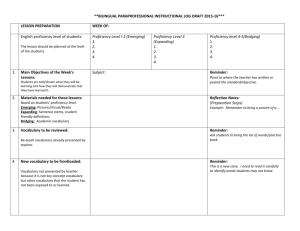
Key assessments and scoring guides used for assessing candidate
advertisement

d. Data and summaries of results on key assessments, including proficiencies identified in the unit’s conceptual framework, disaggregated by program, and for off-campus and distance learning The following alignment demonstrates the consistency and relationships between the institutional standards, candidate proficiencies, dispositions, and diversity proficiencies and professional, national, and state standards. This alignment provides a context for the key assessment chart that follows: Institutional Standards, Proficiencies, Dispositions, and Proficiencies Related to Diversity Alignment INTASC Standards,, NBPTS Propositions, and Ohio Teacher Standards Institutional Standards INTASC S NBPTS Propositions Ohio: … Demonstrating foundation 4: Content 2: Teachers Know the 2 know and understand the knowledge, including knowledge of Knowledge Subjects They Teach and content area for which they have how each individual learns and How to Teach Those instructional responsibility. develops within a unique Subjects to Students. developmental context. Articulating the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and the structures of their discipline. 4: Content Knowledge Collaborating, leading, and engaging in positive systems change. 10: Leadership and Collaboration 2: Learning Differences Demonstrating the moral imperative to teach all students and address the responsibility to teach all students with tenacity. 2: Teachers Know the Subjects They Teach and How to Teach Those Subjects to Students. 5: Teachers are Members of Learning Communities. 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning 2 know and understand the content area for which they have instructional responsibility. 6. collaborate and communicate with students, parents other educators, administrators. 1. understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. Addressing issues of diversity with equity and using skills unique to culturally and individually responsive practice. 2: Learning Differences 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning 1. understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. Using technology to support their practice. 8: Instructional Strategies 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning Using assessment and research to inform their efforts and improve outcomes. 6: Assessment; 7: Planning Instruction 3: Teachers are Responsible for Managing and Monitoring Student Learning. 1. understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. 3. understand and use varies assessments to inform instruction, evaluate and ensure student learning. Demonstrating pedagogical content knowledge, grounded in evidencebased practices, committed to improving the academic and social outcomes of students. Institutional Proficiencies: Ways of knowing, being, and doing going beyond technical skills, engaging in inquiry and reflection so as to bring about changes in their practice 5: Application of Content 2: Teachers Know the Subjects They Teach and How to Teach Those Subjects to Students. INTASC S 9: Professional Learning and Ethical Practice NBPTS 4: Teachers Think Systematically about Their Practice and Learn from Experience. 2 know and understand the content area for which they have instructional responsibility. Ohio 7 assume responsibility for professional growth, performance and involvement. recognizing and addressing a wide range of setting events, persisting in supporting learners in the construction of knowledge and development of efficacy within their unique developmental contexts 2: Learning Differences 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning 1. understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. exploring the funds of knowledge inherent in the historically accumulated and culturally developed bodies of knowledge and skills essential for household or individual functioning and well being. 2: Learning Differences 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning 1. understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. being resilient so as to do their work in challenging situations 9: Professional Learning and Ethical Practice 10: Leadership and Collaboration 9: Professional Learning and Ethical Practice 5: Teachers are Members of Learning Communities. 7 assume responsibility for professional growth, performance and involvement. 6. collaborate and communicate with students, parents other educators, administrators. 4. plan and deliver effective instruction that advances the learning of each individual student. negotiating a place for learning that is formed from student and teacher understandings 7: Planning for Instruction supporting the development of resilience 2: Learning Differences 3: Teachers are Responsible for Managing and Monitoring Student Learning. 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning using technology to strengthen their professional learning and pedagogical knowledge, and enhance the learning of those with whom they work 8: Instructional Strategies 3: Teachers are Responsible for Managing and Monitoring Student Learning. 5. create learning environments that promote high levels of learning and achievement for all students. 1. understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. 4. plan and deliver effective instruction that advances the learning of each individual student. using practices documented to produce positive outcomes, grounded in assessment and research and student-driver teaching and learning 8: Instructional Strategies 3: Teachers are Responsible for Managing and Monitoring Student Learning. 