Respiration- 3 separate but related functions Ventilation or breathing
advertisement

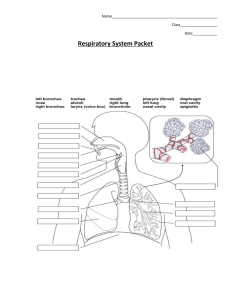
Respiration- 3 separate but related functions Ventilation or breathing- uses diaphragm & internal/external intercostals muscles Gas exchange- between air/blood in lungs and between blood/tissues of body Oxygen utilization- tissues use oxygen during cellular respiration External respiration- ventilation/exchange of gases in lungs Internal respiration- exchange of gases at tissues; cells need oxygen & get rid of carbon dioxide Adults breathe about 15 times/min moving about 6 L of air In strenuous exercise the rate increases to 100 times/min Without breathing 4-5 min you lose consciousness; 7-8 min there is brain damage & more than 10 min means death ANATOMY Upper respiratory system Nose, pharynx, & associated structures Lower respiratory system Larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, pulmonary alveoli & lungs Functionally system is divided into 2 parts Conducting division- all cavities/structures to transport gases to/from pulmonary alveoli Respiratory division- pulmonary alveoli Nose External nose Made of cartilage & supported by nasal bones Nasal cavity Septal cartilage forms nasal septum along with vomer/ethmoid bones 2 halves or nasal fossa formed with the nasal vestibule found behind the nostril Roof of nasal cavity formed by frontal, nasal, ethmoid & sphenoid bones Floor made of palatine/maxillary bones Turbinate or nasal conchae form lateral walls & passageway between conchae are called nasal meatuses Jobs: warms, moistens & cleanses air (ciliated mucous lining) Smell Resonating chamber for voice Paranasal sinuses Found in & named for the maxillary, frontal, sphenoid, & ethmoid bones Connected to nasal cavity by drainage ducts Helps to warm/moisten air as well as some resonating function Reduces weight of skull Pharynx Funnel shaped passageway between nasal/oral cavities Nasopharynx- top portion that is only passageway for air Uvula closes off this area when swallowing Auditory or Eustachian tubes connect from here to middle ear Adenoids found here Oropharynx- middle between soft palate & level of hyoid bone Used for both food & air 2 pairs of tonsils found here Laryngopharynx- lowest part that extends below level of hyoid bone Opens into esophagus & larynx Larynx Positioned in anterior midline of neck at level of 4-6 cervical vertebrae Two jobs- keeps food/fluid from entering trachea & produces sound Made of cartilage structures Laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple)- on anterior side of thyroid cartilage Male sex hormone makes it more prominent in males than females Epiglottis- hyaline cartilage behind base of tongue Closes off larynx during swallowing so it routes food/air where they should go Cricoid cartilage- ring at lower end of larynx Aretenoid cartilages- above cricoids & are the back attachments of vocal cords Muscles in larynx Extrinsic- responsible for elevating larynx during swallowing Intrinsic- change length, position & tension of vocal cords Vocal cords 2 pair of strong connective tissue bands stretched across upper opening of larynx Connected to aretenoid/thyroid cartilages True vocal cords- vibrate to produce sound Ventricular folds- support true cords; males have thicker/longer folds so they vibrate slower & have lower pitches Trachea (windpipe) Rigid tube 4”x1” going from larynx to bronchi C shaped hyaline cartilage “rings” form supporting walls & ensure airway stays open Lining has pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial to sweep particles our of air passage Goblet cells also present Bronchial tree Composed of respiratory tubes that branch into smaller/smaller tubes going to the lungs Trachea branches into principle bronchi which branch into secondary bronchi & then tertiary Bronchioles- smaller tubules with little cartilage; lined with simple cuboidal epithelial; continues to branch into smaller tubes that end in alveolar sacs Pulmonary alveoli Functional units of respiratory system 350 million/lung Provides large surface area for gas exchange Walls are 1 cell layer thick (0.5-1 micrometer) Sac structure surrounded by capillaries Moistened by surfactant for ease of exchange of gases by diffusion Lungs Large spongy paired organs Extend from clavicle to diaphragm Enclosed by ribs Left lung is slightly smaller & has cardiac impression Left has 2 lobes (superior/inferior) Right has 3 lobes(superior, middle, inferior) Pleura Epithelial membranes surrounding lungs & lining thoracic cavity Separates thoracic viscera Protects/lubricates lungs, secretes serous fluid & help form a pressure chamber for breathing Visceral pleura- adheres to outer surface & extends in between lobes Parietal pleura- lines thoracic walls & surface of diaphragm Pleural cavity- very small cavity between visceral/parietal membranes; contains liquid to lubricate; pleuras stuck together by fluid PHYSIOLOGY Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Functions of respiratory system Provides tissue with oxygen that is needed for metabolic processes that fuel body’s activities Provides for excretion of waste carbon dioxide produced during metabolism Movements of the respiratory muscles necessary for oral communication Breathing- mechanical process of taking air into lungs & expelling carbon dioxide Respiration- exchange of gases between living organism & its environment External respiration- involves exchange of gases between atmosphere/blood; occurs in lungs Internal respiration- exchange of gases that takes place between blood/cells; occurs in capillaries of body How do we breathe? As long as nasal passages aren’t blocked, pressure equilibrium is maintained between environment & lungs Inspiration- act of taking air into lungs When atmospheric pressure is higher than lung pressure, air is pushed into lungs Diaphragm/intercostals muscles contract to enlarge the thoracic cavity around lungs (both top to bottom & front to back); larger volume means less pressure in lungs & so air flows into lungs to equalize pressure; these muscles are stimulated by phrenic/intercostals nerves; diaphragm moves about 15 mm down The