Lab Evapor of acetone
advertisement
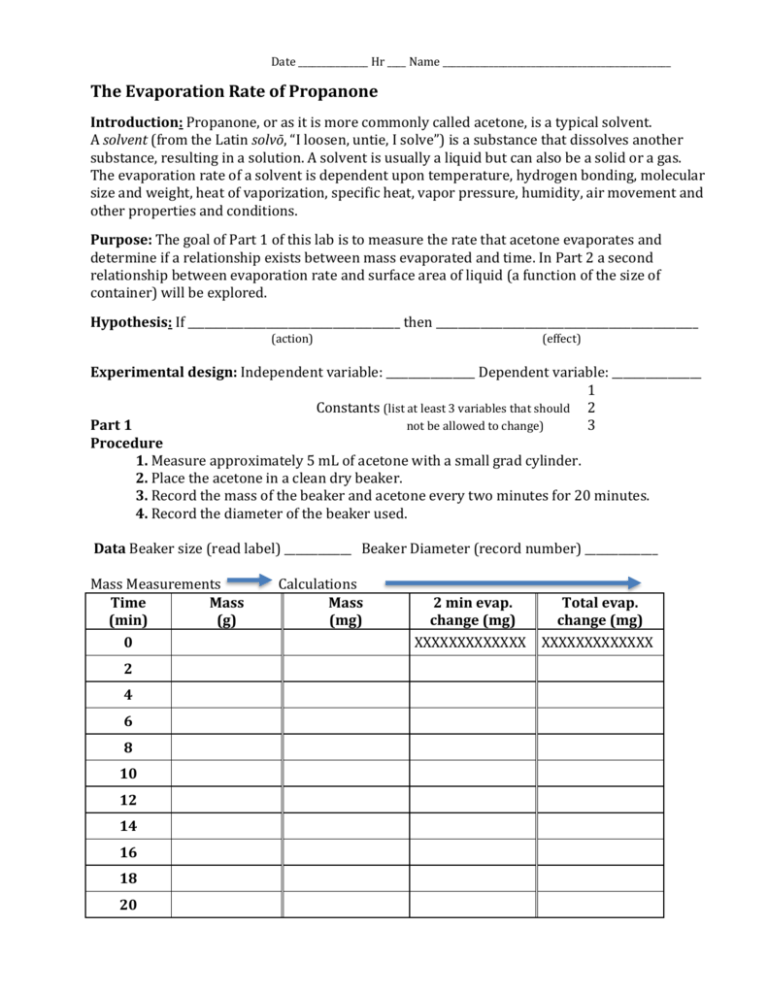
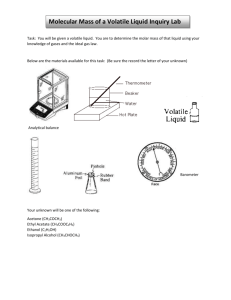
Date _______________ Hr ____ Name _________________________________________________ The Evaporation Rate of Propanone Introduction: Propanone, or as it is more commonly called acetone, is a typical solvent. A solvent (from the Latin solvō, “I loosen, untie, I solve”) is a substance that dissolves another substance, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid or a gas. The evaporation rate of a solvent is dependent upon temperature, hydrogen bonding, molecular size and weight, heat of vaporization, specific heat, vapor pressure, humidity, air movement and other properties and conditions. Purpose: The goal of Part 1 of this lab is to measure the rate that acetone evaporates and determine if a relationship exists between mass evaporated and time. In Part 2 a second relationship between evaporation rate and surface area of liquid (a function of the size of container) will be explored. Hypothesis: If ______________________________________ then _______________________________________________ (action) (effect) Experimental design: Independent variable: ________________ Dependent variable: ________________ 1 Constants (list at least 3 variables that should 2 Part 1 not be allowed to change) 3 Procedure 1. Measure approximately 5 mL of acetone with a small grad cylinder. 2. Place the acetone in a clean dry beaker. 3. Record the mass of the beaker and acetone every two minutes for 20 minutes. 4. Record the diameter of the beaker used. Data Beaker size (read label) ____________ Beaker Diameter (record number) _____________ Mass Measurements Time Mass (min) (g) 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Calculations Mass (mg) 2 min evap. change (mg) XXXXXXXXXXXXX Total evap. change (mg) XXXXXXXXXXXXX Data Analysis - Graphing 1. Plot a graph of your data. The Y-axis should be total change (loss of mass in milligrams; the Xaxis should be time in minutes. Draw the best-fit straight line in pencil. Include a title and label each axis. Data Analysis - Calculations 2. From the graph determine the evaporation rate in mg / min. (Slope = _____________ mg/min) Do the work on the graph as instructed by your teacher. 3. Does the acetone evaporate at a constant rate? ______________ Does the graph show a relationship between mass evaporated and time? __________________ What type of relationship does the graph show? __________________________ Part 2 1. Calculate the surface area of the acetone in square centimeters. (Area of a circle = ____________) 2. Calculate the evaporation rate in mg / min / cm2. (Slope/area) 3. Calculate the grams of acetone used. You cannot find the mass of the acetone by subtracting the empty container from the full container. You can find the mass if you use the 5 mL volume and the density of acetone (0.791 g/mL). Questions - Use your text or other references to answer these questions. 4. What is the formula (ie. formula for water is H2O) for acetone? 5. List 3 uses for acetone. 6. What is the boiling point of acetone in ˚C, ˚F, and K? 7. Use the K-P model to describe what is happening, at the particle level, as the acetone evaporates. Why is this happening, where does the energy come from? 8. What effect would increasing the pressure (at constant temp.) in the room have on the evaporation rate? Group Initials Beaker Volume (mL) 20 20 30 30 50 50 100 100 150 150 250 250 Diameter (cm) Evaporation Rate mg/min. mg/min per cm2