lavoisier - He is the founder of modern chemistry He presented the law of conservation of matter JJ Thomson - He discovered the electron – he won the noble prize of physics for this discovery He realized that the atom contained positive and negatives charges Rutherford - He found that atoms must be made of mostly empty space He found the nucleus He named the positively charged particles in the nucleus protons Chadwick - He discovered the neutron Bohr - Made the first model of the atom Vocabulary Terms 1. BOILING POINT: The temperature at which a liquid turns to a gas 2. MELTING POINT The temperature at which a solid turns to a liquid 3. FREEZING POINT: The temperature at which a liquid turns to a solid (32) 4. FLAMMABILITY: The ability to burn 5. REACTIVITY: The ability of a matter form to react chemically with another form of matter 6. DUCTILE: The ability for a substance to draw into wires so contact can be made 7. PHYSICAL PROPERTITY: Characteristics of matter that can be seen through direct observation such as density, melting point, boiling point, and freezing point 8. PHYSICAL CHANGE: Change in which the identity of the substance does NOT change 9. CHEMICAL PROPERTY: Characteristic of matter that can only be observed when one substance changes into a different substance such as iron into rust 10. CHEMICAL CHANGE: Transforms one type of matter into another kind, which may have different properties 11. PRESSURE: The force applied to an object 12. VISCOCITY: the resistance of a liquid to flow 13. FORCE: exerted pressure- push or pull 14. FLUIID: a substance whose shape can easily change 15. MATTER: Anything that has mass and takes up space 16. ELEMENT: Matter made up of only one kind of atom 17. COMPOUND: A pure substance whose smallest unit is made up of atoms or more than one element 18. ATOM: A small particle that makes up most types of matter on Earth 19. NUCLEUS: Positively charged central part of the atom 20. PROTON: Positively charge particle in the nucleus of the atom 21. NEUTRON: Uncharged particle in the nucleus of the atom 22. ELECTRON: Negatively charged subatomic particle 23. LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER: States that matter is not created or destroyed but only changes its form 24. Atomic #- states the # of protons 25. Chemical symbol: stands for the element name *Rule- the 1st letter is capital, 2nd letter is lower case 26. Atomic mass unit (a.m.u.)- states the number the mass of the particles * always round 27. Period #- found on the left side of the chart- it states the number of energy levels 28. VALENCE: is the energy level farthest from the nucleus 29. To find the # of neutrons: Subtract the atomic number from the estimated a.m.u. 30. QUARKS: Broken down protons and neutrons into smaller parts 31. COMPOUNDS: substances that are made up of more than one type of atom 32. MIXTURE: made up of two or more substances that are physically combined 33. SUBSCRIPT: states the # of atoms per elements 34. MONOATOMIC: one molecule made up of one atom 35. DIATOMIC: one molecule made up of two atoms ……………………………………………………………………………………… Here are some key words to be familiar with: Physical changes: Chemical changes: Evaporating burning Melting digesting Heating corrode Cracking ferment Meting rust Mixing oxidize Boiling tarnish Condense explode The 5 states of matter: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Liquids Solids Gases Plasmas Bose Einstein condensates …………………………………………………………………………………………….. Know how to do the incomplete diagram for elements- part 1 For example, using the element Se Symbol- Se Atomic #- 34 Est. amu- 74 amu #P- 34P #N- 45N #e- 34e Group #- 16A Period #- 4 Mass#- 34P+45N= 79 amu Know the key terms & parts of the elements found on the PTOE 1A 11 3 Na Sodium 22.99707 (23)