4. plan and deliver effective instruction that advances the learning of each individual student. Dispositions initiative on behalf of all learners INTASC S 9: Professional Learning and Ethical Practice Ohio 7 assume responsibility for professional growth, performance and involvement. responsibility to promote effort and excellence in all learners 9: Professional Learning and Ethical Practice NBPTS 4: Teachers Think Systematically about Their Practice and Learn from Experience. 4: Teachers Think Systematically about Their Practice and Learn from Experience. working and communicating appropriately with families and the community. accepting the responsibility for positive outcomes of students or clients. 5: Teachers are Members of Learning Communities. 3: Teachers are Responsible for Managing and Monitoring Student Learning. 7 assume responsibility for professional growth, performance and involvement. rapport with students, peers, and others 10: Leadership and Collaboration 5: Teachers are Members of Learning Communities. 6. collaborate and communicate with students, parents other educators, administrators. a commitment to reflection, assessment, and learning as an ongoing process grounded in inquiry 6.Assessment collaboration with other professionals to improve the overall learning environment for students 10: Leadership and Collaboration 4: Teachers Think Systematically about Their Practice and Learn from Experience. 5: Teachers are Members of Learning Communities. 3. understand and use varies assessments to inform instruction, evaluate and ensure student learning. 6. collaborate and communicate with students, parents other educators, administrators. acknowledging multiple perspectives 2: Learning Differences 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning dedication to teaching the subject matter and in keeping informed and competent in the discipline and its pedagogy appreciating both the content of the subject are and the diverse needs, assets, and interests of the students and value both short and long term planning 5: Application of Content 2: Teachers Know the Subjects They Teach and How to Teach Those Subjects to Students. 4: Teachers Think Systematically about Their Practice and Learn from Experience. 1. understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. 2 know and understand the content area for which they have instructional responsibility. commitment to the expression and use of democratic values in the classroom 3: Learning Environments responsibility for making the classroom and the school a “safe harbor” for learning, in other words, a place that is protected, predictable, and has a positive climate 3: Learning Environments Recognition of the fundamental need of students to develop and maintain a sense of self-worth, and that student misbehavior may be attempts to protect self-esteem 7: Planning for Instruction 2 know and understand the content area for which they have instructional responsibility. 3: Teachers are Responsible for Managing and Monitoring Student Learning. 3: Teachers are Responsible for Managing and Monitoring Student Learning. 5. create learning environments that promote high levels of learning and achievement for all students. 5. create learning environments that promote high levels of learning and achievement for all students. 2: Learning Differences 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning 1. understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. belief that all children can learn and persistence in helping every student achieve success 2: Learning Differences 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning value all students for their potential and people and help them value each other 2: Learning Differences 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning 1. understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. 1. understand student learning and development and respect the diversity of the students they teach. high ethical and professional standards Diversity Proficiencies: to acknowledge/affirm/practice culturally & individually responsive pedagogy in diverse educational environments. 9: Professional Learning and Ethical Practice INTASC S accept the responsibility for the learning of their students or clients 9: Professional Learning and Ethical Practice explore the funds of knowledge inherent in the historically accumulated and culturally developed bodies of knowledge and skills essential for household or individual 2: Learning Differences recognize and address a wide range of setting events, persisting in supporting learners in the construction of knowledge and development of efficacy provide supportive environments that support the development of resilience work with and communicate appropriately with families and the community at large 10: Leadership and Collaboration 4: Teachers Think Systematically about Their Practice and Learn from Experience. NBPTS 7 assume responsibility for professional growth, performance and involvement. Ohio 4: Teachers Think Systematically about Their Practice and Learn from Experience. 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning 7 assume responsibility for professional growth, performance and involvement. 2: Learning Differences 1: Teachers are Committed to Students and Their Learning 4. plan and deliver effective instruction that advances the learning of each individual student. 3: Learning Environments 3: Teachers are Responsible for Managing and Monitoring Student Learning. 5: Teachers are Members of Learning Communities. 5. create learning environments that promote high levels of learning and achievement for all students. 6. collaborate and communicate with students, parents other educators, administrators. 