MIGORI SUB COUNTY JOINT EVALUATION EXAM GEOGRAPHY
advertisement

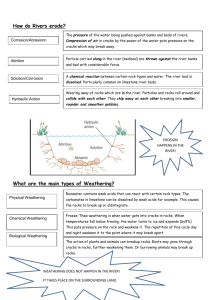
MIGORI SUB COUNTY JOINT EVALUATION EXAM GEOGRAPHY PAPER 1 MARKING SCHEME \SECTION A 1. a. Give three ways in which air pressure affect humidity (3mks) - Pressure increase air temperature - Hot air capable of holding more water than cold air - High pressure increases the air holding capacity hence high humidity b.State two factors that determine the amount of solar radiation reaching the earth (2mks) 2. i. Cloud cover Transparency of atmosphere Angles at which the rays fall Nature of the surface Average of distance of the earth from the sun a. Study the world map below and answer the questions that follow name the fold mountain found in the area marked A,B and C (3mks)\ A –Appalachian mountain B- Rockies C- Ural mountain b.Give two negative effects of faulting (2mks) 3. - Land is disjointed leading to disruption of communication lines, water ,sewages and oil pipes It leads to sinking of land hence loss of life, property and instruction of agriculture land When faults occur across a river ,the river may disappear completely or change its direction of flow Block mountains reverse drainage a. Name two transitional zones of the atmosphere (3mks) Tropopause Stratopause Mesopause b.Give three reasons why cloud concentration is higher in the troposphere (3mks) 4. - Temperature decreases with increase in height Presence of particles in the layer like dust act as condensation in nuclei Has high humidity /water vapor a. What is mass wasting? (2mks) mass wasting is the creeping ,flowing ,sliding or falling of weathered rocks/materials down the slope under the influence of free of gravity\ b.State three factors influencing the nature and speed of mass wasting ( 3mks) Amount of water in the weathered materials Nature of the weathered materials Angle or gradient of the slope Presence of vegetation cover Human activities e.g. mining and construction Tectonic movements 5. - Climatic conditions especially rainfall and temperature a. Name two current in the Atlantic ocean (2mks) gulfstream north Atlantic drift b.State three factors that influence ocean water temperature latitude of ocean ocean currents the depth of the ocean salinity of the ocean water upwelling of water enclosed open seas 6. Drawing ii. Latitude and longitude of the south East cover of map extract 370154Eand 0030’s iii. Physical features found in Grid 0049 - Scarp /steep slope - Spurs - River valley b.ii) On the graph The two points are intervisible c ii) Citing evidence from the map state 5 functions that favour livestock keeping in Karatina (5mks) - Availability of many cattle dips indicate that there is access to veterinary services thus improve cattle health The high altitude – 2000m cost –warm conditions suitable for cattle rearing Availability of transport shows by numerous road/track wet work enhance movement of cattle products Presence of many rivers/source of water ensure enough water for cattle Presence of dense settlement provide market for cattle products iii) Describe the characteristics of the long river profile of river Sagana (6mks) 7. The river has many small tributaries that forms dendrite pattern along the course There are interlocking spurs along the river course/river meanders The river is permanent There are water fall/rapids along the course of Grid 8347 The river floors from North towards the South The main tributaries are river Thego and Ruiru The river becomes wider and wider Southwards as it’s joined by many tributaries. a. What is a mineral ( 2mks) Inorganic substances which occur naturally at or beneath the earth surface ii.Classes to which the following rocks belongs i. ii. iii. Marble – Metamorphic Basalt –Igneous Ironstone –Sedimentary b.i) How intrusive igneous rocks are formed (5mks) - Heat and pressure beneath causes rocks to melt This lead to formation of lines weakness cooling into the earth coast cooling into the earth coast Magma cools and solidifies inside the coast to form intrusive igneous rocks ii.Why coral rocks are widespread at the coast a. b. - Salty water favour growth of coral polyps Warm water with temperatures between 200c and 290c for the growth of coral polyps Clear water which is free from silt or mud to your favour coral growth by receiving sunlight Shallow water of less them 60 meters deep to which sunlight can penetrate for coral growth Well oxygenated water for coral growth Uses of soda ash Catalyst /reagent for making soaps and detergents Catalyst /reagent for making glasses Making table salts Used in the chemical industries Is reasons to prepare objectives Are a guide to possible areas of data collection Are a guide on the actual activities to be carried out in the field Help to ensure that all required data is collected Restrict the researcher on the topic of study ii.Four instruments and how they are to use them - Hammers to break pieces of rocks Shovel/spade to scoop out soil particles when digging out rocks Fork jembe /jembe to dig out rocks Panga to clear bushes so as to access rocks Question 8: marking scheme a) P-Limestone rock Q – Grike R- Clint b) Factors influencing development of Karst sceweg - The surface rock and the underlying rock should