inward movement of air does not inflate lungs like a balloon but rather the expansion of the lungs causes the air to rush in Those who take voice lessons sing with hand at base of rib cage to be sure that they fully expand (open up) their lungs Expiration- act of expelling air from lungs When atmospheric pressure is lower than lung pressure, air leaves the lungs Diaphragm/intercostals muscles relax, size of thoracic cavity decreases all the way around so air pressure inside is greater than outside & air flows out of lungs to equalize pressure How much air are you moving? Total lung capacity- 5-6 L (volume that both lungs hold) Tidal volume- volume of air moved in/out of respiratory passage during normal breathing About 0.5 L Inspiratory reserve volume- volume of air that can be inhaled by deepest possible inspiration in excess of tidal; above tidal volume About 3 L Expiratory reserve volume- volume of air that can be exhaled by deepest possible expiration in excess of tidal About 1.2 L Vital capacity- volume of air that can be exhaled by deepest possible expiration after deepest possible inspiration; inhale/exhale with greatest possible effort Residual air- amount of air remaining in lungs after deepest possible expiration About 1.2 L Eliminated only by collapse of lung Minimal air- air remaining in lungs after lungs have collapsed Blood gases Diffusion of gases occurs from area of high concentration to area of low concentration A difference in the amount of oxygen present in alveoli & the amount of oxygen present in blood of pulmonary vessel causes oxygen to diffuse from alveoli to blood (concentration gradient of gases) Oxygen is carried by RBC as well as blood plasma- each hemoglobin molecule can carry 8 oxygen atoms At the body tissues there is again a difference in the amount of oxygen present there as compared to the bloodstream so oxygen diffuses into the tissues Carbon dioxide diffuses from tissue cells into bloodstream In blood, carbon dioxide 7% stays in gaseous form & dissolves in plasma 20% binds to the hemoglobin to be carried 73% is carried in blood in form of bicarbonate ions in plasma At lungs, carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli People breathe at rate of 16-24 cycles/min but it can be altered voluntarily Breathing is controlled by nerves (phrenic/intercostals) as well as chemically Respiratory musculature is stimulated by nerves regulated by respiratory centers in brain stem In medulla oblongata are inspiratory/expiratory centers that stimulate the phrenic/intercostals nerves; rhythmicity center helps to control breathing Cyclical activity of inspiratory center is all that is needed to sustain resting breathing (most of the lung volume changes now attributed to movements of diaphragm) Expiratory center becomes active when the body’s activity level increases & passive expiration is not rapid or deep enough; now intercostals nerves are added to stimulate intercostals muscles ot move Breathing also influenced by apneustic center & pneumotaxic center of pons Apneustic center prolongs inspiration (taking a deep breath) Pneumotaxic center has an inhibitory effect on inspiration (holding your breath) Respiration is chemically controlled by carbon dioxide in blood An increase in carbon dioxide stimulates respiratory center; this is most powerful stimulus Chemical regulation is responsible for maintaining breathing at day/night without conscious thought Chemoreceptors in medulla oblongata are stimulated by changes in hydrogen ion level & as pH of blood/cerebrospinal fluid drops there is an increase in respiratory rate Other chemoreceptors are found in aortic arch & carotid arteries which respond to changes in oxygen/carbon dioxide levels in blood Some Disorders of Respiratory System Cystic fibrosis Most common lethal inherited disease affecting Caucasians (1 birth in 2500) Gene defect on chromosome 7 Seldom survive past age 30 & death usually due to bacterial infection of lungs & heart failure Symptoms: thick gooey secretions from mucus glands of respiratory tract, pancreas, salivary glands & digestive tract Treatment: usually symptoms are treated with supportive care & antibiotic therapy but there is no cure Asthma Affects 2-6% of US population Exhalation affected more than inhalation Symptoms: constriction of smooth muscles along bronchial tree, edema, swelling of mucus pathways, accelerated production of mucus, inflammation Treatments: treated with use of bronchiodilators during attacks, glucocorticoids that inhibit inflammation, epinephrine promotes bronchodilation Tuberculosis Airborne pathogens spread by coughing, sneezing or speaking Infects 8-10 million worldwide annually As disease progresses, masses of fibrous tissue distort conduction pathways which increases resistance & decreases air flow; also in alveoli surface area for gas exchange is reduced Treatment difficult but includes use of drugs but bacteria can become antibiotic resistant easily Twice as common among blacks as whites Bronchitis Inflammation of bronchial lining which leads to overproduction of mucus & frequent coughing Can be caused by smoking or environmental irritants Emphysema Chronic progressive condition characterized by shortness of breath & inability to tolerate physical exertion Due to destruction of alveoli by inhaling particles/vapors Alveoli break down & this increases the size of the air spaces & decreases surface area Reduces ability of bronchioles to stay open during expiration All smokers will develop at least some emphysema by age 35-40 Permanent/irreversible but can be slowed if smoking is stopped Sleep apnea- stopping breathing while asleep Acute respiratory distress syndrome Reduced surfactant due to accumulation of protein-rich fluid in lungs May occur when person has systemic infection that leads to septic shock Blood leaving lungs has normally low oxygen concentration COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) 5th leading cause of death in US Chronic inflammation with narrowing of airways & destruction of alveoli Most patients are smokers & stopping smoking does not stop progression of disease May develop pneumonia, traveling blood clots or heart failure