Unit 1a Concept Map Bio Basics of Life
advertisement

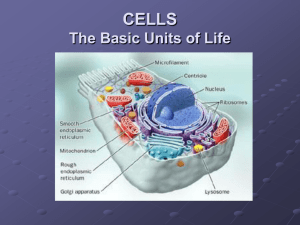
Unit 1A Concept Map Course Essential Question Unit 1a - Biology Basics of Life Organisms share Grade Level: 10 common characteristics of life Subject: Biology Unit Essential Question In what ways do structure, function, and the levels of organization enable prokaryotes and eukaryotes to carry out the characteristics of life? In what ways do prokaryotes and eukaryotes do this similarly and/or differently? PA Eligible Content BIO.A.1.1.1, BIO.A.1.2.1, BIO.A.1.2.2 Lesson Essential Questions What are the characteristics of life? How is cell theory used to explain the existence of life? In what ways can you compare and contrast the structures and function of a prokaryote and a eukaryote? How is form related to function at all levels of organization? What methods do organisms use to reproduce? Concepts 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. There are 8 characteristics of life: a. Organisms are made up of simpler units called cells. b. Organisms need light and/or chemicals to make cellular protoplasm. c. Organisms obtain and use energy through photosynthesis or cellular respiration to carry out their life processes. d. Organisms release waste chemicals produced by cells. e. Organisms seek to maintain homeostasis at all biological levels of organization. f. Organisms grow, develop g. Organisms can reproduce their own kind using DNA. h. Organisms adapt to changes in their environments. The three parts to the cell theory are: all living organisms are made up of cells, cells come from preexisting cells, and cells are the basic unit of structural function in living organisms. Biological levels of organization from smallest to largest include: atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, multicellular organisms, populations, and communities. The pattern of form following function is reflected at all biological levels of organization. A multicellular organization enables life functions such as movement, digestion, internal circulation of nutrients, Vocabulary 1. Biology 2. DNA 3. Stimulus 4. Cell 5. Cell theory 6. Asexual reproduction 7. Sexual reproduction 8. Homeostasis 9. Metabolism 10. Cell specialization 11. Eukaryote 12. Prokaryote 13. Unicellular 14. Multicellular 15. Organ system 16. Tissue 17. Organ 6. 7. 8. excretion of waste and reproduction to be subdivided among specialized groups of cells. The simplest level of multicellular organization is a tissue. Different types of cells and tissues combine to form distinct structures known as organs which perform specific functions. Organs work together as a system to perform common functions. -----------------------------------------------------------------Skills 1. Analyze structural and functional similarities and differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 2. Evaluate relationships between structure and function at various levels of biological organization. Formative Assessments Summative Assessments 1. Ticket out the 1. Quizzes door 2. Unit Test – 1A 2. Think-pair-share 3. Labs: 3. Thumbs up – Bean lab Thumbs down Potato lab(see PH lab 4. Concept Map manual - Lab skill 2 5. Sentence starter Microscope lab prompts 4. Projects (characteristics 6. Collins writing of life drawings) 7. Venn diagram 5. CDT biology 8. Compare assessment contrast 6. Collins writing (pick an 9. 3-2-1 item explain if its living 10. Frayer diagrams or not using 11. KWL characteristics of living 12. Whiteboard things) responses 13. Jigsaw 14. Chunking 15. Foldables 16. Text rendering 17. Guided reading 18. Whiparound 19. Pause-proceedlecture Resources Biology textbook Powerpoints (from textbook resources disk) Biology websites: -biologyjunction.com -biologycorner.com