4. plan and deliver effective instruction that advances the learning of each individual student. Council of Chief State School Officers. (2011, April). Interstate Teacher Assessment and Support Consortium (InTASC) Model Core Teaching Standards: A Resource for State Dialogue. Washington, DC: Author. Core Propositions - www.nbpts.org The following tables align key assessments with these standards, dispositions, and proficiencies. Most programs have information available on AIMS; for those that do not, the data description is linked to the tables. P Key Assessments 1. Content Knowledge 2. Content Knowledge 3. Planning Standards, Proficiencies, Dispositions Institutional Standard: Demonstrating foundation knowledge, including knowledge of how each individual learns and develops within a unique developmental context. Institutional Standard: Articulating the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and the structures of their discipline. Institutional Proficiency:/Diversity: recognizing and addressing a wide range of setting events, persisting in supporting learners in the construction of knowledge and development of efficacy within their unique developmental contexts Institutional Proficiency:/Diversity: exploring the funds of knowledge inherent in the historically accumulated and culturally developed bodies of knowledge and skills essential for household or individual functioning and well being. Institutional Proficiency: negotiating a place for learning that is formed from student and teacher understandings Institutional Standard: Addressing issues of diversity with equity and using skills unique to culturally and individually responsive practice. 4: Professional Practice 5. Impact 6, 7, and 8 (if applicable) Specific standards based assessments) Dispositions Institutional Standard: Demonstrating the moral imperative to teach all students and address the responsibility to teach all students with tenacity. Institutional Proficiency: using practices documented to produce positive outcomes, grounded in assessment and research and student-driver teaching and learning Institutional Proficiency/Diversity: supporting the development of resilience Institutional Standard: Using assessment and research to inform their efforts and improve outcomes. Institutional Proficiency: going beyond technical skills, engaging in inquiry and reflection so as to bring about changes in their practice Institutional Proficiency/Diversity: accepting the responsibility for positive outcomes Institutional Standard: Demonstrating pedagogical content knowledge, grounded in evidence- based practices, committed to improving the academic and social outcomes of students. All Dispositions Programs Available on Aims Advanced Programs on CECH Web Pages Other School Personnel on CECH Web Pages Grades 7-12 Programs: □ English/Language Arts □ Social Studies □ Mathematics □ All Science Programs □ Woodrow Wilson Fellows □ Early Childhood Education prek-3 □ Middle Childhood Education 4-9 □ Intervention Specialist K-12: Mild Moderate Needs □ Intervention Specialist K-12: Moderate Intense Needs □ Intervention Specialist K-12: Mild Moderate Needs for Individuals Holding a Current License □ School Psychology Specialist and PhD □ Building Level Leadership □ District Level Leadership □ Literacy and Second Language Studies M. Ed. (includes Reading Endorsement) □ Special Education M. Ed. □ Curriculum and Instruction M. Ed. Endorsements: □ Early Childhood Education Generalist Grades 4-5 □ Gifted Endorsement □ Middle Childhood Generalist □ Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages Endorsement □ Teacher Leaders Endorsement Early Childhood Learning Community: Associate and B.S. in Ed. degrees TO FACILITATE THIS REVIEW, THESE DATA ARE PRESENTED AS UPLOADED FILES Evidence for All Programs THIS SHOULD BE A LINKI TO 1.4.D TO FACILITATE THIS REVIEW, THESE DATA ARE PRESENTED AS UPLOADED FILES Institutional Standard: Addressing issues of diversity with equity and using skills unique to culturally and individually responsive practice. Use of Technology Mentor/Cooperating Teacher Evaluation of Program Institutional Standard: Using technology to support their practice. Institutional Proficiency: using technology to strengthen their professional learning and pedagogical knowledge, and enhance the learning of those with whom they work Evidence for All Programs Institutional Proficiency: being resilient so as to do their work in challenging situations Evidence for All Programs Institutional Proficiency/Diversity: working and communicating appropriately with families and the community. THIS SHOULD BE A LINK TO THE FILE UNDER STANDARD 1 CALLED USE OF TECHNOLOGY FOR 1.4.E THIS SHOULD BE A LINK TO 1.4.H.1 Institutional Standard/Diversity: Collaborating, leading, and engaging in positive systems change. Institutional Standard: Addressing issues of diversity with equity and using skills unique to culturally and individually responsive practice. Follow-up Institutional Proficiency: being resilient so as to do their work in challenging situations Institutional Proficiency/Diversity: working and communicating appropriately with families and the community. Evidence for All Programs THIS SHOULD BE A LINK TO 1.4.G Institutional Standard/Diversity: Collaborating, leading, and engaging in positive systems change. Institutional Standard: Addressing issues of diversity with equity and using skills unique to culturally and individually responsive practice. Employer Institutional Proficiency: being resilient so as to do their work in challenging situations Evidence for All Programs THIS SHOULD BE A LINK TO 1.4.H Institutional Proficiency/Diversity: working and communicating appropriately with families and the community. Institutional Standard/Diversity: Collaborating, leading, and engaging in positive systems change. Institutional Standard: Addressing issues of diversity with equity and using skills unique to culturally and individually responsive practice. Benchmarks Assessments used at transition points Evidence for all programs THIS SHOULD BE A LINK TO 2.1.1 AND 2.1.2