be thick limestone, dolomite or chalk - The rocks should be hand and well-jointed - The climate should be hot and humid - The water table should be deep below the surface c) Formation of i. A swallow hole (5mks) - Is a vertical hole in the ground through which rain water or river water disappears into the ground - The water widens and deepens the joints to form the vertical holes, as the water sinks through them - The water that has disappeared through the hole moves along the rock joints until it comes out of the ground as a veliclusion spring downhill - When surface run-off or river water disappears into this hole, it is then called a swallow hole or a sink hole ii. A doline (5mks) - Is a round or elliptical hollow on the surface of a limestone region, formed when several small hollows merge - The small hollows are formed when water starts acting on the points of convergence of joints on the surface ‘ - These points of convergence are widened as the solution process continues until the blocks of rock between the hollows are completely dissolved - This leaves a continuous rounded or elliptical depression called a doline d) Influence of limestone landscapes on human activities - Surface and underground features in a karst landscape can attract tourist thereby earning foreign exchange - Limestone landscapes are usually rugged with rocky surfaces, thin soils poor vegetation and inadequate surface water, all of which discourage settlement - Limestone blocks are used for building houses - Limestone is also a raw material for cement manufacturing ,therefore it supports the construction and manufacturing industries c. i. Objectives of the study - To find out the features formed in Karst landscape - To identify the different features within the landscape. - To establish the economic importance of such features - To find out the effect of water action in limestone areas on settlement. *any other relevant (2 x 1 = 2marks) ii) Reasons why they needed to previsit the area (1 mark) - To estimate the time needed to do the study - To estimate the cost of the study - To enable them foresee the possible problems to be encountered while in the field - To decide on the tools and materials to carry - To obtain permission from relevant authorities 8. a. i) Outline two factors that influence the development of drainage patterns (2mks) - Direction of the slope of the land - Difference in the slope of the land - The arrangement of rock layers /rock structure - Faulting/fault guided ii)Give three features of a river in its old stage - Pronounced meanders Braided channel/river braids Ox-bow lake Estuaries Flood plain Natural leaves Distributaries/deltas Slip –off-slopes Bluffs Sagoons/lagonal lakes Deferred tributaries b) Briefly describe how the following factors influence river erosion - Gradient and velocity The steeper the slope the higher the velocity and the more the rate of erosion and vice versa Nature and amount of the load A river carrying a large load and flowing at a high speed will be more effective in erosion work a river carrying a small load and flowing slowly. iii. Nature of the bed rock (2mks) - Less resistant bedrock are eroded faster than the more resistant bedrock c. The diagram below represents a depositional features of a river .Study it and answer the questions that follow Diagram i. Name the parts labeled E,F, and G in the diagram E – Lake F – Main river G - Alluvium swamp land ii. Give one example of the feature represented in the diagram in Kenya (1mk) - A current delta - Birds foot delta - Estuarine delta - Cuspate delta - Inland delta iii. State three conditions necessary for the formation of the features shown in the diagram - The river must have a large load of sediments - There should be no obstacles like lakes or swamp along the rivers course as they tend to block sediments from reaching the river mouth - The river should the flowing slowly upon entering the sea ensure deposition of a lot of materials at the river mouth - The rate of removal of sediments by the tides and currents should be lower than the rate of deposition of materials d. A part from providing water for domestic and industrial uses, highlight three other benefits of rivers in Kenya - Provide fish which is food for human beings Some rivers act as natural boundaries between countries communities and district etc. River deltas and flood plains contain fertile alluvial soils suitable for agriculture Rivers that are navigable provide route nays Rivers leads provide building materials such as gravel and sand Rivers provide fresh water used for irrigation Rivers provide sites suitable for generation of H.E.P River provided good sites for tourist’s attraction e.g. waterfalls. e.Your class intends to conduct a filed study on river deposition around your school i. - Name one stage along the long profit of a river where your study can be conducted The old stage ii. iii. - State two methods you would use to collect data during the study (2mks) Observation Taking photo Taking notes Answering questionnaires Give one benefits of river deposition that you intend to velocity during the study ( 1mk) Valuable minerals e.g. gold and diamond River deltas and flood plains which contains fertile soil for agriculture